Abstract
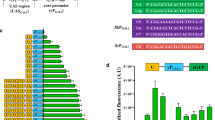
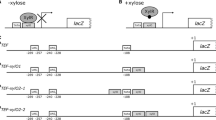
The ability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to utilize galactose is regulated by the nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of a transcriptional repressor, the Gal80 protein. Gal80 interacts with the transcriptional activator Gal4 in the nucleus and inhibits its function, preventing induction of the GAL genes. In response to galactose, the relative amounts of Gal80 in the cytoplasm and the nucleus are modulated by the action of a signal transducer, Gal3. Although it has been speculated that Gal3 binds galactose, this has not been experimentally demonstrated. In this study, we show that replacement of a conserved tyrosine in Gal3 by tryptophan leads to a reduction of its constitutive activity in the absence of galactose. In addition, this mutant protein was fully functional in vivo only when high concentrations of galactose were present in the medium. When overexpressed, the mutant was found to activate the genes GAL1 and GAL7/10 differentially. The implications of these findings for the fine regulation of GAL genes, and its physiological significance, are discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham HD, Howell RR (1969) Human hepatic uridine diphosphate galactose pyrophosphorylase. Its characterization and activity during development. J Biol Chem 244:545–550
Adams A, Gottschiling DE, Kaiser CA, Stearns T (1989) Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Adar R, Sharon N (1996) Mutational studies of the amino acid residues in the combining site of Erythrina corallodendron lectin. Eur J Biochem 239:668–674
Bajwa W, Torchia TE, Hopper JE (1988) Yeast regulatory gene GAL3: carbon regulation; UAS gal elements in common with GAL1, GAL2, GAL7, GAL10, GAL80 and MEL1; encoded protein strikingly similar to yeast and E. coli galactokinase. Mol Cell Biol 8:3439–3447
Bhat PJ, Hopper JE (1990) Analysis of the GAL3 signal transduction pathway activating GAL4 protein dependent transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 125:281–291
Bhat PJ, Hopper JE (1992) Overproduction of GAL1 or GAL3 protein causes galactose-independent activation of the Gal4 protein: evidence for a new model for induction for the yeast GAL/MEL regulon. Mol Cell Biol 12:2701–2707
Bhat PJ, Murthy TVS (2001) Transcriptional control of the GAL/MEL regulon of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mechanism for galactose-mediated signal transduction. Mol Microbiol 40:1059–1066
Bhat PJ, Oh D, Hopper JE (1990) Analysis of the GAL3 signal transduction pathway activating GAL4 protein-dependent transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 125:281–291
Blanck TE, Woods MP, Lebo CM, Xin P, Hopper JE (1997) Novel GAL3 proteins showing altered Gal80p binding cause constitutive transcription of Gal4p activated genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 17:2566–2575
Blume KG, Beutler E (1975) Galactokinase from human erythrocytes. Methods Enzymol 42:47–53
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Citron BA, Donelson JE (1984) Sequence of the Saccharomyces GAL region and its transcription in vivo. J Bacteriol 158:269–278
De Atauri P, Orrell D, Ramsey S, Bolouri H (2004) Evolution of design principles in evolutionary networks. Syst Biol 1:28–40
Douglas HC, Pelroy G (1963) A gene controlling the inducibility of galactose pathway enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 68:155–156
Evans RM (1988) The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 240:889–895
Ferrell JE (1998) How regulated protein translocation can produce switch-like responses. Trends Biochem Sci 23:461–465
Fukasawa T, Obonai K, Segawa T, Nogi Y (1980) The enzymes of the galactose cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Purification and characterization of uridine diphosphoglucose 4-epimerase. J Biol Chem 255:2705–2707
Greger IH, Proudfoot NJ (1998) Poly(A) signals control both transcriptional termination and initiation between the tandem GAL10 and GAL7 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J 17:4771–4779
Hartley A, Glynn SE, Barynin V, Baker PJ, Sedelnikova SE, Verhees C, de Geus D, Oost VJ, Timson DJ, Reece RJ, Rice DW (2004) Substrate specificity and mechanism from the structure of Pyrococcus galactokinase. J Mol Biol 337:387–398
John PT, Davis RW (1981) The organization and transcription of the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces. J Mol Biol 152:285–315
Johnston M (1987) A model fungal gene regulatory mechanism: the GAL genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev 51:458–476
Kew MO, Douglas HC (1976) Genetic co-regulation of galactose and melibiose utilization in Saccharomyces. J Bacteriol 125:33–41
Komeili A, O’Shea EK (2000) Nuclear transport and transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:355–360
Lohr D, Venkov P, Zlatanova J (1995) Transcriptional regulation in the yeast GAL gene family: a complex genetic network. FASEB J 9:777–786
Melcher K, Xu HE (2001) Gal80-Gal80 interaction on adjacent Gal4p binding sites is required for complete GAL gene repression. EMBO J 20:841–851
Menezes RA, Amuel C, Engels R, Gengenbacher U, Labahn J, Hollenberg CP (2003) Sites for interaction between Gal80p and Gal1p in Kluyveromyces lactis: structural model of galactokinase based on homology to the GHMP protein family. J Mol Biol 333:479–492
Murthy TVS (2000) Structure-function correlation of Gal3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PhD thesis, Biotechnology Center, IIT Bombay, India
Peng G, Hopper J (2000) Evidence for Gal3p’s cytoplasmic location and Gal80p’s dual cytoplasmic-nuclear location implicates new mechanisms for controlling Gal4p activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 20:5140–5148
Peng G, Hopper JE (2002) Gene activation by interaction of an inhibitor with a cytoplasmic signaling protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8548–8553
Pilauri V, Bewley M, Diep CQ, Hopper JE (2005) Dimerization in the yeast GAL gene switch. Genetics 169:1903–1914
Platt A, Reece RJ (1998) The yeast galactose genetic switch is mediated by the formation of a Gal4p-Gal80p-Gal3p complex. EMBO J 17:4086–4091
Platt A, Ross HC, Hankin S, Reece RJ (2000) The insertion of two amino acids into a transcriptional inducer converts it into a galactokinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3154–3159
Post-Beittenmiller MA, Hamilton RW, Hopper JE (1984) Regulation of basal and induced levels of the MEL1 transcript in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 4:1238–1245
Suzuki-Fujimoto T, Fukama M, Yano KI, Sakurai H, Vonika A, Johnston SA, Fukasawa T (1996) Analysis of the galactose signal transduction pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: interaction between Gal3p and Gal80p. Mol Cell Biol 16:2504–2508
Thoden JB, Holden HM (2003) Molecular structure of galactokinase. J Biol Chem 278:33305–33311
Thoden JB, Timson DJ, Reece RJ, Holden HM (2005) Molecular structure of human galactokinase: implications for type II galactosemia. J Biol Chem 280:9662–9670
Timson DJ, Ross HC, Reece RJ (2002) Gal3p and Gal1p interact with the transcriptional repressor Gal80p to form a complex of 1:1 stoichiometry. Biochem J 363:515–520
Torchia E, Hopper JE (1986) Genetic and molecular analysis of the GAL3 gene in the expression of the galactose/melibiose regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 113:229–246
Verma M, Bhat PJ, Venkatesh KV (2003) Quantitative analysis of GAL genetic switch of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals that nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Gal80p results in a highly sensitive response to galactose. J Biol Chem 278:48764–48769
Vollenbroich V, Meyer J, Engels R, Cardinali G, Menezes RA, Hollenberg CP (1999) Galactose induction in yeast involves association of Gal80p with Gal1p or Gal3p. Mol Gen Genet 261:495–507
Yano KI, Fukasawa T (1997) Galactose dependent reversible interaction of Gal3p with Gal80p in the induction pathway of Gal4p-activated genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1721–1726
Yarger JA (1980) Autogenous regulation of the inducible structural gene mRNAs in the galactose pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PhD thesis, Pennsylvania State University
Zenke FT, Engles R, Vollenbroich V, Meyer J, Hollenberg CP, Breunig KD (1996) Activation of Gal4p by galactose dependent interaction of galactokinase and Gal80p. Science 272:1662–1665
Zhou T, Daugherty M, Grishin NV, Osterman AL, Zhang H (2000) Structure and mechanism of homoserine kinase: prototype for the GHMP kinase superfamily. Structure Fold Des 8:1247–1257
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Prof. P. V. Balaji and M. S. Sujatha for their help in preparing the manuscript. We also acknowledge financial support from the Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences, India
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Johnston
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshminarasimhan, A., Bhat, P.J. Replacement of a conserved tyrosine by tryptophan in Gal3p of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reduces constitutive activity: implications for signal transduction in the GAL regulon. Mol Genet Genomics 274, 384–393 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0031-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-005-0031-6