Abstract
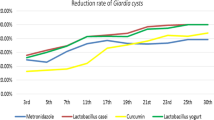
Various antiprotozoal drugs have been used to counteract the spread of giardiasis. However, due to increase in resistance to these compounds, there is an urgent need to find a natural biocompatible product to fight the pathogen in more healthy and effective way. The present study was designed to compare the therapeutic effect of probiotic Lactobacillus casei alone and in conjunction with antiprotozoal drugs on the outcome of giardiasis in murine model. BALB/c mice were challenged with Giardia intestinalis trophozoites, and 1 day after infection, these mice were treated with either probiotic alone or in conjunction with antiprotozoal drugs. Cyst, trophozoite, and lactobacilli counts were monitored vis-a-vis histopathological alterations in the small intestine. It was found that albendazole administered orally 1 day after Giardia infection was the most effective antiprotozoal drug among albendazole, tinidazole, metronidazole, and nitazoxanide. It reduced both the severity and duration of giardiasis. More specifically, oral administration of the probiotic L. casei in conjunction with albendazole further reduced the Giardia infection as was evident by the restored normal gut morphology. This suggests that probiotics and antiprotozoal drugs in combination may be the better alternative therapy for treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and enhanced recovery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benyacoub J, Perez PF, Rochat F, Saudan KY, Reuteler G, Antille N, Humen M, De Antoni GL, Cavadini C, Blum S, Schiffrin EJ (2005) Enterococcus faecium SF68 enhances the immune response to Giardia intestinalis in mice. J Nutri 135:1171–1176
Furness BW, Beach MJ, Roberts JM (2000) Giardiasis surveillance—United States, 1992–1997. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep CDC Surveill Summ 49:1–16
Gardner TB, Hill DR (2001) Treatment of giardiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev 14:114–128
Gendrel D, Treluyer JM, Richard-Lenoble D (2003) Parasitic diarrhea in normal and malnourished children. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 17:189–197
Gretchen CD, Ehrlich PR (1996) Global change and human susceptibility to disease. Annu Rev Energ Env 21:125–144
Haller DS, Blum S, Bode C, Hammes WP, Schiffrin EJ (2000) Activation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by nonpathogenic bacteria in vitro: evidence of NK cells as primary targets. Infect Immun 68:752–775
Humen MA, De Antoni GL, Benyacoub J, Costas MB, Cardozo MI, Kozubsky L, Saudan K, Doenzli-Bruand A, Blum S, Schiffrin EJ, Perez PF (2005) Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 antagonizes Giardia intestinalis in vivo. Infect Immun 7:1265–1269
Isolauri E, Sutas Y, Kankaanpaa P, Arvilommi H, Salminen S (2001) Probiotics: effects on immunity. Am J Clin Nutr 73:444S–450S
Jokipii L, Jokipii AMM (1979) Single-dose metronidazole and tinidazole as therapy for giardiasis: success rates, side effects, and drug absorption and elimination. J Infect Dis 140:984–988
Katelaris PH, Naeem A, Farthing MJ (1994) Activity of metronidazole, azithromycin and three benzimidazoles on Giardia lamblia growth and attachment to a human intestinal cell line. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 8:187–192
Lemee V, Zaharia I, Nevez G, Rabodonirina M, Brasseur P, Ballet JJ, Favennec L (2000) Metronidazole and albendazole susceptibility of 11 clinical isolates of Giardia duodenalis from France. J Antimicrob Chemother 46:819–821
Marteau P, Cuillerier E, Meance S, Gerhardt MF, Myara A, Bouvier M, Bouley C, Tondu F, Bommelaer G, Grimaud JC (2002) Bifidobacterium animal is strain DN-173 010 shortens the colonic transit time in healthy women: a double-blind, randomized, controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:587–593
Mercenier A, Pavan S, Pot B (2002) Probiotics as biotherapeutic agents: present knowledge and future prospects. Curr Pharma Des 8:99–110
Murray CJ, Lopez AD (1997) Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: global burden of disease study. Lancet 349:1498–1504
Shukla G, Sidhu RK (2011) Lactobacillus casei as a probiotic in malnourished Giardia lamblia-infected mice: a biochemical and histopathological study. Can J Microbiol 157:127–135
Shukla G, Devi P, Sehgal R (2008) Effect of Lactobacillus casei as a probiotic on modulation of giardiasis. Dig Dis Sci 53:2671–2679
Shukla G, Sharma G, Goyal N (2010) Probiotic characterization of lactobacilli and yeast strains isolated from whey beverage and therapeutic potential of Lactobacillus yoghurt in murine giardiasis. Am J Biomed Sci 2:248–261
Speelman P (1985) Single-dose tinidazole for the treatment of giardiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27:227–229
Tiwari RP, Hoondal GS, Tewari R (2009) Laboratory techniques in microbiology and biotechnology. Abhishek, Chandigarh
Tripathi DM, Gupta N, Lakshmi V, Saxena KC, Agarwal AK (1999) Antigiardial and immunostimulatory effect of piper longum on giardiasis due to Giardia lamblia. Phytother Res 13:561–565
Upcroft P, Upcroft JA (2001) Drug targets and mechanisms of resistance in the anaerobic protozoa. Clin Microbiol Rev 14:150–164
Vinayak VK, Khanna R, Kum K (1991) Kinetics of intraepithelium and lamina propria lymphocyte responses during Giardia lamblia infection in mice. Microb Pathog 10:343–350
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Mr. Bhandari, Senior Technician, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh India, for maintaining and providing the G. intestinalis (Portland I) culture. English language editing done by Mr. Vivek Khanna is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, G., Kaur, H. & Sharma, L. Comparative therapeutic effect of probiotic Lactobacillus casei alone and in conjunction with antiprotozoal drugs in murine giardiasis. Parasitol Res 112, 2143–2149 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3394-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3394-3