Abstract
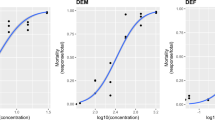
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters are responsible for pumping drugs across membranes and are an important drug detoxification mechanism. Since ABC transporters act on a wide spectrum of chemical compounds, they have been associated with multidrug resistance phenotype in various parasites and cancer cells. Here, we document the presence of a Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus tick population (Jaguar) resistant to four acaricide classes (organophosphates (OP), synthetic pyrethroids (SP), amitraz and macrocyclic lactones (ML)) and reveal that the cattle tick has a multidrug detoxification mechanism based on ABC transporter proteins. Acaricide toxicity was assessed using the larval packet test (LPT), and mortality data were subjected to probit analysis using a susceptible strain (POA) as reference. Larvae were pre-exposed to sub-lethal doses of the ABC-transporter inhibitors, cyclosporin A (CsA) and MK571, and subsequently treated with ivermectin, abamectin, moxidectin, chlorpyriphos, cypermethrin, or amitraz in LPT. Results show that lethal concentrations 50 % (LC50) of ivermectin, abamectin, moxidectin (MLs), and chlorpyriphos (OP) were significantly reduced in larvae exposed to CsA and MK571 inhibitors in the Jaguar resistant population, but LC50 did not change in POA susceptible strain larvae. LC50 of cypermetrin (SP) and amitraz remained unchanged in inhibitor-exposed larvae, compared to larvae from Jaguar and POA strains not exposed to inhibitor. These results suggest that ABC transporter proteins can protect ticks against a wide range of acaricides and have an important implication in drug resistance development as a multidrug detoxification mechanism.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bain LJ, LeBlanc GA (1996) Interaction of structurally diverse pesticides with the human MDR1 gene product P-glycoprotein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 141:288–298
Benavides E, Rodríguez JL, Romero A (2000) Isolation and partial characterization of the Montecitos strain of Boophilus microplus (Canestrini, 1877) multiresistant to different acaricides. Ann NY Acad Sci 916:668–671
Buss DS, McCaffery AR, Callaghan A (2002) Evidence for p-glycoprotein modification of insecticide toxicity in mosquitoes of the Culex pipiens complex. Med Vet Entomol 16:218–222
Castro-Janer E, Martins JR, Mendes MC, Namindome A, Klafke GM, Schumaker TT (2010) Diagnoses of fipronil resistance in Brazilian cattle ticks (Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus) using in vitro larval bioassays. Vet Parasitol 173:300–306
Da Silva Vaz Jr I, Lermen TT, Michelon A, Ferreira CAS, de Freitas DRJ, Termignoni C, Masuda A (2004) Effect of acaricides on the activity of a Boophilus microplus glutathione S-transferase. Vet Parasitol 119:237–245
FAO (1984) Ticks and tick borne disease control. A practical field manual. Volume I. Tick control. Food and Agriculture Organization, Animal Production and Health Division, Rome, p 299
FAO (2004) Resistance management and integrated parasite control in Ruminants—guidelines, executive summary. Food and Agriculture Organization, Animal Production and Health Division, Rome, p 11
Fernández-Salas A, Rodríguez-Vivas RI, Alonso-Díaz MA (2012) First report of a Rhipicephalus microplus tick population multi-resistant to acaricides and ivermectin in the Mexican tropics. Vet Parasitol 183:338–342
Ffrench-Constant RH, Daborn PJ, Le Goff G (2004) The genetics and genomics of insecticide resistance. Trends Genet 20:163–170
Guerrero FD, Pruett JH, Li AY (2002) Molecular and biochemical diagnosis of esterase-mediated pyrethroid resistance in a Mexican strain of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Appl Acarol 28:257–264
Guerrero FD, Lovis L, Martins JR (2012) Acaricide resistance mechanisms in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 21:1–6
Holland IB, Blight MA (1999) ABC-ATPases, adaptable energy generators fuelling transmembrane movement of a variety of molecules in organisms from bacteria to humans. J Mol Biol 293:381–399
Ishikawa T (1992) The ATP-dependent glutathione S-conjugate export pump. Trends Biochem Sci 17:463–468
James CE, Davey MW (2009) Increased expression of ABC transport proteins is associated with ivermectin resistance in the model nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Int J Parasitol 39:213–220
Jonsson NN, Bock RE, Jorgensen WK (2008) Productivity and health effects of anaplasmosis and babesiosis on Bos indicus cattle and their crosses, and the effects of differing intensity of tick control in Australia. Vet Parasitol 155:1–9
Kaminsky R, Bapst B, Stein PA, Strehlau GA, Allan BA, Hosking BC, Rolfe PF, Sager H (2011) Differences in efficacy of monepantel, derquantel and abamectin against multi-resistant nematodes of sheep. Parasitol Res 109:19–23
Lage H (2003) ABC-transporters: implications on drug resistance from microorganisms to human cancers. Int J Antimicrob Agents 22:188–199
Leslie EM, Deeley RG, Cole SP (2005) Multidrug resistance proteins: role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 204:216–237
Lespine A, Alvinerie M, Vercruysse J, Prichard RK, Geldhof P (2008) ABC transporter modulation: a strategy to enhance the activity of macrocyclic lactone anthelmintics. Trends Parasitol 24:293–298
Li AY, Davey RB, Miller RJ, Guerrero FD, George JE (2008) Genetics and mechanisms of permethrin resistance in the Santa Luiza strain of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 45:427–438
Lifschitz A, Entrocasso C, Alvarez L, Lloberas M, Ballent M, Manazza G, Virkel G, Borda B, Lanusse C (2010) Interference with P-glycoprotein improves ivermectin activity against adult resistant nematodes in sheep. Vet Parasitol 172:291–298
Martínez-Valladares M, Famularo MR, Fernández-Pato N, Cordero-Pérez C, Castañón-Ordóñez L, Rojo-Vázquez FA (2012) Characterization of a multidrug resistant Teladorsagia circumcincta isolate from Spain. Parasitol Res 110:2083–2087
Martins JR, Furlong J (2001) Avermectin resistance of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus in Brazil. Vet Rec 149:64
Miller RJ, Davey RB, George JE (2002) Modification of the food and agriculture organisation larval packet test to measure amitraz susceptibility against ixodidae. J Med Entomol 39:645–651
Mounsey KE, Pasay CJ, Arlian LG, Morgan MS, Holt DC, Currie BJ, Walton SF, McCarthy JS (2010) Increased transcription of glutathione S-transferases in acaricide exposed scabies mites. Parasit Vectors 18:3–43
Nolan J, Wilson JT, Green PE, Bird PE (1989) Synthetic pyrethroid resistance in field samples in the cattle tick (Boophilus microplus). Aust Vet J 66:179–182
Ortiz EM, Santamaría VM, Ortiz NA, Soberanes CN, Osorio MJ, Franco BR, Martínez IF, Quezada DR, Fragoso SH (1995) Caracterización of Boophilus microplus resistance to ixodicides in México. In: Seminario internacional de Parasitología Animal. Acapulco, México, 58–66
Patarroyo JH, Costa JO (1980) Susceptibility of Brazilian samples of Boophilus microplus to organophosphorus acaricides. Trop Anim Health Prod 12:6–10
Perry T, Batterham P, Daborn PJ (2011) The biology of insecticidal activity and resistance. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:411–422
Pohl PC, Klafke GM, Carvalho DD, Martins JR, Daffre S, da Silva Vaz Jr I, Masuda A (2011) ABC transporter efflux pumps: a defense mechanism against ivermectin in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Int J Parasit 41:1323–1333
Porretta D, Gargani M, Bellini R, Medici A, Punelli F, Urbanelli S (2008) Defence mechanisms against insecticides temephos and diflubenzuron in the mosquito Aedes caspius: the P-glycoprotein efflux pumps. Med Vet Entomol 22:48–54
Robertson J.R., Preisler H.K., Russell R.M., Plus Polo., (2002) Probit and Logit Analysis User’s Guide. LeOra Software, Petaluna, CA
Rosario-Cruz R, Almazan C, Miller RJ, Dominguez-Garcia DI, Hernandez-Ortiz R, de la Fuente J (2009a) Genetic basis and impact of tick acaricide resistance. Front Biosci 14:2657–2665
Rosario-Cruz R, Guerrero FD, Miller RJ, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Tijerina M, Dominguez-Garcia DI, Hernandez-Ortiz R, Cornel AJ, McAbee RD, Alonso-Diaz MA (2009b) Molecular survey of pyrethroid resistance mechanisms in Mexican field populations of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Parasitol Res 105:1145–1153
Soberanes CN, Santamaría VM, Fragoso SH, García VZ (2002) Primer caso de resistencia al amitraz en la garrapata del ganado Boophilus microplus en México. Tec Pec Mex 40:81–92
Tompkins JB, Stitt LE, Morrissette AM, Ardelli BF (2011) The role of Brugia malayi ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in potentiating drug sensitivity. Parasitol Res 109:1311–1322
Xu M, Molento M, Blackhall W, Ribeiro P, Beech R, Prichard R (1998) Ivermectin resistance in nematodes may be caused by alteration of P-glycoprotein homolog. Mol Biochem Parasitol 91:327–335
Yoon KS, Strycharz JP, Baek JH, Sun W, Kim JH, Kang JS, Pittendrigh BR, Lee SH, Clark JM (2011) Brief exposures of human body lice to sublethal amounts of ivermectin over-transcribes detoxification genes involved in tolerance. Insect Mol Biol 20:687–699
Acknowledgment
We thank the CNPq—Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia em Entomologia Molecular, FINEP, CAPES, CNPq and FAPERGS for supporting our work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supporting Fig. 1
Effect of CsA and MK571 (15 μM) on mortality of susceptible (POA) R. microplus larvae to acaricides determined by LPT, as described in Fig. 1 (PDF 94 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pohl, P.C., Klafke, G.M., Júnior, J.R. et al. ABC transporters as a multidrug detoxification mechanism in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus . Parasitol Res 111, 2345–2351 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3089-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3089-1