Abstract
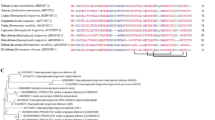
Insects possess both cellular and humoral immune responses. The latter makes them capable to recognize and control invading pathogens after synthesis of a variety of small proteins, also known as antimicrobial peptides. Defensins, cysteine-rich cationic peptides with major activity against Gram-positive bacteria, are one ubiquitous class of antimicrobial peptides, widely distributed in different animal and plant taxa. Regarding triatomines in each of the so far analyzed species, various defensin gene isoforms have been identified. In the present study, these genes were sequenced and used as a molecular marker for phylogenetic analysis. Considering the vectors of Chagas disease the authors are reporting for the first time the presence of these genes in Triatoma sordida (Stål, 1859), Rhodnius nasutus (Stål, 1859), and Panstrongylus megistus (Burmeister, 1835). Members of the Triatoma brasiliensis species complex were included into the study to verify the genetic variability within these taxa. Mainly in their mature peptide, the deduced defensin amino acid sequences were highly conserved. In the dendrogram based on defensin encoding nucleotide, sequences the Triatoma Def3/4 genes were separated from the rest. In the dendrogram based on deduced amino acid sequences the Triatoma Def2/3/4 together with Rhodnius DefA/B pre-propeptides were separated from the rest. In the sub-branches of both the DNA and amino acid dendrograms, the genus Triatoma was separated from the genus Rhodnius as well as from P. megistus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abascal F, Zardoya R, Posada D (2005) ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 21:2104–2105
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Araújo CAC, Waniek PJ, Stock P, Mayer C, Jansen AM, Schaub GA (2006) Sequence characterization and expression patterns of defensin and lysozyme encoding genes from the gut of the reduviid bug, Triatoma brasiliensis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 36:547–560
Araújo CAC, Cabello PH, Jansen AM (2007) Growth behaviour of two Trypanosoma cruzi strains in single and mixed infections: in vitro and in the intestinal tract of the blood-sucking bug, Triatoma brasiliensis. Acta Trop 101:225–231
Araújo CAC, Waniek PJ, Jansen AM (2008) Development of a Trypanosoma cruzi (TcI) isolate in the digestive tract of an unfamiliar vector, Triatoma brasiliensis (Hemiptera, Reduviidae). Acta Trop 107:195–199
Araújo CAC, Waniek PJ, Jansen AM (2009) An overview of Chagas disease and the role of triatomines on its distribution in Brazil. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 9:227–234
Araújo CAC, Waniek PJ, Jansen AM (2014) TcI and TcII co-infection can enhance Trypanosoma cruzi growth in Rhodnius prolixus. Parasit Vectors 7:94
Assumpção TCF, Francischetti IMB, Andersen JF, Schwarz A, Santana JM, Ribeiro JMC (2008) An insight into the sialome of the blood-sucking bug Triatoma infestans, a vector of Chagas’ disease. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:213–232
Azambuja P, Feder D, Garcia ES (2004) Isolation of Serratia marcescens in the midgut of Rhodnius prolixus: impact on the establishment of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi in the vector. Exp Parasitol 107:89–96
Azambuja P, Ratcliffe NA, Garcia ES (2005) Towards an understanding of the interactions of Trypanosoma cruzi and Trypanosoma rangeli within the reduviid insect host Rhodnius prolixus. An Acad Bras Cienc 77:397–404
Bargues MD, Zuriaga MA, Mas-Coma S (2014) Nuclear rDNA pseudogenes in Chagas disease vectors: evolutionary implications of a new 5.8S+ITS-2 paralogous sequence marker in triatomines of North, Central and northern South America. Infect Genet Evol 21:134–156
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Blandón-Naranjo M, Zuriaga MA, Azofeifa G, Zeledón R, Bargues MD (2010) Molecular evidence of intraspecific variability in different habitat-related populations of Triatoma dimidiata (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) from Costa Rica. Parasitol Res 106:895–905
Boulanger N, Bulet P, Lowenberger C (2006) Antimicrobial peptides in the interactions between insects and flagellate parasites. Trends Parasitol 22:262–268
Bulet P, Cociancich S, Reuland M, Sauber F, Bischoff R, Hegy G, Van Dorsselaer A, Hetru C, Hoffmann JA (1992) A novel insect defensin mediates the inducible antibacterial activity in larvae of the dragonfly Aeschna cyanea (Paleoptera, Odonata). Eur J Biochem 209:977–984
Bulet P, Hetru C, Dimarcq JL, Hoffmann D (1999) Antimicrobial peptides in insects; structure and function. Dev Comp Immunol 23:329–344
Bulet P, Stöcklin R, Menin L (2004) Anti-microbial peptides: from invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol Rev 198:169–184
Carvalho Ade O, Gomes VM (2011) Plant defensins and defensin-like peptides—biological activities and biotechnological applications. Curr Pharm Des 17:4270–4293
Castro D, Seabra SH, Garcia ES, Souza W, Azambuja P (2007) Trypanosoma cruzi: ultrastructural studies of adhesion lysis and biofilm formation by Serratia marcescens. Exp Parasitol 117:201–207
Chen JS, Reddy V, Chen JH, Shlykov MA, Zheng WH, Cho J, Yen MR Jr, Saier M (2012) Phylogenetic characterization of transport protein superfamilies: superiority of superfamily tree programs over those based on multiple alignments. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 21:83–96
Costa J, Freitas-Sibajev MGR, Marchon-Silva V, Pires MQ, Pacheco RS (1997) Isoenzymes detect variation in populations of Triatoma brasiliensis (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae). Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 92:459–464
Coura J (2013) Chagas disease: control, elimination and eradication. Is it possible? Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 108:962–967
d’Alençon E, Bierne N, Girard PA, Magdelenat G, Gimenez S, Seninet I, Escoubas JM (2013) Evolutionary history of x-tox genes in three lepidopteran species: origin, evolution of primary and secondary structure and alternative splicing generating a repertoire of immune-related proteins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43:54–64
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772
Dassanayake RS, Silva Gunawardene YIN, Tobe SS (2007) Evolutionary selective trends of insect/mosquito antimicrobial defensin peptides containing cysteine-stabilized α/β motifs. Peptides 28:62–75
de Paula AS, Diotaiuti L, Galvão C (2007) Systematics and biogeography of Rhodniini (Heteroptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae) based on 16S mitochondrial rDNA sequences. J Biogeogr 34:699–712
Dimarcq JL, Bulet P, Hetru C, Hoffmann J (1998) Cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides in invertebrates. Biopolymers 47:465–477
Ganz T (2003) Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nature 3:710–720
Garcia ES, Genta FA, Azambuja P, Schaub GA (2010) Interactions between intestinal compounds of triatomines and Trypanosoma cruzi. Trends Parasitol 26:499–505
Hetru C, Hoffmann D, Bulet P (1998) Antimicrobial peptides from insects. In: Brey PI, Hultmark D (eds) Molecular mechanisms of immune responses in insects. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 40–66
Hoffmann JA (1995) Innate immunity of insects. Curr Opin Immunol 7:4–10
Hoffmann JA (1997) Immune responsiveness in vector insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:11152–11153
Hypsa V, Tietz DF, Zrzavý J, Rego RO, Galvão C, Jurberg J (2002) Phylogeny and biogeography of Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae): molecular evidence of a New World origin of the Asiatic clade. Mol Phylogenet Evol 23:447–457
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic, New York, pp 21–132
Jurberg J, Galvão C (2006) Biology, ecology, and systematics of Triatominae (Heteroptera, Reduviidae), vectors of Chagas disease, and implications for human health. In: Rabitsch W (ed) Hug the Bug. For Love of true Bugs. Festschrift zum 70. Geburtstag von Ernst Heiss. Denisia 19, zugleich Kataloge der OÖ Landesmuseen 50, Linz, pp 1096–1116
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kitani H, Naessens J, Kubo M, Nakamura Y, Iraqi F, Gibson J, Yamakawa M (2009) Synthetic nonamer peptides derived from insect defensin mediate the killing of African trypanosomes in axenic culture. Parasitol Res 105:217–225
Kollien AH, Schaub GA (2000) The development of Trypanosoma cruzi in Triatominae. Parasitol Today 16:381–387
Kollien AH, Schmidt J, Schaub GA (1998) Modes of association of Trypanosoma cruzi with the intestinal tract of the vector Triatoma infestans. Acta Trop 70:127–141
Lamberty M, Ades S, Uttenweiler-Joseph S, Brookharts G, Bushey D, Hoffmann JA, Bulet P (1999) Insect immunity: isolation from the lepidopteran Heliothis virescens of a novel insect defensin with potent antifungal activity. J Biol Chem 274:9320–9326
Lehane MJ (2005) Transmission of parasites by blood-sucking insects. In: Lehane MJ (ed) The biology of blood-sucking in insects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 150–201
Lima MM, Sarquis O (2008) Is Rhodnius nasutus (Hemiptera; Reduviidae) changing its habitat as a consequence of human activity? Parasitol Res 102:797–800
Lopez L, Morales G, Ursic R, Wolff M, Lowenberger C (2003) Isolation and characterization of a novel insect defensin from Rhodnius prolixus, a vector of Chagas disease. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:439–447
Marcilla A, Bargues MD, Ramsey JM, Magallon-Gastelum E, Salazar-Schettino PM, Abad-Franch F, Dujardin JP, Schofield CJ, Mas-Coma S (2001) The ITS-2 of the nuclear rDNA as a molecular marker for populations, species, and phylogenetic relationships in Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae), vectors of Chagas disease. Mol Phylogenet Evol 18:136–142
Marcilla A, Bargues MD, Abad-Franch F, Panzera F, Carcavallo RU, Noireau F, Galvão C, Jurberg J, Miles MA, Dujardin JP, Mas-Coma S (2002) Nuclear rDNA ITS-2 sequences reveal polyphyly of Panstrongylus species (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae), vectors of Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Genet Evol 1:225–235
Martínez FH, Villalobos GC, Cevallos AM, De la Torre P, Laclette JP, Alejandre-Aguilar R, Espinoza B (2006) Taxonomic study of the Phyllosoma complex and other triatomine (Insecta: Hemiptera: Reduviidae) species of epidemiological importance in the transmission of Chagas disease: using ITS-2 and mtCytB sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 41:279–287
Mello CB, Azambuja P, Garcia ES, Ratcliffe NA (1996) Differential in vitro and in vivo behavior of three strains of Trypanosoma cruzi in the gut and hemolymph of Rhodnius prolixus. Exp Parasitol 82:112–121
Monteiro FA, Wesson DM, Dotson EM, Schofield CJ, Beard CB (2000) Phylogeny and molecular taxonomy of the Rhodniini derived from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Am J Trop Med Hyg 62:460–465
Monteiro FA, Donnelly MJ, Beard CB, Costa J (2004) Nested clade and phylogeographic analyses of the Chagas disease vector Triatoma brasiliensis in Northeast Brazil. Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:46–56
Moreira CJ, Waniek PJ, Valente RH, Carvalho PC, Perales J, Feder D, Geraldo RB, Castro HC, Azambuja P, Ratcliffe NA, Mello CB (2014) Isolation and molecular characterization of a major hemolymph serpin from the triatomine, Panstrongylus megistus. Parasit Vectors 7:23
Nayduch D, Cho H, Joyner C (2013) Staphylococcus aureus in the house fly: temporospatial fate of bacteria and expression of the antimicrobial peptide defensin. J Med Entomol 50:171–178
Pfeiler E, Bitler BG, Ramsey JM, Palacios-Cardiel C, Markow TA (2006) Genetic variation, population structure, and phylogenetic relationships of Triatoma rubida and T. recurva (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae) from the Sonoran Desert, insect vectors of the Chagas’ disease parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Phylogenet Evol 41:209–221
Quisberth S, Waleckx E, Monje M, Chang B, Noireau F, Brenière SF (2011) “Andean” and “non-Andean” ITS-2 and mtCytB haplotypes of Triatoma infestans are observed in the Gran Chaco (Bolivia): population genetics and the origin of reinfestation. Infect Genet Evol 11:1006–1014
Ribeiro JMC, Genta FA, Sorgine MHF, Logullo R, Mesquita RD, Paiva-Silva GO, Majerowicz D, Medeiros M, Koerich L, Terra WR, Ferreira C, Pimentel AC, Bisch PM, Leite DC, Diniz MMP, Vianez Junior JSGV, Da Silva ML, Araujo RB, Gandara ACP, Brosson S, Salmon D, Bousbata S, González-Caballero N, Silber AM, Alves-Bezerra M, Gondim KC, Silva-Neto MAC, Atella GC, Araujo H, Dias FA, Polycarpo C, Vionette-Amaral RJ, Fampa P, Melo AC, Tanaka AS, Balczun C, Oliveira JH, Gonçalves RL, Lazoski C, Rivera-Pomar R, Diambra L, Schaub GA, Garcia ES, Azambuja P, Braz GR, Oliveira PL (2014) An insight into the transcriptome of the digestive tract of the bloodsucking bug, Rhodnius prolixus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8:e2594
Schofield CJ, Galvão C (2009) Classification, evolution and species groups within the Triatominae. Acta Trop 110:88–100
Schwarz R, Dayhoff M (1979) Matrices for detecting distant relationships. In: Dayhoff M (ed) Atlas of protein sequences. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington D.C., pp. 353–358
Schwarz A, Medrano-Mercado N, Schaub GA, Struchiner CJ, Bargues MD, Levy MZ, Ribeiro JMC (2014) An updated insight into the sialotranscriptome of Triatoma infestans: developmental stage and geographic variations. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 8:e3372
Seufi AM, Hafez EE, Galal FH (2011) Identification, phylogenetic analysis and expression profile of an anionic insect defensin gene, with antibacterial activity, from bacterial-challenged cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis. BCM Mol Biol 12:47
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tartarotti E, Ceron CR (2005) Ribosomal DNA ITS-1 intergenic spacer polymorphism in triatomines (Triatominae, Heteroptera). Biochem Genet 43:365–373
Tartarotti E, Azeredo-Oliveira MT, Ceron CR (2006) Phylogenetic approach to the study of Triatomines (Triatominae, Heteroptera). Braz J Biol 66:703–708
Thevessin K, Kristensen HH, Thomma BPHJ, Cammue BPA, François IEJA (2007) Therapeutic potential antifungal plant and insect defensins. Drug Discov Today 12:966–971
Thomma BP, Cammue BP, Thevissen K (2003) Mode of action of plant defensins suggests therapeutic potential. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord 3:1–8
Thompson JD, Higgis DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment though sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Vieira CS, Waniek PJ, Mattos DP, Castro DP, Mello CB, Ratcliffe NA, Garcia ES, Azambuja P (2014) Humoral responses in Rhodnius prolixus: bacterial feeding induces differential patterns of antibacterial activity and enhances mRNA levels of antimicrobial peptides in the midgut. Parasit Vectors 7:232
Vieira CS, Mattos DP, Waniek PJ, Santangelo JM, Figueiredo MB, Gumiel M, da Mota FF, Castro DP, Garcia ES, Azambuja P (2015) Rhodnius prolixus interaction with Trypanosoma rangeli: modulation of the immune system and microbiota population. Parasit Vectors 8:135
Waniek PJ, Hendgen-Cotta UB, Stock P, Mayer C, Kollien AH, Schaub GA (2005) Serine proteinases of the human body louse (Pediculus humanus): sequence characterization and expression patterns. Parasitol Res 97:486–500
Waniek PJ, Castro HC, Sathler PC, Miceli L, Jansen AM, Araújo CAC (2009) Two novel defensin-encoding genes of the Chagas disease vector Triatoma brasiliensis (Reduviidae, Triatominae): gene expression and peptide-structure modeling. J Insect Physiol 55:840–848
Waniek PJ, Jansen AM, Araújo CAC (2011) Trypanosoma cruzi infection modulates the expression of Triatoma brasiliensis def1 in the midgut. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 11:845–847
Weirauch C (2008) Cladistic analysis of Reduviidae (Heteroptera: Cimicomorpha) based on morphological characters. Syst Entomol 33:229–274
Weirauch C, Munro JB (2009) Molecular phylogeny of the assassin bugs (Hemiptera: Reduviidae), based on mitochondrial and nuclear ribosomal genes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 53:287–299
Wiesner J, Vilcinskas A (2010) Antimicrobial peptides: the ancient arm of the human immune system. Virulence 1:440–464
Yao H, Song J, Liu C, Luo K, Han J, Li Y, Pang X, Xu H, Zhu Y, Xiao P, Chen S (2010) Use of ITS2 region as the universal DNA barcode for plants and animals. PLoS One 5:e13102
Zhu S (2008) Discovery of six families of fungal defensing-like peptides provides insights into origin and evolution of the CSαβ defensins. Mol Immunol 45:828–838
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa no Estado do Rio de Janeiro-FAPERJ (E-26/100.456/2007; E-26/110.403/2011), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico-CNPq (PDJ: 151187/2009-6). CNPq – Ministério da Saúde/Secretaria de Vigilância Sanitária (SVS). Authors also thank Pesquisador Visitante FIOCRUZ/CNPq (158817/2010-9). CACA is a Post-doctor fellow by Capes/PNPD in Biodiversidade e Saúde-IOC/FIOCRUZ Research Fellow and PJW is a PDS FAPERJ Fellow (E-26/200.117/2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental file 1
Similarity in percent of cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences of Hemipteran defensins analyzed in the present study. (DOC 251 kb)
Supplemental file 2
Maximum likelihood dendrogram of Triatominae defensin encoding cDNA sequences. One sequence of Pyrrhocoris apterus and two of Nilaparvata lugens were used as outgroup. Branch labels show the percentages of bootstrap samples supporting that branch. (PPT 130 kb)
Supplemental file 3
Maximum likelihood dendrogram of deduced Triatominae defensin amino acid sequences. Sequences of Pyrrhocoris apterus and Nilaparvata lugens were used as outgroup. Branch labels show the percentages of bootstrap samples supporting that branch. (PPT 124 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Araújo, C.A.C., Lima, A.C.B., Jansen, A.M. et al. Genes encoding defensins of important Chagas disease vectors used for phylogenetic studies. Parasitol Res 114, 4503–4511 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4694-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4694-6