Abstract
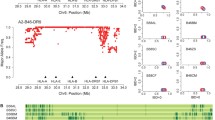
A significant proportion of the human genome is contained within haplotype blocks across which pairwise linkage disequilibrium (LD) is very high. However, LD is also often high between markers at more remote distances, and within different haplotype blocks. Here, we evaluate the origins of haplotype block structure in the three genes for alpha1 adrenergic receptors (alpha1-AR) in the human genome ( ADRA1A, ADRA1B and ADRA1D) by genotyping dense single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker maps, and show that LD signals between distant markers are due to the presence of extended haplotype superblocks in individuals with ancient chromosomes which have escaped historic recombination. ARs mediate the physiological effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine, and are targets of many therapeutic drugs. This work has identified haplotype backgrounds of alpha1-AR missense variants, haplotype block structures in US Caucasians and African Americans, and haplotype tag SNPs for each block, and we present strong evidence for ancient haplotype block superstructure at these genes which has been partially disrupted by recombination, and evidence for reinstatement of linkage disequilibrium by subsequent recombination events. ADRA1A is comprised of four haplotype blocks in US Caucasians, while in African Americans Block 1 is split. ADRA1B has four blocks in US Caucasians, but in African Americans only the first two blocks are present. ADRA1D has two blocks in US Caucasians, and the first block is replaced by two smaller blocks in African Americans. For both ADRA1A and ADRA1B, haplotype superstructures may represent a novel, higher-level hierarchy in the human genome, which may reduce redundancy of testing by further aggregation of genotype data.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolonna AA, Arranz MJ, Munro J, Osborne S, Petouni M, Martinez M, Kerwin RW (2000) No influence of adrenergic receptor polymorphisms on schizophrenia and antipsychotic response. Neurosci Lett 280:65-68
Buscher R, Herrmann V, Ring KM, Kailasam MT, O’Connor DT, Parmer RJ, Insel PA (1999) Variability in phenylephrine response and essential hypertension: a search for human alpha(1B)-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291:793-798
Daly MJ, Rioux JD, Schaffner SF, Hudson TJ, Lander ES (2001) High-resolution haplotype structure in the human genome. Nat Genet 29:229-232
Drouin C, Darracq L, Trovero F, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Cotecchia S, Tassin JP (2002) Alpha1b-adrenergic receptors control locomotor and rewarding effects of psychostimulants and opiates. J Neurosci 22:2873-2884
Gabriel S, et al (2003) The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296:2225-2229
Hoehe MR, Berrettini WH, Schwinn DA, Hsieh WT (1992) A two-allele Pst I RFLP for the alpha-1C adrenergic receptor gene ( ADRA1C). Hum Mol Genet 1:349-353
Hong CJ, Wang YC, Liu TY, Liu HC, Tsai SJ (2001) A study of alpha-adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms and Alzheimer disease. J Neural Transm 108:445-450
Hsu JW, Wang YC, Lin CC, Bai YM, Chen JY, Chiu HJ, Tsai SJ, Hong CJ (2000) No evidence for association of alpha 1a adrenoceptor gene polymorphism and clozapine-induced urinary incontinence. Neuropsychobiology 42:62-65
Johnson GC, et al (2001) Haplotype tagging for the identification of common disease genes. Nat Genet 29:233-237
Ke X, Cardon L (2003) Efficient selective screening of haplotype tag SNPs. Bioinformatics 19:287-288
Keffel S, Alexandrov A, Goepel M, Michel MC (2000) Alpha(1)-adrenoceptor subtypes differentially couple to growth promotion and inhibition in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 272:906-911
Kunieda T, Zuscik MJ, Boongird A, Perez DM, Luders HO, Najm IM (2002) Systemic overexpression of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor in mice: an animal model of epilepsy. Epilepsia 43:1324-1329
Ramirez MT, Sah VP, Zhao XL, Hunter JJ, Chien KR, Brown JH (1997) The MEKK-JNK pathway is stimulated by alpha1-adrenergic receptor and ras activation and is associated with in vitro and in vivo cardiac hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 272:14057-14061
Reich DE, Cargill M, Bolk S, Ireland J, Sabeti PC, Richter DJ, Lavery T, Kouyoumjian R, Farhadian SF, Ward R, Lander ES (2001) Linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nature 411:199-204
Reich DE, Schaffner SF, Daly MJ, McVean G, Mullikin JC, Higgins JM, Richter DJ, Lander ES, Altshuler D (2002) Human genome sequence variation and the influence of gene history, mutation and recombination. Nat Genet 32:135-142
Ruan Y, Kan H, Parmentier JH, Fatima S, Allen LF, Malik KU (1998) Alpha-1A adrenergic receptor stimulation with phenylephrine promotes arachidonic acid release by activation of phospholipase D in rat-1 fibroblasts: inhibition by protein kinase A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:576-585
Shibata K, Hirasawa A, Moriyama N, Kawabe K, Ogawa S, Tsujimoto G (1996) Alpha 1a-adrenoceptor polymorphism: pharmacological characterization and association with benign prostatic hypertrophy. Br J Pharmacol 118:1403-1408
Stephens M, Smith N. J., P D (2001) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68:978-989
Tanoue A, Koba M, Miyawaki S, Koshimizu TA, Hosoda C, Oshikawa S, Tsujimoto G (2002) Role of the alpha1D-adrenegric receptor in the development of salt-induced hypertension. Hypertension 40:101-106
Tsai SJ, Wang YC, Hong CJ (2001) Allelic variants of the alpha1a adrenoceptor and the promoter region of the alpha2a adrenoceptor and temperament factors. Am J Med Genet 105:96-98
Wall J, Pritchard J (2003) Haplotype blocks and linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nat Rev Genet 4:587-597
Xiao L, Pimental DR, Amin JK, Singh K, Sawyer DB, Colucci WS (2001) MEK1/2-ERK1/2 mediates alpha1-adrenergic receptor-stimulated hypertrophy in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:779-787
Xie HG, Kim RB, Stein CM, Gainer JV, Brown NJ, Wood AJ (1999) Alpha1A-adrenergic receptor polymorphism: association with ethnicity but not essential hypertension. Pharmacogenetics 9:651-656
Xie J, Ho Lee Y, Wang C, Mo Chung J, Chung K (2001) Differential expression of alpha1-adrenoceptor subtype mRNAs in the dorsal root ganglion after spinal nerve ligation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 93:164-172
Xing M, Insel PA (1996) Protein kinase C-dependent activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and mitogen-activated protein kinase by alpha 1-adrenergic receptors in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Clin Invest 97:1302-1310
Zhong H, Murphy TJ, Minneman KP (2000) Activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription by alpha(1A)-adrenergic receptor stimulation in PC12 cells. Mol Pharmacol 57:961-967
Zuscik MJ, Sands S, Ross SA, Waugh DJ, Gaivin RJ, Morilak D, Perez DM (2000) Overexpression of the alpha1B-adrenergic receptor causes apoptotic neurodegeneration: multiple system atrophy. Nat Med 6:1388-1394
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Alec Roy for a subset of his population dataset and to Longina Akhtar for assistance with cell culture. This work was supported by NIDCR Intramural Grant Z01, NIAAA Intramural Grant Z01 AA000301 (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md., USA) and the Comprehensive Neuroscience Program Grant USUHS G192BR-C4 (Henry Jackson Foundation, Rockville, Md., USA). BB is supported by the Comprehensive Neuroscience Program (National Naval Medical Center, Bethesda, Md., USA)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. R. McCombie
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buzas, B., Belfer, I., Hipp, H. et al. Haplotype block and superblock structures of the alpha1-adrenergic receptor genes reveal echoes from the chromosomal past. Mol Genet Genomics 272, 519–529 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1074-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-1074-9