Abstract
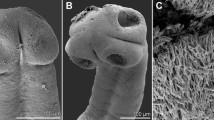
Pygidiopsis cambodiensis n. sp. is described based on adult flukes recovered from Syrian golden hamsters experimentally infected with metacercariae from mullets (Liza macrolepis) purchased at a local fish market in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. The specimens were examined by light and scanning electron microscopy. Among the 13 species so far assigned to Pygidiopsis, the new species belongs to the summa-type (including Pygidiopsis pelecani, Pygidiopsis phalacrocoracis, Pygidiopsis piclaumoreli, Pygidiopsis plana, and Pygidiopsis summa) which lack circumoral spines and have vitelline follicles extending posteriorly from the level of the ovary some distance into the post-testicular space and the uterus not exceeding the acetabulum anteriorly. The new species differs from the other five species of the summa-type particularly in the morphology of the ventrogenital complex, including the genital sac, gonotyl, and gonotyl spines (= rodlets). The genital sac is well developed, sucker-like, slightly larger than the ventral sucker, muscular, and equipped with two gonotyls on the ventral side of the sac. Gonotyls are protruding pad-like, and the number of rodlets on the left gonotyl is four to five and that on the right gonotyl is 10–11 in two rows. This is the fifth Pygidiopsis species reported in Asia, following P. summa (Japan, Korea, and Vietnam), P. phalacrocorasis (Japan), P. pelecani (China), and Pygidiopsis marivillai (Philippines).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chai JY, Seo BS, Lee SH, Hong ST (1986) Growth and development of Pygidiopsis summa in rats and mice with a supplementary note on its morphological characters. Korean J Parasitol 24:55–62
Chai JY, Kim IM, Seo M, Guk SM, Kim JL, Sohn WM, Lee SH (1997) A new focus of Heterophyes nocens, Pygidiopsis summa, and other intestinal flukes in a coastal area of Muan-gun, Chollanam-do. Korean J Parasitol 35:233–238
Chai JY, Song TE, Han ET, Guk SM, Park YK, Choi MH, Lee SH (1998) Two endemic foci of heterophyids and other intestinal fluke infections in southern and western coastal areas in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 36:155–161
Chai JY, Sohn WM, Choi SY, Lee SH (2002) Surface ultrastructure of Pygidiopsis summa (Digenea: Heterophyidae) adult flukes. Korean J Parasitol 40:107–112
Chai JY, Park JH, Han ET, Shin EH, Kim JL, Guk SM, Hong KS, Lee SH, Rim HJ (2004) Prevalence of Heterophyes nocens and Pygidiopsis summa infections among residents of the western and southern coastal islands of the Republic of Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 71:617–622
Chai JY, Shin EH, Lee SH, Rim HJ (2009) Foodborne intestinal flukes in Southeast Asia. Korean J Parasitol 47(suppl):S69–S102
Chai JY, Park YJ, Park JH, Jung BK, Shin EH (2014) Mucosal immune responses of mice experimentally infected with Pygidiopsis summa (Trematoda: Heterophyidae). Korean J Parasitol 52:27–33
Diaz MT, Gómez E, Bashirullah A, Guilarte DV (2014) Partial life cycle of Pygidiopsis australis Ostrowski de Nuñez, 1996 (Digenea: Heterophyidae) in Venezuela. Revista Cientifica (FCV-LUZ) 24:83–87
Dollfus RP, Capron A (1958) Un Pygidiopsis (Heterophyidae) de sterna de la cote du Sénégal. Bull Inst Française d’Afrique Noire, Série A: Sciences Naturelles 20:306–310
Dronen NO, Blend CK, Davis AJ (2004) Emendation of the subfamily Caliguirinae and Pygidiopsinae (Digenea) with a redescription of Caiguiria anterouteria (Digenea: Heterophyidae) and reassignment of Pygidiopsis crassus to Caiguiria. Zootaxa 417:1–12
Dronen NO, Blend CK, Davis AJ (2005) Caiguiria himantopae n. sp. (Digenea: Heterophyidae) and other endohelminths from the black-necked stilt, Himantopus mexicanus (Recurvirostridae), from the Galveston area of the Texas Gulf Coast, USA. Comp Parasitol 72:22–27
Køie M (1990) Pygidiopsis ardeae n. sp. (Digenea: Heterophyidae: Pygidiopsinae) in the grey heron Ardea cinera L. from Denmark. Syst Parasitol 15:141–149
Køie M (1992) Scanning electron microscopy of cercariae, metacercariae and adults of Pygidiopsis ardeae Køie, 1990 (Digenea: Heterophyidae). Parasitol Res 78:469–474
Linton E (1928) Notes on trematode parasites of birds. Proc US Nat Mus 73:1–36
Looss A (1907) Notizen zur Helminthologie Aegyptens. VII. Ueber einige neue Trematoden der äegyptischen Fauna. Centralbl f Bakt I 43:478–490
Nasir P, Diaz MT (1971) Studies on freshwater larval trematodes. XXVII. Partial life cycle of Caiguiria anterouteria gen. n., sp. n., subfam. n. (Trematoda: Digenea). Proc Helminthol Soc Washington 38:21–23
Onji Y, Nishio T (1916) On the trematodes whose intermediate host is brackish water fish. Chiba Igaku Semmon Gakko Zasshi 81 & 82:229–249 (in Japanese)
Ostrowski de Núñez M (1995) Life history of Pygidiopsis crassus n. sp. (Trematoda, Digenea, Heterophyidae) in the Neotropical Region. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz (Rio de Janeiro) 90:13–19
Ostrowski de Núñez M (1996) Life history studies of heterophyid trematodes in the Neotropical Region: Pygidiopsis australis sp. n., a sibling species of P. pindoramensis Travassos, 1929. Acta Parasitol 41:13–19
Pearson J (2008) Family Heterophyidae Leiper, 1909. In: Bray RA, Gibson DI (eds) Key to the Trematoda. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 113–140
Refuerzo PG, Garcia EY (1937) Pygidiopsis marivillai, a new heterophyid trematode from the Philippines. Phil J Sci 64:359–363
Seo BS, Hong ST, Chai JY (1981) Studies on intestinal trematodes in Korea. III. Natural human infections of Pygidiopsis summa and Heterophyes heterophyes nocens. Seoul J Med 22:228–235
Simões SBE, Barbosa HS, Santos CP (2005) Redescription and surface ultrastructure of Pygidiopsis macrostomum (Digenea: Heterophyidae). J Parasitol 91:931–936
Simões SBE, Scholz T, Barbosa HS, Santos CP (2006) Taxonomic status, redescription, and surface ultrastructure of Ascocotyle (Phagicola) pindoramensis n. comb. (Digenea: Heterophyidae). J Parasitol 92:501–508
Simões SBE, Barbosa HS, Santos CP (2009) The life history of Pygidiopsis macrostomum Travassos, 1928 (Digenea: Heterophyidae). Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz (Rio de Janeiro) 104:106–111
Takahashi S (1929) On the eggs of several kinds of intestinal trematodes, which resemble that of Clonorchis sinensis, especially the eggs of Stellantchasmus falcatus and Pygidiopsis summus found in human stools, with a supplement on the examinations of the helminthic parasites of the dogs and cats in Okayama Prefecture. Okayama Igakkai Zasshi 41:1502–1513
Travassos L (1928) Informaçoes sobre alguns Heterophyidae dos animais domesticos do Brasil. Ann Fac Med São Paulo 3:1–4
Travassos L (1929) Sur une nouvelle espèce du genre Pygidiopsis, Pygidiopsis pindoramensis n. sp. Compt Rend Soc Bresil Biol (Paris) 100:956–957
Wang PQ (1982) Notes on some digenetic trematodes of birds in Fujian Province. Wuyi Sci J 2:75–90
Witenberg G (1929) Studies on the trematode-family Heterophyidae. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 23:131–268
Yamaguti S (1939) Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part 25. Trematodes of birds, IV. Jpn J Zool 8:131–210
Yamaguti S (1958) Systema helminthum. Vol. I. The digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. Interscience Publishers Inc., New York, pp 699–724
Yamaguti S (1971) Synopsis of digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. Vols. I & II. Keigaku, Tokyo, Japan, pp 633–634
Yokogawa M, Sano M, Itabashi T, Kachi S (1965) Studies on the intestinal flukes. II. Epidemiological studies on heterophyid trematodes of man in Chiba Prefecture. Jpn J Parasitol 14:577–585
Youssef MM, Mansour NS, Awadalla HN, Hammouda NA, Khalifa R, Boulos LM (1987) Heterophyid parasites of man from Idku, Maryut and Manzala lake areas in Egypt. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 17:475–479
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Sinuon Muth and Dr. Duong Socheat, Center for Parasitology, Entomology, and Malaria Control, Phnom Penh, Cambodia, who invited us to Cambodia on the occasion of Korea–Cambodia International Collaboration on Intestinal Parasite Control in Cambodia (2006–2011). We also appreciate the staff of Korea Association of Health Promotion who helped this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohn, WM., Kim, DG., Jung, BK. et al. Pygidiopsis cambodiensis n. sp. (Digenea: Heterophyidae) from experimental hamsters infected with metacercariae in mullets from Cambodia. Parasitol Res 115, 123–130 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4727-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4727-1