Abstract
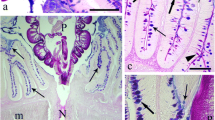
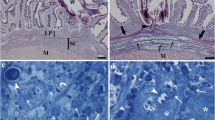
The intestinal myxosporean parasite Enteromyxum leei causes severe desquamative enteritis in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) (Teleostei) that impairs nutrient absorption causing anorexia and cachexia. In fish, as in terrestrial vertebrates, intestinal goblet cells are responsible for the adherent mucus secretion overlying epithelial cells, which constitutes a first line of innate immune defense against offending microorganisms but serves also as substrate and nutrient source for the commensal microflora. The secreted intestinal mucus of parasitized (n = 6) and unexposed (n = 8) gilthead sea bream was isolated, concentrated, and subjected to downward gel chromatography. Carbohydrate and protein contents (via PAS and Bradford stainings), terminal glycosylation (via lectin ELISA), and Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio alginolyticus adhesion were analyzed for the isolated intestinal mucins. Parasitized fish, compared with unexposed fish, presented intestinal mucus mucins with a lower glycoprotein content and glycosylation degree at the anterior and middle intestine, whereas both glycoprotein content and glycosylation degree increased at the posterior intestine section, though only significantly for the total carbohydrate content. Additionally, a slight molecular size increase was detected in the mucin glycoproteins of parasitized fish. Terminal glycosylation of the mucus glycoproteins in parasitized fish pointed to an immature mucin secretion (N-acetyl-α-d-galactosamine increase, α-l-fucose, and neuraminic-acid-α-2-6-galactose reduction). Bacterial adhesion to large-sized mucus glycoproteins (>2,000 kDa) of parasitized fish was significantly lower than in unexposed fish.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez-Pellitero P (2011) Mucosal intestinal immunity and response to parasite infections in ectothermic vertebrates. Immunology and immune system disorders. Nova Science Publishers, Inc, New York
Álvarez-Pellitero P, Palenzuela O, Sitjà-Bobadilla A (2008) Histopathology and cellular response in Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa) infections of Diplodus puntazzo (Teleostei). Parasitol Int 57:110–120
Ascencio F, Martínez-Arias W, Romero MJ, Wadstrom T (1998) Analysis of the interaction of Aeromonas caviae, A. hydrophila and A. sobria with mucins. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 20:219–229. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.1998.tb01130.x
Balebona MC, Moriñigo MA, Faris A, Krovacek K, Mansson I, Bordas MA, Borrego JJ (1995) Influence of salinity and Ph on the adhesion of pathogenic Vibrio strains to Sparus aurata skin mucus. Aquaculture 132:113–120
Bansil R, Turner BS (2006) Mucin structure, aggregation, physiological functions and biomedical applications. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 11:164–170. doi:10.1016/j.cocis.2005.11.001
Bergstrom KSB, Guttman JA, Rumi M, Ma CX, Bouzari S, Khan MA, Gibson DL, Vogl AW, Vallance BA (2008) Modulation of intestinal goblet cell function during infection by an attaching and effacing bacterial pathogen. Infect Immun 76:796–811
Bergstrom KSB, Kissoon-Singh V, Gibson DL, Ma CX, Montero M, Sham HP, Ryz N, Huang TN, Velcich A, Finlay BB, Chadee K, Vallance BA (2010) Muc2 protects against lethal infectious colitis by disassociating pathogenic and commensal bacteria from the colonic mucosa. PLoS Pathog 6. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000902
Bordas MA, Balebona MC, Chabrillon M, Rodriguez-Maroto JM, Morinigo MA (2003) Influence of temperature and salinity on the adhesion to mucous surfaces of gilt-head seabream (Sparus aurata L.) of pathogenic strains of Vibrio alginolyticus and Listonella anguillarum. Bull Eur Assoc Fish Pathol 23:273–280
Carrasson M, Grau A, Dopazo LR, Crespo S (2006) A histological, histochemical and ultrastructural study of the digestive tract of Dentex dentex (Pisces, Sparidae). Histol Histopathol 21:579–593
Cheng YF, Li MY, Wang SR, Peng HJ, Reid S, Ni NT, Fang H, Xu WF, Wang BH (2010) Carbohydrate biomarkers for future disease detection and treatment. Sci China Chem 53:3–20
Cuadrado M (2009) Enteromixosi produïda per Enteromyxum leei (Diamant, Lom i Dyková, 1994) en espàrids d’interès comercial del Mediterrani. Ph. D. Thesis, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Barcelona
Dezfuli BS, Pironi F, Campisi M, Shinn AP, Giari L (2010) The response of intestinal mucous cells to the presence of enteric helminths: their distribution, histochemistry and fine structure. J Fish Dis 33:481–488. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2761.2010.01146.x
Diamant A (1997) Fish-to-fish transmission of a marine myxosporean. Dis Aquat Org 30(2):99–105
Domeneghini C, Straini RP, Veggetti A (1998) Gut glycoconjugates in Sparus aurata L. (Pisces, Teleostei). A comparative histochemical study in larval and adult ages. Histol Histopathol 13:359–372
Enss ML, Schmidtwittig U, Heim HK, Sewing KF (1995) Prostaglandin E(2) alters terminal glycosylation of high-molecular-weight glycoproteins released by pig gastric mucous cells in-vitro. Prostag Leukot Ess Fat Acids 52:333–340
Estensoro I, Bermúdez R, Losada AP, Quiroga MI, Álvarez-Pellitero P, Sitjà-Bobadilla A (2009) Effect of Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa) on gastrointestinal neuromodulators and cell apoptosis of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). In: Book of abstracts of the 14th European Association of Fish Pathologists International Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, p 264
Estensoro I, Redondo MJ, Álvarez-Pellitero P, Sitjà-Bobadilla A (2010) Novel horizontal transmission route for Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa) by anal intubation of gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata. Dis Aquat Org 92:51–58
Estensoro I, Benedito-Palos L, Palenzuela O, Kaushik S, Sitjà-Bobadilla A, Pérez-Sánchez J (2011) The nutritional background of the host alters the disease course in a fish-myxosporean system. Vet Parasitol 175:141–150. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.09.015
Estensoro I, Redondo MJ, Salesa B, Kaushik S, Pérez-Sánchez J, Sitjà-Bobadilla A (2012a) Effect of the nutritional background and the infection by the parasite Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) on the mucosal carbohydrate pattern of the intestine of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Dis Aquat Org. doi:10.3354/dao02486
Estensoro I, Calduch-Giner JA, Kaushik S, Pérez-Sánchez J, Sitjà-Bobadilla A (2012b) Modulation of the IgM gene expression and the IgM immunoreactive cell distribution by the nutritional background in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) challenged with Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa). Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:401–410. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2012.05.029
Fleurance R, Sauvegrain C, Marques A, Le Breton A, Guereaud C, Cherel Y, Wyers M (2008) Histopathological changes caused by Enteromyxum leei infection in farmed sea bream Sparus aurata. Dis Aquat Org 79:219–228
Hicks SJ, Theodoropoulos G, Carrington SD, Corfield AP (2000) The role of mucins in host–parasite interactions. Part I—protozoan parasites. Parasitol Today 16(11):476–481
Huang ZH, Ma AJ, Wang XA (2011) The immune response of turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.), skin to high water temperature. J Fish Dis 34:619–627
Kim YS, Ho SB (2010) Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: recent insights and progress. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 12:319–330
Leknes IL (2010) Histochemical study on the intestine goblet cells in cichlid and poecilid species (Teleostei). Tissue Cell 42:61–64. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2009.09.001
Lodemel JB, Mayhew TM, Myklebust R, Olsen RE, Espelid S, Ringo E (2001) Effect of three dietary oils on disease susceptibility in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus L.) during cohabitant challenge with Aeromonas salmonicida ssp salmonicida. Aquac Res 32:935–945. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2109.2001.00621.x
Losada AP, Bermúdez R, Faílde LD, Quiroga MI (2012) Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of iNOS expression in turbot (Psetta maxima) infected with Enteromyxum scophthalmi. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:243–248. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2011.11.007
Magnadottir B (2006) Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:137–151. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2004.09.006
Neuhaus H, van der Marel M, Caspari N, Meyer W, Enss M-L, Steinhagen D (2007a) Biochemical and histochemical effects of perorally applied endotoxin on intestinal mucin glycoproteins of the common carp Cyprinus carpio. Dis Aquat Org 77:17–27. doi:10.3354/dao01836
Neuhaus H, van der Marel M, Caspari N, Meyer W, Enss ML, Steinhagen D (2007b) Biochemical and histochemical study on the intestinal mucosa of the common carp Cyprinus carpio L., with special consideration of mucin glycoproteins. J Fish Biol 70:1523–1534
Palenzuela O (2006) Myxozoan infections in Mediterranean mariculture. Parassitologia 48(1–2):27–29
Pedini V, Scocco P, Gargiulo AM, Ceccarelli P, Lorvik S (2002) Glycoconjugate characterization in the intestine of Umbrina cirrosa by means of lectin histochemistry. J Fish Biol 61:1363–1372. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2002.tb02482.x
Redondo MJ, Álvarez-Pellitero P (2009) Lectin histochemical detection of terminal carbohydrate residues in the enteric myxozoan Enteromyxum leei parasitizing gilthead seabream Sparus aurata (Pisces: Teleostei): a study using light and transmission electron microscopy. Folia Parasitol 56:259–267
Redondo MJ, Álvarez-Pellitero P (2010) Carbohydrate patterns in the digestive tract of Sparus aurata L. and Psetta maxima (L.) (Teleostei) parasitized by Enteromyxum leei and E. scophthalmi (Myxozoa). Parasitol Int 59:445–453
Rigos G, Katharios P (2010) Pathological obstacles of newly-introduced fish species in Mediterranean mariculture: a review. Rev Fish Biol Fisher 20:47–70
Roberts SD, Powell MD (2005) The viscosity and glycoprotein biochemistry of salmonid mucus varies with species, salinity and the presence of amoebic gill disease. J Comp Physiol B-Biochem Syst Environ Physiol 175:1–11. doi:10.1007/s00360-004-0453-1
Rodríguez I, Novoa B, Figueras A (2008) Immune response of zebrafish (Danio rerio) against a newly isolated bacterial pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:239–249. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2008.05.002
Roussel P, Delmotte P (2004) The diversity of epithelial secreted mucins. Curr Org Chem 8:413–437. doi:10.2174/1385272043485846
Sahoo PK, Das Mahapatra K, Saha JN, Barat A, Sahoo M, Mohanty BR, Gjerde B, Odegard J, Rye M, Salte R (2008) Family association between immune parameters and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila infection in the Indian major carp, Labeo rohita. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:163–169. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2008.04.003
Sarasquete C, Gisbert E, Ribeiro L, Vieira L, Dinis MT (2001) Glyconjugates in epidermal, branchial and digestive mucous cells and gastric glands of gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata, Senegal sole, Solea senegalensis and Siberian sturgeon, Acipenser baeri development. Eur J Histochem 45:267–278
Schroers V, Van der Marel M, Steinhagen D (2008) Influence of carp intestinal mucus molecular size and glycosylation on bacterial adhesion. Dis Aquat Org 81:135–142. doi:10.3354/dao01947
Schroers V, Van der Marel M, Neuhaus H, Steinhagen D (2009) Changes of intestinal mucus glycoproteins after peroral application of Aeromonas hydrophila to common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 288:184–189
Sitjà-Bobadilla A, Palenzuela O (2012) Enteromyxum species. In: Woo PTK, Buchmann K (eds) Fish parasites: pathology and protection. CAB International, Oxfordshire, pp 163–176
Sitjà-Bobadilla A, Diamant A, Palenzuela O, Álvarez-Pellitero P (2007) Effect of host factors and experimental conditions on the horizontal transmission of Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa) to gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L., and European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). J Fish Dis 30:243–250
Sitjà-Bobadilla A, Calduch-Giner J, Saera-Vila A, Palenzuela O, Álvarez-Pellitero P, Pérez-Sánchez J (2008) Chronic exposure to the parasite Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) modulates the immune response and the expression of growth, redox and immune relevant genes in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L. Fish Shellfish Immunol 24:610–619
Theodoropoulos G, Hicks SJ, Corfield AP, Miller BG, Carrington SD (2001) The role of mucins in host–parasite interactions: part II—helminth parasites. Trends Parasitol 17:130–135
Torrecillas S, Makol A, Caballero MJ, Montero D, Gines R, Sweetman J, Izquierdo M (2011) Improved feed utilization, intestinal mucus production and immune parameters in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed mannan oligosaccharides (MOS). Aquac Nutr 17:223–233. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2095.2009.00730.x
Tse SK, Chadee K (1991) The interaction between intestinal mucus glycoproteins and enetric infections. Parasitol Today 7:163–172. doi:10.1016/0169-4758(91)90121-4
Van der Marel M, Schroers V, Neuhaus H, Steinhagen D (2008) Chemotaxis towards, adhesion to, and growth in carp gut mucus of two Aeromonas hydrophila strains with different pathogenicity for common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J Fish Dis 31:321–330
Van der Marel M, Caspari N, Neuhaus H, Meyer W, Enss ML, Steinhagen D (2010) Changes in skin mucus of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L., after exposure to water with a high bacterial load. J Fish Dis 33:431–439
Vesterlund S, Paltta J, Karp M, Ouwehand AC (2005) Adhesion of bacteria to resected human colonic tissue: quantitative analysis of bacterial adhesion and viability. Res Microbiol 156:238–244. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2004.08.012
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MICINN) through the project AGL2009-13282-C02-01. Additional funding was obtained from the Generalitat Valenciana (research grants PROMETEO 2010/006, ISIC 2012/003). IE received a Spanish PhD fellowship (FPI) from MICINN and performed the analyses during an internship in the Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover.
Competing interests
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Estensoro, I., Jung-Schroers, V., Álvarez-Pellitero, P. et al. Effects of Enteromyxum leei (Myxozoa) infection on gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) (Teleostei) intestinal mucus: glycoprotein profile and bacterial adhesion. Parasitol Res 112, 567–576 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3168-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3168-3