Abstract
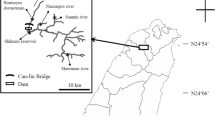
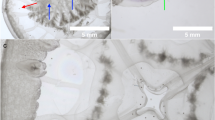
A parasitological survey for Metagonimus yokogawai metacercariae was carried out by examining a total of 321 freshwater fish comprising of 7 species. Of the 321 fish samples examined, 182 (56.7 %) were found to be infected with M. yokogawai metacercariae. The prevalence of M. yokogawai metacercariae in Opsariichthys pachycephalus was 93.4 % (86/92), Zacco platypus 75.0 % (30/40), Distoechodon turmirostris 61.3 % (38/62), Varicorhinus barbatulus 56.5 % (13/23), Hemibarbus labeo 33.3 % (1/3), Acrossocheilus formosanus 15.9 % (14/88), and 0 % in Sinibrama macrops (0/13), respectively. This is the first record of M. yokogawai infection in Z. platypus, D. turmirostris, V. barbatulus, and H. labeo in Taiwan. The major site of predilection of the metacercariae in the fishes was in the scale, but some metacercariae were also observed in the flesh and fins. The M. yokogawai metacercariae were orally inoculated into mice, rat, gerbil, and golden hamster to study their infectivity and also to obtain the adult worms for taxonomic study. Worm recovery in hamsters was 75.3 %, in mice was 70.0 %, in rats was 23.3 %, and in gerbils was 6.0 %, respectively. Moreover, larger worms were recovered from the golden hamster. Golden hamster was thus found to be the most susceptible experimental rodent host for the infectivity study of Metagonimus. Besides M. yokogawai, metacercariae of Centrocestus formosanus was also observed in the fishes examined.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn YK (1993) Intestinal fluke of genus Metagonimus and their second intermediate host in Kangwon-do. Korean J Parasitol 31:331–340
Akahane H, Kusano F, Hayashi K (1983) An epidemiological study on metagonimiasis in Shiga Prefecture, with special reference to the infection pattern of Metagonimus yokogawai metacercariae of ayu (Plecoglossue altivelis) reared in ponds. Jpn J Parasitol 32:85–90 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Chai JY, Lee SH (2002) Food-borne intestinal trematode infections in the Republic of Korea. Parasitol Int 51:129–154
Chai JY, Seo BS, Lee SH (1984) Study on Metagonimus yokogawai (Katsurada, 1912) in Korea VII Susceptibility of various strains of mice to Metagonimus infection and effect of prednisolone. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 22:153–160
Chai JY, Sohn WM, Kim MH, Hong ST, Lee SH (1991) Three morphological types of the genus Metagonimus encysted in the dace, Tribolodon tazamowskii, caught from the Sumjin River. Korean J Parasitol 29:217–225
Chai JY, Kim J, Lee SH (1995) Invasion of Metagonimus yokogawai into the submucosa layer of the small intestine of immuno-suppressed mice. Korean J Parasitol 33:313–321
Dung DT, De NV, Waikagul J, Dalsgaard A, Chai JY, Sohn WM, Murrell KD (2007) Fishborne zoonotic intestinal trematodes, Vietnam. Emerg Infect Dis 13:1828–1833
Fan PC (1970) The metacercarial infection in freshwater fishes in Taiwan Islands. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Pub Hlth 1:156
Fried B, Abruzzi A (2010) Food-borne trematode infections of humans in the United States of America. Parasitol Res 106:1263–1280
Fried B, Graczyk TK, Tamang L (2004) Food-borne intestinal trematodiases in humans. Parasitol Res 93:159–170
Guk SM, Park JK, Seo M, Han ET, Kim JL, Chai JI (2005) Susceptibility of inbred mouse strain to infection with three species of Metagonimus prevalent in the Republic of Korea. J Parasitol 91:12–16
Gushima M (1939) On the development of Metagonimus yokogawai in the mouse and the chicken. Igaku Kenkyu 13:637–655 (in Japanese)
Huh S, Sohn WM, Chai JY (1993) Intestinal parasites of cats purchased in Seoul. Korean J Parasitol 31:371–373
Ito J (1964) Metagonimus and other human heterophyid trematodes. Progress of Medical Parasitology in Japan 1:316–393
Kim CH, Kim NM, Lee CH, Park JS (1987) Studies on the Metagonimus fluke in the Daecheong Reservoir and the upper stream of Geum River, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 25:69–82
Kino H, Suzuki T, Oishi H, Suzuki S, Yamagiwa S, Ishiguro M (2006) Geographical distribution of Metagonimus yokogawai and M. miyatai in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan, and their site preferences in the sweetfish, Plecoglossus altivelis, and hamsters. Parasitol Int 55:201–206
Lai TS (1982) Two new fish intermediate host of Metagonimus yokogawai: Acrosscheilus formosanus and Zacco pachycephalus found in Taipei, Taiwan. Journal of Medical Research 4:1283–1290 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li MH, Liao CW, Lee YL, Ooi HK, Du WY, Lu SC, Huang HI, Su KE, Fan CK (2010) Infectivity and development of Metagonimus yokagawai in experimentally infected domestic ducks (Cairina moschata). Vet Parasitol 168:45–50
Miyamoto K (1985) Studies on zoonoses in Hokkaido 7. Survey of natural definitive hosts of Metagonimus yokogawai. Jpn J Parasitol 34:371–376
Nishigori M (1924) On a new trematode, Stamnosoma formosanum n. sp. and its development. Taiwan Igakkai Zasshi 234:181–228
Nishigori M (1937) The life cycles of two new species of Heterophyidae found in Formosa. Taiwan Igakkai Zasshi 264:294–322
Ooi HK, Chen CI (1997) The importance of updating epidemiological data. Parasitol Today 13:40
Ooi HK, Chen CI, Lin SC, Tung KC, Wang JS, Kamiya M (1997) Metacercariae in fishes of Sun Moon Lake which is an endemic area for Clonorchis sinensis in Taiwan. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Pub Hlth 28:222–223
Oshima T, Kagei N, Kihata M (1966) A simple method for estimating the total number of metacercariae of Metagonimus yokogawai in sweetfish Plecoglossus altivelis: a new proposal of the infections index of fish. Jpn J Parasitol 15:161–167
Rim HJ, Kim KH, Joo KH (1996) Classification and host specificity of Metagonimus spp. from Korean freshwater fish. Korean J Parasitol 34:7–14
Saito S (1972) On the differences between Metagonimus yokogawai and Metagonimus takahashii I. The morphological comparisions. Jpn J Parasitol 21:449–458 (in Japanese with English summary)
Saito S, Chai JY, Kim KH, Lee SH, Rim HJ (1997) Metagonimus miyatai sp. nov. (Digenea: Heterophyidae), a new intestinal trematode transmitted by freshwater fishes in Japan and Korea. Korean J Parasitol 35:223–232
Seo BS, Hong NT (1969) Study on Metagonimus yokogawai (Katsurada, 1912) in Korea. 1. On the metacercaria, its distribution in the second intermediate host and the development in the final host. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 7:129–142 (in Korean with English abstract)
Sohn WM, Eom KS, Min DY, Rim HJ, Hoang EH, Yang Y, Li X (2009) Fishborne trematode metacercariae in freshwater fish from Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. Korean J Parasitol 47:249–257
Wang JS, Tung KC, Cheng HW (1980) Studies on the control of zoonotic clonorchiasis. 1. An epidemiological survey in several areas of Taiwan. Nat Sci Council Monthly ROC 8:113–122, Chinese with English summary
Wang CR, Qiu JH, Zhao JP, Xu LM, Yu WC, Zhu XQ (2006) Prevalence of helminthes in adult dogs in Heilongjiang Province, the People’s Republic of China. Parasitol Res 99:627–630
Yokogawa S (1913) On a new trematode, of which second intermediate host of Plecoglossus altivelis, with establishment of a new genus for this trematode. Okayama Igakkai zasshi 266:337–358 (in Japanese)
Acknowledgment
This study was supported partially by a grant (CTU101-P-01) from Central Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, MH., Huang, HI., Chen, PL. et al. Metagonimus yokogawai: metacercariae survey in fishes and its development to adult worms in various rodents. Parasitol Res 112, 1647–1653 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3320-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-013-3320-8