Abstract
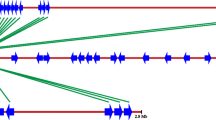
Plant genomes contain numerous genes (R-genes) that play a role in initiating defence measures against their particular pathogens. Defence mechanisms controlled by R-genes have been the focus of extensive research over the past several years. The majority of the R-genes described so far belong to a super-family of genes (150–600 members) that encode proteins with a nucleotide binding site (NBS), some leucine-rich repeats (LRR) and an N-terminal domain that shows similarity to the Toll and Interleukin-1 receptors (TIR) or a N-terminal coiled-coil (CC) domain. Analysis of four regions of the melon (Cucumis melo) genome, including two sequenced BACs, identified 14 TIR–NBS–LRR genes. Known disease resistance genes have been mapped in three of these regions. Transcriptional expression was detected for predicted genes that are possibly involved in defence responses to pathogen attack. TIR–NBS–LRR genes appear to be clustered in the melon genome. They contain all the conserved motifs that have previously been described for their counterparts in other species, although differences were also detected. The results presented here may contribute to a better understanding of the genomic distribution and evolution of this group of resistance gene homologues and their variability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Asakawa S, Abe I, Kudoh Y, Kishi N, Wang Y, Kubota R, Kudoh J, Kawasaki K, Minoshima S, Shimizu N (1997) Human BAC library: construction and rapid screening. Gene 191:69–79
Ashfield T, Bocian A, Held D, Henk AD, Marek LF, Danesh D, Penuela S, Meksem K, Lightfoot DA, Young ND, Shoemaker RC, Innes RW (2003) Genetic and physical localization of the soybean Rpg1-b disease resistance gene reveals a complex locus containing several tightly linked families of NBS–LRR genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:817–826
Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1994) RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265:1856–1860
Boyes DC, Nam J, Dangl JL (1998) The Arabidopsis thaliana RPM1 disease resistance gene product is a peripheral plasma membrane protein that is degraded coincident with the hypersensitive response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15849–15854
Brodie R, Roper RL, Upton C (2004) JDotter: a Java interface to multiple DotPlots generated by Dotter. Bioinformatics 20:279–281
Casacuberta E, Puigdoménech P, Monfort A (2000) Distribution of microsatellites in relation to coding sequences within the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Plant Sci 157:97–104
Coelho AC (2004) Identification of molecular markers in Quercus suber linked to resistance to Phytophthora cinnamomi. PhD Thesis, FERN, Universidade do Algarve
Ellis JG, Lawrence GJ, Luck JE, Dodds PN (1999) Identification of regions in alleles of the flax rust resistance gene L that determine differences in gene-for-gene specificity. Plant Cell 11:495–506
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP—Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 3-2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Flor HH (1956) The complementary genic systems in flax and flax rust. Adv Genet 8:29–54
Garcia-Mas J, van Leeuwen H, Monfort A, de Vicente MC, Puigdoménech P, Arús P (2001) Cloning and mapping of resistance gene homologues in melon. Plant Sci 161:165–172
Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P (1998) Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res 8:195–202
Hammond-Kosack KE, Parker JE (2003) Deciphering plant–pathogen communication: fresh perspectives for molecular resistance breeding. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:177–193
He CY, Tian AG, Zhang JS, Zhang ZY, Gai JY, Chen SY (2003) Isolation and characterization of a full-length resistance gene homolog from soybean. Theor Appl Genet 106:786–793
Jones DA, Jones JDG (1997) The role of leucine-rich repeat proteins in plant defences. Adv Bot Res 24:90–167
Le QH, Wright S, Yu Z, Bureau T (2000) Transposon diversity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:7376–7381
Leister D (2004) Tandem and segmental gene duplication and recombination in the evolution of plant disease resistance gene. Trends Genet 20:116–122
Logemann J, Schell J, Willmitzer L (1987) Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem 163:16–20
Luck JE, Lawrence GJ, Dodds PN, Shepherd KW, Ellis JG (2000) Regions outside of the leucine-rich repeats of flax rust resistance proteins play a role in specificity determination. Plant Cell 12:1367–1377
Meyers BC, Dickerman AW, Michelmore RW, Sivaramakrishnan S, Sobral BW, Young ND (1999) Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. Plant J 20:317–332
Meyers BC, Kozik A, Griego A, Kuang H, Michelmore RW (2003) Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:809–834
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130
Mindrinos M, Katagiri F, Yu GL, Ausubel FM (1994) The A. thaliana disease resistance gene RPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeats. Cell 78:1089–1099
Monforte AJ, Olive M, Gonzalo MJ, Alvarez JM, Dolcet-Sanjuan R, Arús P (2004) Identification of quantitative trait loci involved in fruit quality traits in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Theor Appl Genet 108:750–758
Oliver M, Garcia-Ma J, Cardús M, Pueyo N, López-Sesé AI, Arroyo M, Gómez-Paniagua H, Arús P, Vicente MC (2001) Construction of a reference linkage map for melon. Genome 44:836–845
Page RDM (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comp Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Parniske M, Hammond-Kosack KE, Golstein C, Thomas CM, Jones DA, Harrison K, Wulff BBH, Jones JDG (1997) Novel disease resistance specificities result from sequence exchange between tandemly repeated genes at the Cf4/9 locus of tomato. Cell 91:821–832
Ray S, Anderson JM, Urmeev FI, Goodwin SB (2003) Rapid induction of a protein disulfide isomerase and defense-related genes in wheat in response to the hemibiotrophic fungal pathogen Mycosphaerella graminicola. Plant Mol Biol 53:701–714
Richly E, Kurth J, Leister D (2002) Mode of amplification and reorganization of resistance genes during recent Arabidopsis thaliana evolution. Mol Biol Evol 19:76–84
Sawant SV, Kiran K, Singh PK, Tuli R (2001) Sequence architecture downstream of the initiator codon enhances gene expression and protein stability in plants. Plant Physiol 126:1630–1636
Sharp PA (1981) Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell 23:643–646
Smith RF, Wiese BA, Wojzynski MK, Davison DB, Worley KC (1996) BCM Search Launcher—an integrated interface to molecular biology data base search and analysis services available on the World Wide Web. Genome Res 6:454–462
Soltis PS, Soltis DE, Chase MW (1999) Angiosperm phylogeny inferred from multiple genes as a tool for comparative biology. Nature 402:402–404
Staden R (1996) The Staden sequence analysis package. Mol Biotechnol 5:233–241
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L., Cartinhour S, McCouch S. (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Research 22:4673–4680
van Leeuwen H, Monfort A, Zhang HB, Puigdoménech P (2003) Identification and characterisation of a melon genomic region containing a resistance gene cluster from a constructed BAC library. Microcolinearity between Cucumis melo and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 51:703–718
Vander Hoorn RA, Kruijt M, Roth R, Brandwagt BF, Joosten MH, De Wit PJ (2001) Intragenic recombination generated two distinct Cf genes that mediate AVR9 recognition in the natural population of Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10493–10498
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994) The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to Toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 78:1101–1115
Young ND (2000) The genetic architecture of resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:285–290
Zhang HB, Choi S, Woo SS, Li Z, Wing RA (1996) Construction and characterisation of two rice bacterial artificial chromosome libraries from the parents of a permanent recombinant inbred mapping population. Mol Breed 2:11–24
Zhou T, Wang Y, Chen JQ, Araki H, Jing Z, Jiang K, Shen J, Tian D (2004) Genome-wide identification of NBS genes in japonica rice reveals significant expansion of divergent non-TIR NBS-LRR genes. Mol Genet Genomics 271:402–415
Zhu H, Cannon SB, Young ND, Cook DR (2002) Phylogeny and genomic organization of the TIR and non-TIR NBS–LRR resistance gene family in Medicago truncatula. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:529–539
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mercé Miquel from the IBMB Sequencing Service for the DNA sequencing, Montserrat Martin for providing the TRV infected melon leaves, and David Lightfoot for providing much useful discussion and helpful comments on the manuscript. Funds for this project were provided by Grant No. 2FD97-0286-(02–01) from the Comisión Interdepartamental de Ciencia y Tecnologia (CICYT) and Grant No. 2000FI-00316 to Hans van Leeuwen from the Comissió Interdepartamental de Recerca i Tecnologia (CIRIT). This work was carried out within the context of the Centre de Referencia de Biotecnologia (CERBA) of the Generalitat de Catalunya.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M.-A. Grandbastien
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Leeuwen, H., Garcia-Mas, J., Coca, M. et al. Analysis of the melon genome in regions encompassing TIR-NBS-LRR resistance genes. Mol Genet Genomics 273, 240–251 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1104-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1104-7