Abstract
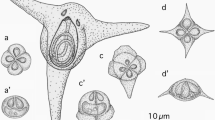
An examination of 18 fishes caught in the South China Sea detected two Unicapsula spp. in the myofibers of the trunk muscles of carangid fishes: Unicapsula aequilobata n. sp. in the Japanese scad, Decapterus maruadsi, and Unicapsula seriolae in the yellowstripe scad, Selaroides leptolepis. They formed thin filamentous pseudocysts of 0.9–2.0 (mean 1.4) mm by 0.03–0.06 (0.04) mm (n = 5) and 0.9–3.4 (2.1) mm by 0.02–0.05 (0.04) mm (n = 12), respectively. Myxospores of U. aequilobata n. sp. are composed of three equal shell valves and measured 6.7–8.5 (7.3) μm in length and 7.1–8.8 (7.6) μm in width, and contained a prominent polar capsule (PC) 3.2–3.8 (3.6) μm in diameter (n = 18) and two rudimentary PCs. A nucleotide sequence (5127 bp) of the ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA) array was obtained for the genetic characterization of this new species. Based on morphological and phylogenetic criteria, we erect U. aequilobata n. sp. as the sixteenth species in the genus Unicapsula. Nucleotide sequences of the 18S and 28S rDNA obtained from U. seriolae from the yellowstripe scad were almost identical (99.6–100% or 99.0–99.6%, respectively) to those from fish found in the seawaters around Australia and Japan. Consequently, this is a new host and geographical distribution records for U. seriolae. In addition, we illustrated the predicted secondary structure of the available 5.8S rDNA sequences of multivalvulid species, including those obtained from U. aequilobata n. sp., to assess the significance of interspecific nucleotide variations in this short rDNA unit.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe N, Maehara T, Kashino M, Ohyama M (2011) Identification of parasites found in fresh fish by morphological and sequencing analyses. Ann Rep Osaka City Inst Public Health Environ Sci 73:29–37 (in Japanese with English summary)
Anisimova M, Gascuel O (2006) Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: a fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst Biol 55:539–552
Aseeva NL, Krasin VK (2001) On new records of the family Trilosporidae (Myxosporida: Multivalvulida) from fishes of Pacific Ocean. Parazitologiya 35:353–356
Burger MAA, Barnes AC, Adlard RD (2008) Wildlife as reservoirs for parasites infecting commercial species: host specificity and a redescription of Kudoa amamiensis from teleost fish in Australia. J Fish Dis 31:835–844
Davis HS (1924) A new myxosporidian parasite, the cause of “wormy” halibut. Report of the U. S. Commercial Fisheries for 1923, Appendix 8:1–5
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie J-M, Gascuel O (2008) Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36:465–469
Diamant A, Ucko M, Paperna I, Colorni A, Lipshitz A (2005) Kudoa iwatai (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in wild and cultured fish in the Red Sea: Redescription and molecular phylogeny. J Parasitol 91:1175–1189
Diebakate C, Fall M, Faye N, Toguebaye BS (1999) Unicapsula marquesi n. sp. (Myxosporea, Multivalvulida) parasite des branchies de Polydactylus Quadrifilis (Cuvier, 1829) (Poisson, Polynemidae) des côtes sénégalaises (Afrique de l’Ouest). Parasite 6:231–235
Egusa S (1986) The order Multivalvulida Shulman, 1959 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea): a review. Fish Pathol 21:261–274 (in Japanese with English summary)
Egusa S, Nakajima K (1980) Kudoa amamiensis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) found in cultured yellowtails and wild damselfishes from Amami-Ohshima and Okinawa, Japan. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 46:1193–1198
Egusa S, Shiomitsu T (1983) Two new species of the genus Kudoa (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from marine cultured fishes in Japan. Fish Pathol 18:163–171 (in Japanese with English summary)
Fiala I, Bartošová-Sojková P, Whipps CM (2015) Classification and phylogenetics of Myxozoa. In: Okamura B, Gruhl A, Bartholomew JL (eds) Myxozoan evolution, ecology and development. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 85–110
Gottschling M, Pötner J (2004) Secondary structure models of the nuclear internal transcribed spacer regions and 5.8S rRNA in Calciodinelloideae (Peridiniaceae) and other dinoflagellates. Nucleic Acids Res 32:307–315
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Kasai A, Li Y-C, Mafie E, Sato H (2016a) Morphological and molecular genetic characterization of two Kudoa spp., K. musculoliquefaciens, and K. pleurogrammi n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida), causing myoliquefaction of commercial marine fish. Parasitol Res 115:1883–1892
Kasai A, Li Y-C, Mafie E, Sato H (2016b) New host records of monacanthid fish for three Kudoa spp. (K. septempunctata, K. thyrsites, and K. shiomitsui) prevalent in the olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), with the description of K. parathyrsites n. sp. from a black scraper (Thamnaconus modestus). Parasitol Res 115:2741–2755
Kasai A, Tsuduki H, Jimenez LA, Li Y-C, Tanaka S, Sato H (2017) Incidence of three Kudoa spp., K. neothunni, K. hexapunctata, and K. thunni (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida), in Thunnus tunas distributed in the western Pacific Ocean. Parasitol Res 116:1137–1150
Kawai T, Sekizuka T, Yahata Y, Kuroda M, Kumeda Y, Iijima Y, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y, Ohnishi T (2012) Identification of Kudoa septempunctata as the causative agent of novel food poisoning outbreaks in Japan by consumption of Paralichthys olivaceus in raw fish. Clin Infect Dis 54:1046–1052
Lester RJG (1982) Unicapsula seriolae n. sp. (Myxosporea, Multivalvulida) from Australian yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi. J Protozool 29:584–587
Li Y-C, Sato H, Tanaka S, Ohnishi T, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y (2013) Characterization of the ribosomal RNA gene of Kudoa neothunni (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in tunas (Thunnus spp.) and Kudoa scomberi n. sp. in a chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus). Parasitol Res 112:1991–2003
Li Y-C, Tamemasa S, Zhang J-Y, Sato H (2020a) Phylogenetic characterisation of seven Unicapsula spp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from commercial fish in southern China and Japan. Parasitology 147:448–464
Li Y-C, Inoue K, Zhang J-Y, Sato H (2020b) Phylogenetic relationships of three Kudoa spp. with morphologically similar myxospores (K. iwatai, K. lutjanus, and K. bora), with the redescription of K. uncinata and K. petala and description of a new species (K. fujitai n. sp.) in fishes in the South China Sea. Parasitol Res 119:1221–1236
Li Y-C, Inoue K, Tanaka S, Zhang J-Y, Sato H (2020c) Identification of four new Kudoa spp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in commercial fishes collected from South China Sea, Atlantic Ocean, and Bering Sea by integrated taxonomic approach. Parasitol Res 119:2113–2128
Lom J, Arthur JR (1989) A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. J Fish Dis 12:151–156
Lom J, Dyková I (2006) Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitol 53:1–36
Matsukane Y, Sato H, Tanaka S, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y (2010) Kudoa septempunctata n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from an aquacultured olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) imported from Korea. Parasitol Res 107:865–872
Miller TL, Adlard RD (2013) Unicapsula species (Myxosporea: Trilosporidae) of Australian marine fishes, including the description of Unicapsula andersenae n. sp. in five teleost families off Queensland, Australia. Parasitol Res 112:2945–2957
Moran JDW, Whitaker DJ, Kent ML (1999) A review of the myxosporean genus Kudoa Meglitsh, 1947, and its impact on the international aquaculture industry and commercial fisheries. Aquaculture 172:163–196
Ohnishi T, Obara T, Arai S, Yoshinari T, Sugita-Konishi Y (2018) Quantitative analysis of Unicapsula seriolae in greater amberjack associated with unidentified food-borne disease. Food Hyg Safe Sci 59:24–29
Parker JD, Warner MC (1970) Effects of fixation, dehydration and staining on dimensions of myxosporidian and microsporidian spores. J Wildl Dis 6:448–456
Reimschuessel R, Gieseker CM, Driscoll C, Baya A, Kane AS, Blazer VS, Evans JJ, Kent ML, Moran JDW, Poynton SL (2003) Myxosporean plasmodial infection associated with ulcerative lesions in young-of-the-year Atlantic menhaden in a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay, and possible links to Kudoa clupeidae. Dis Aquat Org 53:143–166
Sarkar NK (1999) Some new Myxosporidia (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) of the genera Myxobolus Butschli, 1882 Unicapsula Davis, 1942 Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947 Ortholinea Shulman, 1962 and Neoparvicapsula Gaevskaya, Kovaleva and Shulman, 1982. Proc Zool Soc Calcutta 52:38–48
Sugita-Konishi Y, Sato H, Ohnishi T (2014) Novel foodborne disease associated with consumption of raw fish, olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Food Safe 2:141–150
Suzuki J, Murata R, Sadamasu K, Kai A (2012) Cases of food poisoning caused possibly by Kudoa spp. in the Tokyo metropolitan area. IASR 33:153–155 (in Japanese)
Suzuki J, Murata R, Yokoyama H, Sadamasu K, Kai A (2015) Detection rate of diarrhea-causing Kudoa hexapunctata in pacific Bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis from Japanese waters. Int J FoodMicrobiol 194:1–6
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tomochi H, Li Y-C, Tran BT, Yanagida T, Sato H (2014) Three Unicapsula species (Myxosporea: Trilosporidae) of Asian marine fishes, including the description of Unicapsula setoensis n. sp. in the yellowfin goby (Acanthogobius flavimanus) from the Inland Sea of Japan. Parasitol Res 113:3807–3816
Vaughn JC, Sperbeck SJ, Ramsey WJ, Lawrence CB (1984) A universal model for the secondary structure of 5.8S ribosomal RNA molecules, their contact sites with 28S ribosomal RNAs, and their prokaryotic equivalent. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7479–7502
Ward RD, Zemlak TS, Innes BH, Last PR, Hebert DN (2005) DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos Trans R Soc B (Biol Sci) 360:1847–1857
Whipps CM, Kent ML (2006) Phylogeography of the cosmopolitan marine parasite Kudoa thyrsites (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). J Eukaryot Microbiol 53:364–373
Whipps CM, Adlard RD, Bryant MS, Kent ML (2003) Two unusual myxozoans, Kudoa quadricornis n. sp. (Multivalvulida) from the muscle of goldspotted trevally (Carangoides fulvoguttatus) and Kudoa permulticapsula n. sp. (Multivalvulida) from the muscle of Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus commerson) from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. J Parasitol 89:168–173
Whipps CM, Grossel G, Adlard RD, Yokoyama H, Bryant MS, Munday BL, Kent ML (2004) Phylogeny of the Multivalvulidae (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) based on comparative ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. J Parasitol 90:618–622
Yasunaga N, Hatai K, Ogawa S, Yasumoto S (1981) An unknown myxozoa found in brain of cultured sea bass, Lateolabrax japonicus and cultured Japanese striped knifejaw, Oplegnathus fasciatus. Fish Pathol 16:51–54 (in Japanese with English summary)
Yokoyama H, Itoh N (2005) Two multivalvulid myxozoans causing postmortem myoliquefaction: Kudoa megacapsula n. sp. from red barracuda (Sphyraena pinguis) and Kudoa thyrsites from splendid alfonso (Beryx splendens). J Parasitol 91:1132–1137
Yokoyama H, Whipps CM, Kent ML, Mizuno K, Kawakami H (2004) Kudoa thyrsites from Japanese flounder and Kudoa lateolabracis n. sp. from Chinese Sea bass: causative myxozoans of post-mortem myoliquefaction. Fish Pathol 39:79–85
Yokoyama H, Abe N, Maehara T, Suzuki J (2014) First record of Unicapsula seriolae (Myxozoa: Multivalvulida) from the muscle of Malabar grouper Epinephelus malabaricus in Japan. Parasitol Int 63:561–566
Zhang JB, Hanner R (2011) DNA barcoding is a useful tool for the identification of marine fishes from Japan. Biochem Syst Ecol 39:31–42
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Ph.D. Researcher (No: R17022) from the Faculty of Agricultural Science, Guangdong Ocean University (YCL); Grant-in-Aid for Food Science and Research 2019 from The TOYO SUISAN FOUNDATION (HS); Grant-in-Aid for International Collaboration Research 2019 from the Goho Llife Sciences International Fund (JYZ); and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI grant number 18K05995 (HS). We are especially thankful for the international research grant for SG from Yamaguchi University for her collaborative research in Yamaguchi University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Section Editor: Christopher Whipps
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, K., Li, YC., Ghosh, S. et al. Identification of a new species, Unicapsula aequilobata n. sp., and Unicapsula seriolae (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in carangid fish from the South China Sea. Parasitol Res 120, 2379–2389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07108-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07108-9