Abstract
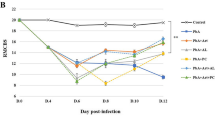
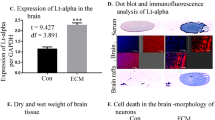
Cerebral malaria (CM) is the most severe complication of Plasmodium falciparum in humans and major cause of death. SP600125 is a specific, small molecule inhibitor of JNK that prevents the phosphorylation of c-Jun and blocks the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and attenuates neuronal apoptosis in several neurodegenerative disorders. We evaluated the effect of SP600125 treatment on the survival of Plasmodium berghei ANKA (PbA)-infected C57BL/6J mice. Administration of SP600125 improved survival in PbA-infected C57BL6J mice but has no effect on parasitemia. Further, SP600125 administration resulted in attenuation of neuronal cell death along with inhibition of proinflammatory mediators TNF-α and COX-2 and proapoptotic mediators p-c-Jun and active caspase 3 in PbA-infected mice. The promising findings of this study make SP600125 a potential agent for supportive therapy to alleviate inflammation and neuronal cell death associated with CM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand SS, Babu PP (2011) c-Jun N terminal kinases (JNK) are activated in the brain during the pathology of experimental cerebral malaria. Neurosci Lett 488:118–122
Ball HJ, MacDougall HG, McGregor IS, Hunt NH (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2 in the pathogenesis of murine cerebral malaria. J Infect Dis 189:751–758
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O’Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, Bhagwat SS, Manning AM, Anderson DW (2002) SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:13681–13686
Das M, Sabio G, Jiang F, Rincón M, Flavell RA, Davis RJ (2009) Induction of hepatitis by JNK-mediated expression of TNF-alpha. Cell 136:249–60
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239–252
de Souza JB, Riley EM (2002) Cerebral malaria: the contribution of studies in animal models to our understanding of immunopathogenesis. Microbes Infect 4:291–300
Fan M, Goodwin M, Vu T, Brantley-Finley C, Gaarde WA, Chambers TC (2000) Vinblastine-induced phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL is mediated by JNK and occurs in parallel with inactivation of the Raf-1/MEK/ERK cascade. J Biol Chem 275:29980–29985
Gao Y, Signore AP, Yin W, Cao G, Yin XM, Sun F, Luo Y, Graham SH, Chen J (2005) Neuroprotection against focal ischemic brain injury by inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and attenuation of the mitochondrial apoptosis-signaling pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:694–712
Gillardon F, Spranger M, Tiesler C, Hossmann KA (1999) Expression of cell death-associated phospho-c-Jun and p53-activated gene 608 in hippocampal CA1 neurons following global ischemia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 73:138–143
Grau GE, Fajardo LF, Piguet PF, Allet B, Lambert PH, Vassalli P (1987) Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) as an essential mediator in murine cerebral malaria. Science 237:1210–1212
Guan QH, Pei DS, Liu XM, Wang XT, Xu TL, Zhang GY (2006) Neuroprotection against ischemic brain injury by SP600125 via suppressing the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of apoptosis. Brain Res 1092:36–46
Herdegen T, Skene P, Bahr M (1997) The c-Jun transcription factor—bipotential mediator of neuronal death, survival and regeneration. Trends Neurosci 20:227–231
Hunot S, Vila M, Teismann P, Davis RJ, Hirsch EC, Przedborski S, Rakic P, Flavell RA (2004) JNK-mediated induction of cyclooxygenase 2 is required for neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:665–70
Idro R, Jenkins NE, Newton CR (2005) Pathogenesis, clinical features, and neurological outcome of cerebral malaria. Lancet Neurol 4:827–840
Karin M, Liu Z, Zandi E (1997) AP-1 function and regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:240–246
Kenzel S, Mancuso G, Malley R, Teti G, Golenbock DT, Henneke P (2006) c-Jun kinase is a critical signaling molecule in a neonatal model of group B streptococcal sepsis. J Immunol 176:3181–3188
Lackner P, Burger C, Pfaller K, Heussler V, Helbok R, Morandell M, Broessner G, Tannich E, Schmutzhard E, Beer R (2007) Apoptosis in experimental cerebral malaria: spatial profile of cleaved caspase-3 and ultrastructural alterations in different disease stages. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 33:560–571
Lei K, Nimnual A, Zong WX, Kennedy NJ, Flavell RA, Thompson CB, Bar-Sagi D, Davis RJ (2002) The Bax subfamily of Bcl2-related proteins is essential for apoptotic signal transduction by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Mol Cell Biol 22:4929–4942
Liu J, Lin A (2005) Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res 15:36–42
Ma N, Harding AJ, Pamphlett R, Chaudhri G, Hunt NH (1997) Increased c-Fos expression in the brain during experimental murine cerebral malaria: possible association with neurologic complications. J Infect Dis 175:1480–1489
Maundrell K, Antonsson B, Magnenat E, Camps M, Muda M, Chabert C, Gillieron C, Boschert U, Vial KE, Martinou JC, Arkinstall S (1997) Bcl-2 undergoes phosphorylation by c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinases in the presence of the constitutively active GTP-binding protein Rac1. J Biol Chem 272:25238–25242
Medana IM, Hunt NH, Chan-Ling T (1997) Early activation of microglia in the pathogenesis of fatal murine cerebral malaria. Glia 19:91–103
Nakahara T, Uchi H, Urabe K, Chen Q, Furue M, Moroi Y (2004) Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase on lipopolysaccharide induced maturation of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Int Immunol 16:1701–1709
Nieminen R, Lahti A, Jalonen U, Kankaanranta H, Moilanen E (2006) JNK inhibitor SP600125 reduces COX-2 expression by attenuating mRNA in activated murine J774 macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 6:987–996
Pongponratn E, Turner GD, Day NP, Phu NH, Simpson JA, Stepniewska K, Mai NT, Viriyavejakul P, Looareesuwan S, Hien TT, Ferguson DJ, White NJ (2003) An ultrastructural study of the brain in fatal Plasmodium falciparum malaria. AmJTrop Med Hyg 69:345–359
Potter S, Chan-Ling T, Ball HJ, Mansour H, Mitchell A, Maluish L, Hunt NH (2006) Perforin mediated apoptosis of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells during experimental cerebral malaria. Int J Parasitol 36:485–496
Rhoades KL, Golub SH, Economou JS (1992) The regulation of the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter region in macrophage, T cell, and B cell lines. J Biol Chem 267:22102–22107
Rössler OG, Steinmüller L, Giehl KM, Thiel G (2002) Role of c-Jun concentration in neuronal cell death. J Neurosci Res 70:655–664
Schlingensiepen KH, Wollnik F, Kunst M, Schlingensiepen R, Herdegen T, Brysch W (1994) The role of Jun transcription factor expression and phosphorylation in neuronal differentiation, neuronal cell death, and plastic adaptations in vivo. Cell Mol Neurobiol 14:487–505
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-Jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874:123–130
Smeyne RJ, Vendrell M, Hayward M, Baker SJ, Miao GG, Schilling K, Robertson LM, Curran T, Morgan JI (1993) Continuous c-fos expression precedes programmed cell death in vivo. Nature 363:166–169
Snow RW, Guerra CA, Noor AM, Myint HY, Hay SI (2005) The global distribution of clinical episodes of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 434:214–217
Tsuruta F, Sunayama J, Mori Y, Hattori S, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y, Yoshioka K, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) JNK promotes Bax translocation to mitochondria through phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins. EMBO J 23:1889–1899
Venters HD, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (2000) A new concept in neurodegeneration: TNFalpha is a silencer of survival signals. Trends Neurosci 23:175–180
Waisberg M, Tarasenko T, Vickers BK, Scott BL, Willcocks LC, Molina-Cruz A, Pierce MA, Huang CY, Torres-Velez FJ, Smith KG, Barillas-Mury C, Miller LH, Pierce SK, Bolland S (2011) Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus protects against cerebral malaria in mice. PNAS 108:1122–1127
Wang W, Shi L, Xie Y, Ma C, Li W, Su X, Huang S, Chen R, Zhu Z, Mao Z, Han Y, Li M (2004) SP600125, a new JNK inhibitor, protects dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Res 48:195–202
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wei Z, Li H, Zhou H, Zhang Z, Zhang Z (2009) JNK inhibitor protects dopaminergic neurons by reducing COX-2 expression in the MPTP mouse model of subacute Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 285:172–177
Ward P, Equinet L, Packer J, Doerig C (2003) Protein kinases of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: the kinome of a divergent eukaryote. BMC Genomics 5:79
Wiese L, Kurtzhals JA, Penkowa M (2006) Neuronal apoptosis, metallothionein expression and proinflammatory responses during cerebral malaria in mice. Exp Neurol 200:216–226
Yamamoto K, Ichijo H, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 is phosphorylated and inactivated by an ASK1/Jun N-terminal protein kinase pathway normally activated at G(2)/M. Mol Cell Biol 19:8469–8478
Yatsushige H, Ostrowski RP, Tsubokawa T, Colohan A, Zhang JH (2007) Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosci Res 85:1436–1448
Acknowledgments
The authors thank DBT, CSIR, DST, Government of India, New Delhi, and UGC-SAP for financial assistance. S.S.A. and M. M. would like to thank the CSIR for awarding Senior Research Fellowship. The authors greatly acknowledge Miss. Nalini for her technical assistance with confocal microscope.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand, S.S., Maruthi, M. & Babu, P.P. The specific, reversible JNK inhibitor SP600125 improves survivability and attenuates neuronal cell death in experimental cerebral malaria (ECM). Parasitol Res 112, 1959–1966 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3352-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3352-0