Abstract
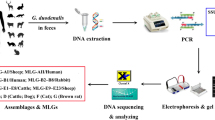
Giardia duodenalis is a zoonotic protozoan that parasitizes the upper small intestine of human and many mammals including dogs. To develop a restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method for typing zoonotic (A, B) and host-specific (C, D) assemblages of G. duodenalis from dog, β-giardin gene was amplified with design primer pairs B3 and B4. The PCR products were digested with restriction enzyme Afa I and Msp I; then, PCR-RFLP method was compared with HRM genotyping and sequencing method for G. duodenalis from dog. The results showed that each of assemblages A–D had unique restriction pattern, which was consistent with the predictive results. Among 21 samples tested by PCR-RFLP, 1 human-derived and 8 dog-derived G. duodenalis were identified as assemblage A; 5 dog-derived G. duodenalis as assemblage C; 7 dog-derived G. duodenalis as assemblage D, which were coincided with the HRM genotyping and sequencing results. It is concluded that the PCR-RFLP is quick, easy, and accurate method for the sequence typing of G. duodenalis zoonotic and specific assemblages from dogs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mohammed HI (2011) Genotypes of Giardia intestinalis clinical isolates of gastrointestinal symptomatic and asymptomatic Saudi children. Parasitol Res 108(6):1375–1381
Bouzid M, Steverding D, Tyler KM (2008) Detection and surveillance of waterborne protozoan parasites. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19:302–306
Caccio SM, Ryan U (2008) Molecular epidemiology of giardiasis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 160(2):75–80
Cacciò SM, Thompson RCA, Mclauchlin J, Smith HV (2005) Unravelling Cryptosporidium and Giardia epidemiology. Trends Parasitol 21(9):430–437
Carlin EP, Bowman DD, Scarlett JM, Garrett J, Lorentzen L (2006) Prevalence of Giardia in symptomatic dogs and cats throughout the United States as determined by the IDEXX SNAP Giardia test. Vet Ther 7(3):199–206
Epe C, Rehkter G, Schnieder T, Lorentzen L, Kreienbrock L (2010) Giardia in symptomatic dogs and cats in Europe—results of a European study. Vet Parasitol 173(1–2):32–38
Ey PL, Andrews RH, Mayrhofer G (1993a) Differentiation of major genotypes of Giardia intestinalis by polymerase chain reaction analysis of a gene encoding a trophozoite surface antigen. Parasitol 106:347–356
Ey PL, Andrews RH, Mayrhofer G, Darby JM (1993b) Giardia intestinalis: detection of major genotypes by restriction analysis of gene amplification products. Int J Parasitol 23:591–600
Ey PL, Bruderer T, Wehrli C, Koehler P (1996) Comparison of genetic groups determined by molecular and immunological analyses of Giardia isolated from animals and humans in Switzerland and Australia. Parasitol Res 82:52–60
Ey PL, Mansouri M, Kulda J, Nohyankova AE, Monis PT, Andrews RH, Mayrhofer G (1997) Genetic analysis of Giardia from hoofed farm animals reveals artiodactyl-specific and potentially zoonotic genotypes. J Euk Microbiol 44:626–635
Faubert G (2000) Immune response to Giardia duodenalis. Clin Microbiol Rev 13(1):35–54
Geurden T, Vercruysse J, Claerebout E (2010) Is Giardia a significant pathogen in production animals? Exp Parasitol 124(1):98–106
Giangaspero A, Berrilli F, Brandonisio O (2007) Giardia and Cryptosporidium and public health: the epidemiological scenario from the Italian perspective. Parasitol Res 101(5):1169–1182
Gillin FD, Reiner DS, Mccaffery JM (1996) Cell biology of the primitive eukaryote Giardia lamblia. Ann Rev Microbiol 50:679–705
Hunter PR, Thompson RC (2005) The zoonotic transmission of Giardia and Cryptosporidium. Int J Parasitol 35(11):1181–1190
Karanis P, Ey P (1998) Characterization of axenic isolates of Giardia intestinalis established from humans and animals in Germany. Parasitol Res 84:442–449
Karanis P, Ongerth J (2009) LAMP—a powerful and flexible tool for monitoring microbial pathogens. Trends Parasitol 25:498–499
Karanis P, Schoenen D, Seitz HM (1996) Giardia and Cryptosporidium in backwash water from rapid sand filters used for drinking water production. Zentralbl Bakteriol 284:107–114
Koehler AV, Bradbury RS, Stevens MA, Haydon SR, Jex AR, Gasser RB (2013) Genetic characterization of selected parasites from people with histories of gastrointestinal disorders using a mutation scanning-coupled approach. Electrophoresis 34(12):1720
Lalle M, Pozio E, Capelli G, Bruschi F, Crotti D, Cacciò SM (2005) Genetic heterogeneity at the β-giardin locus among human and animal isolates of Giardia duodenalis and identification of potentially zoonotic subgenotypes. Int J Parasitol 35(2):207–213
Lane S, Lloyd D (2002) Current trends in research into the waterborne parasite Giardia. Crit Rev Microbiol 28(2):123–147
Lefebvre SL, Waltner-Toews D, Peregrine AS, Reid-Smith R, Hodge L, Arroyo LG, Weese JS (2006) Prevalence of zoonotic agents in dogs visiting hospitalized people in Ontario: implications for infection control. J Hosp Inf 62(4):458–466
Monis PT, Andrews RH, Mayrhofer G, Mackrill J, Kulda J, Isaac-Renton JL, Ey PL (1998) Novel lineages of Giardia intestinalis identified by genetic analysis of organisms isolated from dogs in Australia. Parasitology 116:17–19
Pantchev N, Broglia A, Paoletti B, Globokar Vrhovec M, Bertram A, Nöckler K, Cacciò SM (2014) Occurrence and molecular typing of Giardia isolates in pet rabbits, chinchillas, guinea pigs and ferrets collected in Europe during 2006–2012. Vet Rec 04/2014; doi:10.1136/vr.102236
Plutzer J, Karanis P (2009) Rapid identification of Giardia duodenalis by loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) from faecal and environmental samples and comparative findings by PCR and real-time PCR methods. Parasitol Res 104:1527–1533
Plutzer J, Ongerth J, Karanis P (2010a) Giardia taxonomy, phylogeny and epidemiology: facts and open questions. Int J Hygiene Environ Health 213:321–333
Plutzer J, Törökné A, Karanis P (2010b) Combination of ARAD microfibre filtration and LAMP methodology for simple, rapid and cost-effective detection of human pathogenic Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in drinking water. Lett Appl Microbiol 50:82–88
Ryan U, Simone C (2013) Zoonotic potential of Giardia. Int J Parasitol 43(12–13):943
Silva FMPE, Marina MM, Raimundo SL, João P, Jr A (2012) Molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis in dogs from Brazil. Parasitol Res 110:325–334
Sotiriadou I, Pantchev N, Gassmann D, Karanis P (2013) Molecular identification of Giardia and Cryptosporidium from dogs and cats. Parasite 2013:20–8
Tan LP, Yu XG, Abdullahi AY, Wu S, Zheng GC, Hu W, Song MR, Wang Z, Jiang B, Li GQ (2015) Development of a rapid HRM genotyping method for detection of dog-derived Giardia lamblia. Parasitol Res 114:4081–4086
Thompson RC, Hopkins RM, Homan WL (2000) Nomenclature and genetic groupings of Giardia infecting mammals. Parasitol Today 16:210–213
Vanni I, Caccio’ SM, van Lith L, Lebbad M, Sva¨rd SG, Pozio E, Tosini F (2012) Detection of Giardia duodenalis assemblages A and B in human feces by simple, assemblage-specific PCR assays. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1776
Vasilopulos RJ, Rickard LG, Mackin AJ, Pharr GT, Huston CL (2007) Genotypic analysis of Giardia duodenalis in domestic cats. J Vet Int Med 21(2):352
Wang Z, Vora GJ, Stenger DA (2004) Detection and genotyping of Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, Giardia lamblia, and Cryptosporidium parvum by oligonucleotide microarray. J Clin Microbiol 42(7):3262–3271
Zhang P, Liu YJ, Alsarakibi M, Li J, Liu T, Li Y, Li GQ (2012) Application of HRM assays with EvaGreen dye for genotyping Giardia duodenalis zoonotic assemblages. Parasitol Res 111(5):2157–2163
Zheng GC, Alsarakibi M, Liu YJ, Hu W, Luo Q, Tan LP, Li GQ (2014) Genotyping of Giardia duodenalis isolates from dogs in Guangdong, China based on multi-locus sequence. Korean J Parasitol 52(3):299–304
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31272551). The authors would like to thank the humane shelter’s personnel for helping to collect clinical samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Liping Tan and Sheng Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, L., Wu, S., Abdullahi, A.Y. et al. PCR-RFLP method to detect zoonotic and host-specific Giardia duodenalis assemblages in dog fecal samples. Parasitol Res 115, 2045–2050 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4948-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4948-y