Abstract
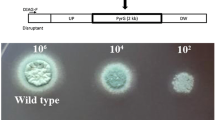
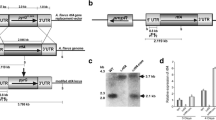
The Aspergillus parasiticus aflJ gene, which is located in the aflatoxin biosynthetic gene cluster and is transcribed divergently from the aflatoxin pathway regulatory gene aflR, encodes a 438-amino acid protein. Transformation with aflJ plus aflR, but not aflJ alone, increased the accumulation of aflatoxin precursors substantially in an O-methylsterigmatocystin-accumulating A. parasiticus strain. Disruption of aflJ resulted in non-pigmented mutants that lost the ability to synthesize aflatoxin intermediates. Transcript profiling by real time RT-PCR indicated that the lack of aflJ transcripts in the aflJ knockout mutants is associated with a significant decrease in the transcript levels of the genes for early ( pksA and nor1), middle ( ver1) and later ( omtA) steps in the aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway, with the degree of reduction ranging from 5- to 20-fold. Deletion of aflJ, however, did not have any effect on the aflR transcript level, and vice versa. Two-hybrid assays showed that AFLJ did not interact with aflatoxin biosynthetic enzymes, including NOR1, VER1, OMTA and ORDA. But AFLJ interacted with full-length AFLR, and the DNA-binding domain of AFLR was found not to be essential for this interaction. Simultaneous substitution of Arg427, Arg429, and Arg431 in the C-terminal region of AFLR with Leu residues abolished its ability to interact with AFLJ. Replacement of Asp436, which was previously shown to be crucial for AFLR's activation activity, with His, in contrast, had little effect on the interaction. On the other hand, deletions in most regions of AFLJ appeared to destroy its function, despite the fact that random amino acid substitution(s) in its C-terminal region did not drastically affect its capacity to interact with AFLR. The results show that aflJ is involved in the expression of aflatoxin structural genes and support the hypothesis that aflJ is a coactivator gene.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adye J, Mateles RI (1964) Incorporation of labeled compounds into aflatoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta 86:418–420
Cary JW, Ehrlich KC, Wright M, Chang P-K, Bhatnagar D (2000) Generation of aflR disruption mutants of Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:680–684
Chang P-K, Cary JW, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Bennett JW, Linz JE, Woloshuk CP, Payne GA (1993) Cloning of the Aspergillus parasiticus apa-2 gene associated with the regulation of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3273–3279
Chang P-K, Cary JW, Yu J, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE (1995) The Aspergillus parasiticus polyketide synthase gene pksA, a homolog of Aspergillus nidulans wA, is required for aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet 248:270–277
Chang P-K, Ehrlich KC, Linz JE, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Bennett JW (1996) Characterization of the Aspergillus parasiticus niaD and niiA gene cluster. Curr Genet 30:68–75
Chang P-K, Yu J, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE (1999a) Repressor-AFLR interaction modulates aflatoxin biosynthesis in Aspergillus parasiticus. Mycopathologia 147:105–112
Chang P-K, Yu J, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE (1999b) The carboxy-terminal portion of the aflatoxin pathway regulatory protein AFLR of Aspergillus parasiticus activates GAL1::lacZ gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2508–2516
Chang P-K, Bennett JW, Cotty PJ (2002) Association of aflatoxin biosynthesis and sclerotial development in Aspergillus parasiticus. Mycopathologia 153:41–48
Ehrlich KC, Montalbano BG, Cary JW (1999) Binding of the C6-zinc cluster protein, AFLR, to the promoters of aflatoxin pathway biosynthesis genes in Aspergillus parasiticus. Gene 230:249–257
Fernandes M, Keller NP, Adams TH (1998) Sequence-specific binding by Aspergillus nidulans AFLR, a C6 zinc cluster protein regulating mycotoxin biosynthesis. Mol Microbiol 28:1355–1365
Hicks JK, Yu J-H, Keller NP, Adams TH (1997) Aspergillus sporulation and mycotoxin production both require inactivation of the FadA Gα protein-dependent signaling pathway. EMBO J 16:4916–4923
Hicks JK, Lockington RA, Strauss J, Dieringer D, Kubicek CP, Kelly J, Keller NP (2001) RcoA has pleiotropic effects on Aspergillus nidulans cellular development. Mol Microbiol 39:1482–1493
Ho SN, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77:61–68
Horng JS, Chang P-K, Pestka JJ, Linz JE (1990) Development of a homologous transformation system for Aspergillus parasiticus with the gene encoding nitrate reductase. Mol Gen Genet 224:294–296
Ito H, Fukada Y, Murata K, Kimura A (1983) Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol 153:163–168
Kang JS, Kim SH, Hwang MS, Han SJ, Lee YC, Kim YJ (2001) The structural and functional organization of the yeast Mediator complex. J Biol Chem 276:42003–42010
Kim YJ, Bjorklund S, Li Y, Sayre MH, Kornberg RD (1994) A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell 77:599–608
Kornberg RD (1999) Eukaryotic transcriptional control. Trends Cell Biol 9:46–49
Larschan E, Winston F (2001) The S. cerevisiae SAGA complex functions in vivo as a coactivator for transcriptional activation by Gal4. Genes Dev 15:1946–1956
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Mizuno T, Harashima S (2000) Activation of basal transcription by a mutation in SIN4, a yeast global repressor, occurs through a mechanism different from activator-mediated transcriptional enhancement. Mol Gen Genet 263:48–59
Meyers DM, Bhatnagar D, Payne GA (1998) Characterization of aflJ, a gene involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3713–3717
Näär AM, Beaurang PA, Zhou S, Abraham S, Solomon W, Tjian R (1999) Composite co-activator ARC mediates chromatin-directed transcriptional activation. Nature 398:828–832
Näär AM, Lemon BD, Tjian R (2001) Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu Rev Biochem 70:475–501
Narlikar GJ, Fan HY, Kingston (2002) Cooperation between complexes that regulate chromatin structure and transcription. Cell 108:475-487
Payne GA, Brown MP (1998) Genetics and physiology of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Phytopathol 36:329–362
Ptashine M, Gann A (1997) Transcriptional activation by recruitment. Nature 386:569-577
Shimizu K, Keller NP (2001) Genetic involvement of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase in a G protein signaling pathway regulating morphological and chemical transitions in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 157:591–600
Skory CD, Chang P-K, Cary JW, Linz JE (1992) Isolation and characterization of a gene from Aspergillus parasiticus associated with conversion of versicolorin A to sterigmatocystin in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3527–3537
Small AJ,Todd RB, Zanker MC, Delimitrou S, Hynes MJ, Davis MA (2001) Functional analysis of TamA, a coactivator of nitrogen-regulated gene expression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Genet Genomics 265:636–646
Tag A, Hicks J, Garifullina G, Ake C Jr, Phillips TD, Beremand M, Keller NP (2000) G-protein signaling mediates differential production of toxic secondary metabolites. Mol Microbiol 38:658–665
Takemaru K, Harashima S, Ueda H, Hirose S (1998) Yeast coactivator MBF1 mediates GCN4-dependent transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 18:4971–4976
Trail F, Chang P-K, Cary J, Linz JE (1994) Structural and functional analysis of the nor-1 gene involved in the biosynthesis of aflatoxins by Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4078-4085
Yu J, Cary JW, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE, Keller NP, Chu FS (1993) Cloning and characterization of a cDNA from Aspergillus parasiticus encoding an O-methyltransferase involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3564-3571
Yu J-H, Butchko RAE, Fernandes M, Keller NP, Leonard TJ, Adams TH (1996) Conservation of structure and function of the aflatoxin regulatory gene aflR from Aspergillus nidulans and A. flavus. Curr Genet 29:549–555
Yu J, Chang P-K, Ehrlich KC, Cary JW, Montalbano BG, Dyer JM, Bhatnagar D, Cleveland TE (1998) Characterization of critical amino acids of an Aspergillus parasiticus cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase encoded by ordA that is involved in biosynthesis of aflatoxin B1, G1, B2, and G2. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4834–4841
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Leslie Scharfenstein and Michelle Faust for their technical assistance. This work was in part supported by the USDA NRI Competitive Grants Program (No. 2001-02523)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. A. M. J. J. van den Hondel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, PK. The Aspergillus parasiticus protein AFLJ interacts with the aflatoxin pathway-specific regulator AFLR. Mol Gen Genomics 268, 711–719 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0809-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0809-3