Abstract
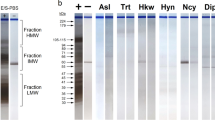
Currently, diagnosis of Parascaris equorum infection in equids is limited to patent infections. The goals of this study were to culture P. equorum larvae in vitro and identify excretory-secretory (ES) products for prepatent diagnostic testing. Parascaris equorum L2/L3 larvae were hatched and cultured for up to 3 weeks for ES product collection. Fifth stage (L5) P. equorum were also cultured for ES product collection. Examination of ES fractions by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and silver stain revealed L2/L3 products ranging from 12–94 kDa and L5 products ranging from 12–189 kDa. Western blot analyses were conducted using polyclonal antibodies produced against P. equorum or Baylisascaris procyonis L2/L3 ES products, sera from rabbits inoculated with B. procyonis or Toxocara canis eggs, and sera from animals naturally infected with P. equorum or T. canis. Western blot results indicated parasite antigens migrating at 19 and 34 kDa may be useful for specifically detecting P. equorum infections.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abebe W, Tsuji N, Kasuga-Aoki H, Miyoshi T, Isobe T, Arakawa T, Matsumoto Y, Yoshihara S (2002) Lung-stage protein profile and antigenic relationship between Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum. J Parasitol 88(4):826–828
Andersen UV, Howe DK, Dangoudoubiyam S, Toft N, Reinemeyer CR, Lyons ET, Olsen SN, Monrad J, Nejsum P, Nielsen MK (2013) SvSXP: a Strongylus vulgaris antigen with potential for prepatent diagnosis. Parasit Vectors 6:84
Bello T (1985) The insidious invasive verminous antigens of the horse. J Equine Vet Sci 5(3):163–167
Boyce WM, Branstetter BA, Kazacos KR (1988) In vitro culture of Baylisascaris procyonis and initial analysis of larval excretory-secretory antigens. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 55(1):15–18
Brown PJ, Clayton HM (1979) Hepatic pathology of experimental Parascaris equorum infection in worm-free foals. J Comp Pathol 89(1):115–123
Clayton HM, Duncan JL (1978) Clinical signs associated with Parascaris equorum infection in worm-free pony foals and yearlings. Vet Parasitol 4:69–78
Clayton HM, Duncan JL (1979) The migration and development of Parascaris equorum in the horse. Int J Parasitol 94:285–292
Concetti A, Fioretti E, Barra D, Ascoli F (1984) Protease inhibitors from the parasitic worm Parascaris equorum. Eur J Biochem 145(2):417–421
Dangoudoubiyam S, Kazacos KR (2009) Differentiation of larva migrans caused by Baylisascaris procyonis and Toxocara species by Western blotting. Clin Vaccine Immunol 16(11):1563–1568
de Savigny DH (1975) In vitro maintenance of Toxocara canis larvae and a simple method for the production of Toxocara ES antigen for use in serodiagnostic tests for visceral larva migrans. J Parasitol 61(4):781–782
Dowdall SM, Proudman CJ, Love S, Klei TR, Matthews JB (2003) Purification and analyses of the specificity of two putative diagnostic antigens for larval cyathostomin infection in horses. Res Vet Sci 75(3):223–229
Fillaux J, Magnaval JF (2013) Laboratory diagnosis of human toxocariasis. Vet Parasitol 193(4):327–336
Hawley JH, Peanasky RJ (1992) Ascaris suum: are trypsin inhibitors involved in species specificity of Ascarid nematodes? Exp Parasitol 75(1):112–118
Iddawela RD, Rajapakse RPVJ, Perera NAND, Agatsuma T (2007) Characterization of a Toxocara canis species-specific excretory-secretory antigen (TcES-57) and development of a double sandwich ELISA for diagnosis of visceral larva migrans. Korean J Parasitol 45(1):19–26
Kasuga-Aoki H, Tsuji N, Suzuki K, Arakawa T, Matsumoto Y, Isobe T (2001) Identification of larval-stage antigens of Ascaris suum recognized with immune sera from pigs. J Vet Med Sci 63(6):683–685
Kazacos KR (2001) Baylisascaris procyonis and related species. Parasitic diseases of wild mammals. Samuel WM, Pybus MJ, and Kocan AA. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, NJ.
Kazacos KR, Wirtz WL, Burger PP, Christmas CS (1981) Raccoon ascarid larvae as a cause of fatal central nervous system disease in subhuman primates. J Am Vet Med Assoc 179(11):1089–1094
Kennedy MW, Qureshi F (1986) Stage-specific secreted antigens of the parasitic larval stages of the nematode Ascaris. Immunology 58(3):515–522
Kennedy MW, Maizels RM, Meghji M, Young L, Qureshi F, Smith HV (1987a) Species-specific and common epitopes on the secreted and surface antigens of Toxocara cati and Toxocara canis infective larvae. Parasite Immunol 9(4):407–420
Kennedy MW, Qureshi F, Haswell-Elkins M, Elkins DB (1987b) Homology and heterology between the secreted antigens of the parasitic larval stages of Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum. Clin Exp Immunol 67(1):20–30
Kennedy MW, Qureshi F, Fraser EM, Haswell-Elkins MR, Elkins DB, Smith HV (1989) Antigenic relationships between the surface-exposed, secreted and somatic materials of the nematode parasites Ascaris lumbricoides, Ascaris suum, and Toxocara canis. Clin Exp Immunol 75(3):493–500
Knox DP, Kennedy MW (1988) Proteinases released by the parasitic larval stages of Ascaris suum, and their inhibition by antibody. Mol Biochem Parasitol 28(3):207–216
Loukas A, Doedens A, Hintz M, Maizels RM (2000) Identification of a new C-type lectin, TES-70, secreted by infective larvae of Toxocara canis, which binds to host ligands. Parasitology 121(5):545–554
Lyons ET, Drudge JH, Tolliver SC (1976) Studies on the development and chemotherapy of larvae of Parascaris equorum (Nematoda: Ascaridoidea) in experimentally and naturally infected foals. J Parasitol 62(3):453–459
Lyons ET, Drudge JH, Tolliver SC (1988) Natural infection with Eimeria leuckarti: prevalence of oocysts in feces of horse foals on several farms in Kentucky during 1986. Am J Vet Res 49(1):96–98
Lysek H, Malinsky J, Janisch R (1985) Ultrastructure of eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides Linnaeus, 1758. I. Egg-shells. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 32(4):381–384
Magnaval JF, Fabre R, Maurieres P, Charlet JP, de Larrard B (1991) Application of the Western blotting procedure for the immunodiagnosis of human toxocariasis. Parasitol Res 77:697–702
Nunes CM, Tundisi RN, Garcia JF, Heinemann MB, Ogassawara S, Richtzenhain LJ (1997) Cross-reactions between Toxocara canis and Ascaris suum in the diagnosis of visceral larva migrans by Western blotting technique. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 39(5):253–256
Rajapakse RP, Vasanthathilake VW, Lloyd S, Fernando ST (1992) Collection of eggs and hatching and culturing second-stage larvae of Toxocara vitulorum in vitro. J Parasitol 78(6):1090–1092
Rhoads ML, Fetterer RH, Urban JF (1998) Effect of protease class-specific inhibitors on in vitro development of the third- to fourth-stage larvae of Ascaris suum. J Parasitol 84(4):686–690
Rogers RA (1956) A study of eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides var. suum with the electron microscope. J Parasitol 42(2):97–108
Smyth JD (1990) In vitro cultivation of parasitic helminths. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Speiser F, Gottstein B (1984) A collaborative study on larval excretory/secretory antigens of Toxocara canis for the immunodiagnosis of human toxocariasis with ELISA. Acta Trop 41(4):361–372
Srihakim S, Swerczek TW (1978) Pathologic changes and pathogenesis of Parascaris equorum infection in parasite-free pony foals. Am J Vet Res 39(7):1155–1160
Sugane K, Oshima T (1983) Purification and characterization of excretory and secretory antigen of Toxocara canis larvae. Immunology 50(1):113–120
Urban JF (1982) Development of immune responsiveness to Ascaris suum antigens in pigs vaccinated with ultraviolet-attenuated eggs. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 3:399–409
Urban JF, Douvres FW, Tromba FG (1981) A rapid method for hatching Ascaris suum eggs in vitro. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 48(2):241–243
Acknowledgments
We thank the University of Kentucky’s College of Agriculture for funding this research. The authors are grateful to Frank Berry, Bryan Cassill, Dr. Chris Christensen, Kristen Fox, Dr. Eugene Lyons, Dr. Martin Nielsen, Dr. William Silvia, Laura Strasinger, Dr. Elizabeth Ubelhor, and Stacy White for their assistance with specimen collection. We also thank Dr. Noel Inocencio, Jessica Gould, Lynn Ennis, and Sara Tanner for sharing their laboratory expertise.
This investigation (Manuscript No. 14-07-056) was approved by the director of the University of Kentucky Agricultural Experiment Station. All research conducted was in compliance with the current laws of the United States.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burk, S.V., Dangoudoubiyam, S., Brewster-Barnes, T. et al. In vitro culture of Parascaris equorum larvae and initial investigation of parasite excretory-secretory products. Parasitol Res 113, 4217–4224 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4097-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4097-0