Abstract
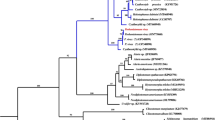
Protostrongylids are important pulmonary parasites of ungulates, particularly caprines. Their complex life cycles involve terrestrian gastropods as intermediate hosts. Morphological discrimination of larvae in feces and snails is impossible to the species level, and molecular data are missing for many species. To improve diagnosis and epidemiology of protostrongylids, this study describes internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS-2) sequences for five protostrongylid and one metastrongylid species from Uzbekistan. Morphological and molecular analyses identified Protostrongylus rufescens, Protostrongylus hobmaieri, Protostrongylus sp., Spiculocaulus leuckarti, and Cystocaulus ocreatus. Sequence differences between ITS-2 were sufficient to allow species identification, e.g., in the Protostrongylinae intraspecific and interspecific genetic distances ranged between 0–0.01 and 0.05 and 0.16, respectively. There was one exception in the Elaphostrongylidae with identical ITS-2 sequences in Elaphostrongylus cervi and Elaphostrongylus rangiferi questioning their status as valid species. Maximum likelihood analysis sequences largely supported the currently assumed phylogenetic relationships among Protostrongylidae as predicted using morphological characters. The monophyly of the subfamilies Varestrongylinae, Elaphostrongylinae, and Protostrongylinae was corroborated with support values in Shimodaira-Hasegawa or Bayesian modifications of the approximate likelihood ratio test (aLRT) ≥97 %, but support for Muellerinae was weak (8 and 52 %, respectively) since Muellerius capillaris differs significantly from the other Muellerinae. On the genus level, paraphyly of the genus Protostrongylus was confirmed since the members of the genera Spiculocaulus and Orthostrongylus were located within the Protostrongylus cluster (aLRT ≥99 %). Maximum likelihood unequivocally assigned every unique sequence to the correct species confirming suitability of ITS-2 regions for diagnosis protostrongylids except of E. cervi and E. rangiferi.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RC (1978) Keys to the genera of the superfamily Metastrongyloidea, No. 5. In: Anderson RC, Chabaud AG, Wilmott S (eds) CIH keys to the nematode parasites of vertebrates. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, England, pp 1–40
Anderson RC (2000) Nematode parasites of vertebrates: their development and transmission, 2nd edn. CAB International, Wallinford
Anisimova M, Gil M, Dufayard FJ, Dessimoz C, Gascuel O (2011) Survey of branch support methods demonstrates accuracy, power, and robustness of fast likelihood-based approximation schemes. Syst Biol 60:685–699
Asmundsson I, Mortenson J, Hoberg EP (2008) Muscleworms, Parelaphostrongylus andersoni (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae), discovered in Columbia white-tailed deer from Oregon and Washington: implications for biogeography and host associations. J Wildl Dis 44:16–27
Boev SN (1975) Protostrongylids. Fundamentals of nematology, vol 25, in Russian. Nauka, Moscow
Brooks DR, Hoberg EP (2006) Systematics and emerging infections diseases: from management to solution. J Parasitol 92:426–429
Carreno RA, Hoberg EP (1999) Evolutionary relationships among the Protostrongylidae(Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea) as inferred from morphological characters, with consideration of parasite-host coevolution. J Parasitol 85:638–648
Carreno RA, Nadler SA (2003) Phylogenetic analysis of the Metastrongyloidea (Nematoda: Strongylida) inferred from ribosomal RNA gene sequences. J Parasitol 89:965–973
Carreno RA, Caporossi D, Beade MS, Marull CA, Uhart MM, Markwardt DD, Nadler SA (2012) Discovery of an undescribed protostrongylid nematode from the endangered pampas deer (Ozotoceros bezoarticus celer) in Argentina. J Wildl Dis 48:724–731
Chilton NB, Huby-Chilton F, Gasser RB, Beveridge I (2006) The evolutionary origins of nematodes within the order Strongylida are related to predilection sites within hosts. Mol Phylogenet Evol 40:118–128
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772
Dougherty EC, Goble FC (1946) The genus Protostrongylus Kamenskii, 1905 (Nematoda: Metastrongylidae), and its relatives: preliminary notes. J Parasitol 32:7–16
Gajadhar A, Steeves-Gurnsey T, Kendall J, Lankester M, Stéen M (2000) Differentiation of dorsal-spinedelaphostrongyline larvae by polymerase chain reaction amplification of ITS-2 of rDNA. J Wildl Dis 36:713–722
Gasser RB, Bott NJ, Chilton NB, Hunt P, Beveridge I (2008) Toward practical, DNA-based diagnostic methods for parasitic nematodes of livestock—bionomic and biotechnological implications. Biotechnol Adv 26:325–334
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Gasser RB, Chilton NB, Hoste H, Beveridge I (1993) Rapid sequencing of rDNA from single worms and eggs of parasitic helminths. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2525–2526
Hoberg EP, Polley L, Gunn A, Nishi JS (1995) Umingmakstrongylus pallikuukensis gen. nov. et sp. nov. (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae) from muskoxen, Ovibosmoschatus, in the central Canadian Arctic, with comments on biology and biogeography. Can J Zool 73:2266–2282
Huby-Chilton F, Chilton NB, Lankester MW, Gadjadhar AA (2006) Single-strand confirmation polymorphism (SSCP) as a new diagnostic tool to distinguish dorsal-spined larvae of the Elaphostrongylinae (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae) from cervids. Vet Parasitol 135:153–162
Jabbar A, Mohandas N, Jex AR, Gasser RB (2013) The mitochondrial genome of Protostrongylusrufescens—implications for population and systematic studies. Parasite Vectors 6:263
Jenkins EJ, Appleyard GD, Hoberg EP et al (2005) Geographic distribution of the muscle-dwelling nematode Parelaphostrongylus odocoilei in North America, using molecular identification of first stage larvae. J Parasitol 91:574–584
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780
Kontrimavichus VL, Delamure SL, Boev SN (1976) Metastrongyloids of domestic and wild animals. Fundamentals of nematology, vol 26. Nauka, Moskow, in Russian
Kuchboev AE (2009) Population ecology, systematics of nematodes of the family Protostrongylidae Leiper, 1926 and functional-metabolic processes within the system parasite-host. Dissertation for the degree of Doctor of Biology, Tashkent
Kuchboev AE, Hoberg EP (2011) Morphological and ultrastructural changes in tissues of intermediate and definitive hosts infected by Protostrongylidae. Turk J Zool 35:1–7
Kulmamatov EN, Isakova DT, Azimov DA (1994) Helminths of vertebrates in mountain ecosystems of Uzbekistan. Fan Publishers, Tashkent (in Russian)
Kutz SJ, Hoberg EP, Polley L (2000) Emergence of third-stage larvae of Umingmakstrongylus pallikuukensis from three gastropod intermediate host species. J Parasitol 86:743–749
Kutz SJ, Asmundsson I, Hoberg EP et al (2007) Serendipitous discovery of a novel protostrongylid (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea) in caribou (Rangifer tarandus), muskoxen (Ovibos moschatus) and moose (Alces alces) from high latitudes of North America based on DNA sequence comparisons. Can J Zool 85:1143–1156
Lesage C, Jouet D, Patrelle C, Guitton JS, Decors A, Ferté H (2014) Protostrongylus pulmonalis (Frölich, 1802) and P. oryctolagi Baboš, 1955 (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae), parasites of the lungs of European hare (Lepus europaeus L.) in France: morphological and molecular approaches. Parasitol Res 113:2103–2111
Lankester M (2001) Extrapulmonary lungworms of cervids. In: Samuel WM, Pybus M, Kocan AA (eds) Parasitic diseases of wild mammals. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 228–278
Lehnert K, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Schaudien D, Bleidorn C, Wohlsein P, Siebert U (2010) Transmission of lungworms of harbour porpoises and harbour seals: molecular tools determine potential vertebrate intermediate hosts. Int J Parasitol 40:845–853
Movsesyan SO, Bojahchjan GA, Arutjunova LD, Chubarj FA (2009) Protostrongylides (Protostrongylidae) and helminthosis of small ruminants caused by them in Armenia. Russ Parasitol J 4:10–29, in Russian, with English abstract
Murakami M, Inoshima Y, El-Dakhly KM, Yanai T, Ishiguro N (2011) Genetic characterization of Protostrongylus shiozawai from Japanese serows (Capricornis crispus). J Parasitol 97:1178–1180
Nikolsky YD (1961) The methods of the qualitative and quantitative microscopic examination of helminth larvae for the intra-vital diagnosis of helminthosis in small cattle. The Proceedings of UzNIVI, Samarkand, 14, pp. 153–160 (in Russian)
Ohbayashi M, Ueno H (1974) A new lungworm, Protostrongylus (Davtianostrongylus) shiozawai n. sp. from the Japanese serow, Capricornis crispus (Temminck). Jap J Vet Res 22:111–115
Panayotova-Pencheva MS (2011) Species composition and morphology of protostrongylids (Nematoda: Protostrongylidae) in ruminants from Bulgaria. Parasitol Res 109:1015–1020
Schmidt HA, von Haeseler A (2009) Phylogenetic inference using maximum likelihood methods. In: Lemey P, Salemi M, Vandamme A-M (eds) The phylogenetc handbook, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 181–209
Skrjabin KI (1928) The method of complete helminthological dissection of vertebrates, including humans. Moscow State University, Moscow, 25 pp
Stéen M, Chabaud AG, Rehbinder C (1989) Species of the genus Elaphostrongylus parasite of Swedish cervidae. A description of E. alces n. sp. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 64:134–142
Strimmer K, von Haeseler A (1997) Likelihood-mapping: a simple method to visualize phylogenetic content of a sequence alignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6815–6819
Verocai GG, Lejeune M, Finstad GL, Kutz SJ (2013) A Nearctic parasite in a Palearctic host: Parelaphostrongylus andersoni (Nematoda; Protostrongylidae) infecting semi-domesticated reindeer in Alaska. Int J Parasitol Parasite Wildl 2:119–123
Vicente J, Fernández de Mera IG, Gortazar C (2006) Epidemiology and risk factors analysis of elaphostrongylosis in red deer (Cervuselaphus) from Spain. Parasitol Res 98:77–85
Acknowledgments
This work has been carried out within the frames of DEUTSCHER AKADEMISCHER AUSTAUSCHDIENST (DAAD) scholarship grant (Germany) in 2012 between Institute of Parasitology and Tropical Veterinary Medicine, Free University of Berlin, Germany, and the Institute of the Gene Pool Plants and Animals of Uzbekistan Academy of Sciences. We thank the associates of the Institute of Parasitology and Tropical Veterinary Medicine Dr. J. Fanke and Mrs. S. Ramünke for constant assistance provided regarding morphological and molecular studies during the whole period of work on this grant.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
(XLSX 248 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuchboev, A.E., Krücken, J., Ruziev, B.H. et al. Molecular phylogeny and diagnosis of species of the family Protostrongylidae from caprine hosts in Uzbekistan. Parasitol Res 114, 1355–1364 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4313-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4313-6