Abstract
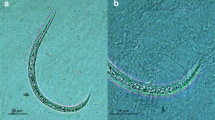
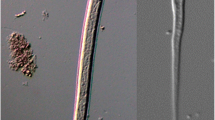
Angiostrongylus vasorum is a parasitic nematode that can cause serious and potentially fatal disease in dogs and other canids. The aim of this study was to determine the intermediate slug species infected in nature by sampling sites in Greater London and Hertfordshire located within a known hyperendemic region. Overall, A. vasorum larvae were recovered from 6/381 slugs (1.6 %) by tissue digestion, and their identity was confirmed by PCR. Infected slugs originated from three different sites in the Greater London area: one in Waltham Forest and two in Bromley. Slugs parasitised by A. vasorum were identified by a combination of external morphological characteristics and molecular techniques and belonged to three different families: the Arionidae, the Milacidae and the Limacidae. This includes two new host records for the parasite: Arion distinctus and Tandonia sowerbyi. This is the first record of A. vasorum in the family Milacidae, indicating that the parasite has a broader intermediate host range than previously recognised.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson R (2005) An annotated list of the non-marine Mollusca of Britain and Ireland. J Conchol 38:607–637
Backeljau T, Van Beeck M (1986) Epiphallus anatomy in the Arion hortensis species aggregate (Mollusca, Pulmonata). Zool Scr 15:61–68. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.1986.tb00209.x
Barr NB, Cook A, Elder P, Molongoski J, Prasher D, Robinson DG (2009) Application of a DNA barcode using the 16S rRNA gene to diagnose pest Arion species in the USA. J Molluscan Stud 75:187–191. doi:10.1093/mollus/eyn047
Bolt G, Monrad J, Koch J, Jensen AL (1994) Canine angiostrongylosis: a review. Vet Rec 135:447–452. doi:10.1136/vr.135.19.447
Borst A, Box ATA, Fluit AC (2004) False-positive results and contamination in nucleic acid amplification assays: suggestions for a prevent and destroy strategy. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:289–299. doi:10.1007/s10096-004-1100-1
Bourque A, Whitney H, Conboy G (2005) Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in a coyote (Canis latrans) from Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. J Wildl Dis 41:816–819. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-41.4.816
Cameron RAD, Eversham B, Jackson N (1983) A field key to the slugs of the British Isles. Field Stud 5:807–824
Chapman PS, Boag AK, Guitian J, Boswood A (2004) Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in 23 dogs (1999–2002). J Small Anim Pract 45:435–440. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.2004.tb00261.x
Chen D, Zhang Y, Shen H, Wei Y, Huang D, Tan Q, Lan X, Li Q, Chen Z, Li Z (2011) Epidemiological survey of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in the west-central region of Guangdong Province, China. Parasitol Res 109:305–314. doi:10.1007/s00436-011-2255-1
Davies SM (1977) The Arion hortensis complex, with notes on A. intermedius Normand (Pulmonata: Arionidae). J Conchol 29:173–187
Davies SM (1979) Segregates of the Arion hortensis complex (Pulmonata: Arionidae), with the description of a new species, Arion owenii. J Conchol 30:123–127
De Winter AJ (1984) The Arion hortensis complex (Pulmonata: Arionidae): designation of types, descriptions, and distributional patterns, with special reference to the Netherlands. Zool Meded 59:1–17
Dreijers E, Reise H, Hutchinson JMC (2013) Mating of the slugs Arion lusitanicus auct. non Mabille and A. rufus (L.): different genitalia and mating behaviours are incomplete barriers to interspecific sperm exchange. J Molluscan Stud 79:51–63. doi:10.1093/mollus/eys033
Eckert J, Lämmler G (1972) Angiostrongylose bei Mensch und Tier. Z Parasitenkd 39:303–322. doi:10.1007/BF00329093
Ferdushy T, Kapel CMO, Webster P, Al-Sabi MNS, Grønvold J (2009) The occurrence of Angiostrongylus vasorum in terrestrial slugs from forests and parks in the Copenhagen area, Denmark. J Helminthol 83:379–383. doi:10.1017/S0022149X09377706
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299
Gasser RB, Chilton NB, Hoste H, Beveridge I (1993) Rapid sequencing of rDNA from single worms and eggs of parasitic helminths. Nucleic Acids Res 21:2525–2526
Guilhon J, Cens B (1973) Angiostrongylus vasorum (Baillet, 1866). Etude biologique et morphologique. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 48:567–596
Helm J, Gilleard JS, Jackson M, Redman E, Bell R (2009) A case of canine Angiostrongylus vasorum in Scotland confirmed by PCR and sequence analysis. J Small Anim Pract 50:255–259. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.2009.00741.x
Jefferies R, Morgan ER, Shaw SE (2009) A SYBR green real-time PCR assay for the detection of the nematode Angiostrongylus vasorum in definitive and intermediate hosts. Vet Parasitol 166:112–118. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.07.042
Jones GW, Neal C, Turner GR (1980) Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in dogs in Cornwall. Vet Rec 106:83
Kirk L, Limon G, Guitian J, Hermosilla C, Fox M (2014) Angiostrongylus vasorum in United Kingdom mainland—a nationwide postal questionnaire survey of veterinary practices. Vet Rec 175:118. doi:10.1136/vr.102196
Mc Donnell RJ, Paine TD, Stouthamer R, Gormally MJ, Harwood JD (2008) Molecular and morphological evidence for the occurrence of two new species of invasive slugs in Kentucky, Arion intermedius Normand and Arion hortensis Férussac (Arionidae: Stylommatophora). J Ky Acad Sci 69:117–123. doi:10.3101/1098-7096-69.2.117
Morgan E, Shaw S (2010) Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in dogs: continuing spread and developments in diagnosis and treatment. J Small Anim Pract 51:616–621. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.2010.01000.x
Morgan ER, Shaw SE, Brennan SF, De Waal TD, Jones BR, Mulcahy G (2005) Angiostrongylus vasorum: a real heartbreaker. Trends Parasitol 21:49–51. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2004.11.006
Morgan ER, Tomlinson A, Hunter S, Nichols T, Roberts E, Fox MT, Taylor MA (2008) Angiostrongylus vasorum and Eucoleus aerophilus in foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Great Britain. Vet Parasitol 154:48–57. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.02.030
Morgan ER, Jefferies R, Krajewski M, Ward P, Shaw SE (2009) Canine pulmonary angiostrongylosis: the influence of climate on parasite distribution. Parasitol Int 58:406–410. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2009.08.003
Patteson MW, Wotton PR, Lucke VM, Wright AI, Gibbs C (1987) Angiostrongylus vasorum in a terrier. Vet Rec 120:349
Pfleger V, Chatfield J (1988) A guide to the snails of Britain and Europe. Hamlyn, London
Roth S, Hatteland BA, Solhøy T (2012) Some notes on reproductive biology and mating behaviour of Arion vulgaris Moquin-Tandon 1855 in Norway including a mating experiment with a hybrid of Arion rufus (Linnaeus 1758) x ater (Linnaeus 1758). J Conchol 41:249–257
Schnyder M, Fahrion A, Riond B, Ossent P, Webster P, Kranjc A, Glaus T, Deplazes P (2010) Clinical, laboratory and pathological findings in dogs experimentally infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum. Parasitol Res 107:1471–1480. doi:10.1007/s00436-010-2021-9
Schnyder M, Schaper R, Bilbrough G, Morgan ER, Deplazes P (2013) Seroepidemiological survey for canine angiostrongylosis in dogs from Germany and the UK using combined detection of Angiostrongylus vasorum antigen and specific antibodies. Parasitology 140:1442–1450. doi:10.1017/S0031182013001091
Segovia JM, Torres J, Miquel J, Llaneza L, Feliu C (2001) Helminths in the wolf, Canis lupus, from north-western Spain. J Helminthol 75:183–192. doi:10.1079/JOH200152
Shaw DJ, Grenfell BT, Dobson AP (1998) Patterns of macroparasite aggregation in wildlife host populations. Parasitology 117:597–608. doi:10.1017/s0031182098003448
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539. doi:10.1038/msb.2011.75
Simpson VR, Neal C (1982) Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in dogs and slugs. Vet Rec 111:303–304
Soroka M, Skujiene G (2011) Species identification of slugs of genus Arion Férussac, 1819 (Mollusca, Pulmonata) on the basis of genetics studies. Ekologija 57:70–80. doi:10.6001/ekologija.v57i2.1887
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Taubert A, Pantchev N, Vrhovec MG, Bauer C, Hermosilla C (2009) Lungworm infections (Angiostrongylus vasorum, Crenosoma vulpis, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus) in dogs and cats in Germany and Denmark in 2003-2007. Vet Parasitol 159:175–180. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.10.005
Trees AJ (1987) Angiostrongylus vasorum in dogs in Wales. Vet Rec 120:424
Yamakawa Y, McGarry JW, Denk D, Dukes-McEwan J, Macdonald N, Mas A, McConnell F, Tatton B, Valentine EG, Wayne J, Williams JM, Hetzel U (2009) Emerging canine angiostrongylosis in northern England: five fatal cases. Vet Rec 164:149–152. doi:10.1136/vr.164.5.149
Yousif F, Lämmler G (1975) The suitability of several aquatic snails as intermediate hosts for Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Z Parasitenkd 47:203–210. doi:10.1007/BF00418203
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W (2000) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7:203–214. doi:10.1089/10665270050081478
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Emma Wanostrocht for sample collection and The Royal Veterinary College for financial support (Royal Veterinary College manuscript number 715).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zainab Patel and A. Christina Gill contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, Z., Gill, A.C., Fox, M.T. et al. Molecular identification of novel intermediate host species of Angiostrongylus vasorum in Greater London. Parasitol Res 113, 4363–4369 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4111-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4111-6