Abstract
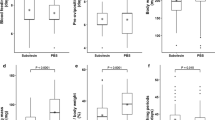
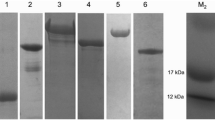
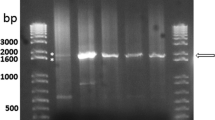
With an aim to evaluate the protective potentiality of rBm86 against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Indian Veterinary Research Institute (IVRI)-I line and Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum IVRI-II line infestations on crossbred (Bos indicus × Bos taurus) calves, 20 animals of 3 months of age were randomly divided in to four equal groups and maintained in tick-proof conditions. Animals of groups 1 and 2 were immunized with 2 ml of rBm86 (100 μg)-based vaccine (procured from Revetmex S.A. de C.V, Mexico City, Mexico) thrice at 30 days interval. Animals of groups 3 and 4 were kept as negative control and inoculated with PBS only. Each animal of group 1 and 3 was challenged with 7-day-old 50 unfed adults of H. anatolicum anatolicum (1:1, male and female), and each animal of groups 2 and 4 was challenged with 6–8-day-old R. (B.) microplus larvae obtained from 50 mg of eggs, on 17th day of the last immunization. The efficacy of rBm86 against tick infestations was determined as percentage reduction in number of adults dropped (DT%), engorged body weight (DR%), egg masses (DO%), and immunogen efficacy (E%). The calculated data were 11.8, 10.8, 15.0, and 25.1 %, respectively, for DT, DR, DO, and E% against H. anatolicum anatolicum infestation, while in the case of R. (B.) microplus infestation, the corresponding data were 6.4, 11.24, 40.7, and 44.5 %, respectively. The results indicated partial effectiveness of rBm86 antigen(s) in imparting protection against homologous and heterologous challenge infestations of Indian ticks. The results indicated identification of more effective antigen(s) for the development of vaccine against economically important tick species in India.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed J, Alp H, Aksin M, Seitzer U (2007) Current status of ticks in Asia. Parasitol Res 101(Suppl 2):S159–S162
Aguilar-Tipacamú G, Miller RJ, Hernández-Ortiz R, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Vásquez-Peláez C, García-Vázquez Z, Olvera-Valencia F, Rosario-Cruz R (2008) Inheritance of pyrethroid resistance and a sodium channel gene mutation in the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Parasitol Res 103:633–639
Almazán C, Lagunes R, Villar M, Canales M, Rosario-Cruz R, Jongejan F, de la Fuente J (2010) Identification and characterization of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus candidate protective antigens for the control of cattle tick infestations. Parasitol Res 106:471–479
Biswas S (2003) Effects of ticks on animal production system. Proc. Nat. Seminar Leather Industry in Today’s Perspective 14–15 November, Kolkata, India
Canales M, Naranjo V, Almazán C, Molina R, Tsuruta SA, Szabó MPJ, Manzano-Roman R, de la Lastra JMP, Kocan KM, Jiménez MI, Lucientes J, Villar M, de la Fuente J (2009) Conservation and immunogenicity of the mosquito ortholog of the tick-protective antigen, subolesin. Parasitol Res 105:97–111
Carreón D, de la Lastra JMP, Almazán C, Canales M, Ruiz-Fons F, Boadella M, Moreno-Cid JA, Villar M, Gortázar C, Reglero M, Villarreal R, de la Fuente J (2012) Vaccination with BM86, subolesin and akirin protective antigens for the control of tick infestations in white tailed deer and red deer. Vaccine 30:273–279
Das G, Ghosh S, Khan MH, Sharma JK (2000) Immunization of crossbred cattle against Hyalomma anatolicum anantolicum purified antigen. Exp Appl Acarol 24:645–659
de la Fuente J, Kocan KM (2003) Advances in the identification of protective antigens for recombinant vaccines against tick infestations. Exp Rev Vaccines 2:583–593
de la Fuente J, Kocan KM (2006) Strategies for development of vaccine for control of ixodid tick species. Parasite Immunol 28:275–283
de la Fuente J, Almazan C, Canales M, de la Lastra JM, Kocan KM, Willadsen P (2007) A ten-year review of commercial vaccine performance for control of tick infestations on cattle. Ani Heal Res Rev 8:23–28
de la Fuente J, Rodriguez M, Garcia-Garcia JC (2000) Immunological control of ticks through vaccination with Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus gut antigens. Ann NY Acad Sci 916:617–621
de la Fuente J, Rodriguez M, Motero C, and Lleonart R (1995) Control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infestations in cattle vaccinated with a rBm86 antigen preparation. Evidences of control of chemical-resistant strains and Babesia bovis transmission. Seminario, Internacional de Parasitologia Animal “Resitencia y control en garrapatas y moscas de importancia veterinaria” Acapulco, Mexico, pp. 101–111
de la Fuente J, Rodriguez M, Redondo M (1998) Field studies and cost effectiveness analysis of vaccination with Gavac™ against the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vaccine 16:366–373
Devendra C (1995) Animal production systems in South-East and East Asia: potential challenge for research. In Global agenda for livestock research. Proceedings of a constitution. International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), Nairobi, Kenya, 18–20 January, 1995, pp. 41–48
de Vos S, Zeinstra L, Taoufic O, Willadsen P, Jongejan F (2001) Evidence for the utility from Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in vaccination against other tick species. Exp Appl Acarol 25:245–261
Floyd RB, Sutherst RW, Hungerford J (1995) Modeling the field efficacy of a genetically engineered vaccine against the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Int J Parasitol 25:285–291
Fragoso H, Hoshmand RP (1998) Protection against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus infestation in cattle vaccinated with Boophilus microplus Bm86 containing vaccine Gavac. Vaccine 16:1990–1992
Garcia-Garcia JC, Gonzalez IL, Gonzalez DM (1999) Sequence variation in the Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Bm86 locus and implication for immunoprotection in cattle vaccinated with this antigen. Exp Appl Acarol 23:883–895
Garcia-Garcia JC, Montero C, Redondo M (2000) Control of ticks resistance to immunization with Bm86 in cattle vaccinated with the recombinant antigen Bm95 isolated from the cattle ticks, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vaccine 18:2275–2287
Ghosh S, Sharma AK, Kumar S, Tiwari SS, Rastogi S, Srivastava S, Singh M, Kumar R, Paul S, Ray DD, Rawat AKS (2011) In vitro and in vivo efficacy of Acorus calamus extract against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Parasitol Res 108:361–370
Ghosh S, Azhahianambi P (2007) Laboratory rearing of Theileria annulata-free Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum ticks. Exp Appl Acarol 43:137–146
Ghosh S, Azhahianambi P, de la Fuente J (2006) Control of ticks of ruminants, with special emphasis on livestock farming systems in India: present and future possibilities for integrated control—a review. Exp Appl Acarol 40:49–66
Ghosh S, Bansal GC, Gupta SC, Ray DD, Khan MN et al (2007) Status of ticks distribution in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. Parasitol Res 101:S207–S216
Ghosh S, Singh NK, Das G (2005) Assessment of duration of immunity in crossbred cattle immunized with glycoproteins isolated from Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Parasitol Res 95:319–326
Gutteridge WE (1997) Designer drugs: pipe dreams or realities. Parasitol 114:S145–S151
Kumar B, Kumar R, Azhahianambi P, Ray DD, Chaudhuri P, de la Fuente J, Ghosh S (2012) Comparative protective efficacy of rHaa86 and rBm86 against Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infestation in cattle. Parasite Immunol. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.2012.01356.x
Sachin K, Souvik P, Kumar SA, Rinesh K, Shankar TS, Pallab C, Ray DD, Rawat AKS, Ghosh S (2011) Diazinon resistant ststus in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from different agro-climatic regions of India. Vet Parasitol 181:274–281
Perez-Perez D, Bechara GH, Machado RZ, Andrade GM et al (2010) Efficacy of Bm86 antigen against immature instars and adults of the dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille, 1806). Vet Parasitol 167:321–326
Penichet M, Rodriguez M, Castellano O, Mandado S, Rojas Y, Rubiera R, Sanchez P, Lleonart R, de la fuente J (1994) Detection of Bm86 antigen in different strain of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and effectiveness of immunization with recombinant Bm86. Parasite Immunol 16:493–500
Martinez-Velazquez M, Castillo-Herrera GA, Rosario-Cruz R, Flores-Fernandez JM, Lopez-Ramirez J, Hernandez-Gutierrez R, Lugo-Cervantes EC (2011) Acaricidal effect and chemical composition of essential oils extracted from Cuminum cyminum, Pimenta dioica and Ocimum basilicum against the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 108:481–487
Monteiro CMO, Prata MCA, Furlong J, Faza AP, Mendes AS, Andaló V, Moino-Junior A (2010) Heterorhabditis amazonensis (Rhabditidae: Heterorhabditidae), strain RSC-5, for biological control of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 106:821–826
Pirali-Kheirabadi K, Haddadzadeh H, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M, Bokaie S, Zare R, Ghazavi M, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M (2007) Biological control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus by different strains of Metarhizium anisopliae, Beauveria bassiana and Lecanicillium psalliotae fungi. Parasitol Res 100:1297–1302
Rand KN, Moore T, Sriskantha A, Spring K, Tellam R, Willadsen P, Cobon SG (1989) Cloning and expression of a protective antigen from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 86:9657–9661
Rodriguez Valle M, Mendez L, Valdez M, Redondo M, Espinosa CM, Vargas M, Cruz RL, Barrios HP, Seoane G, Ramirez ES, Boue O, Vigil JL, Machado H, Nordelo CB, Pineiro MJ (2004) Integrated control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus ticks in Cuba based on vaccination with the anti-tick vaccine Gavac. Exp Appl Acarol 34:375–382
Rees HH (2004) Hormonal control of tick development and reproduction. Parasitology 129:S127–S143
Rosario-Cruz R, Guerrero FD, Miller RJ, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Tijerina M, Dominguez-Garcia GI, Hernandez-Ortiz R, Cornel AJ, McAbee RD, Alonso-Diaz MA (2009) Molecular survey of pyrethroid resistance mechanisms in Mexican field populations of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Parasitol Res 105:1145–1153
Ren Q, Sun M, Guan G, Li Y, Liu Z, Liu A, Ma M, Niu Q, Liu J, Yin H, Luo J (2011) Biological control of engorged female Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis (Acari: Ixodidae) ticks with different Chinese isolates of Beauveria bassiana. Parasitol Res 109:1059–1064
Rodriguez M, Penichet ML, Mouris AE (1995) Control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus populations in grazing cattle vaccinated with recombinant BM-86 antigen preparation. Vet Parasitol 57:339–349
Rodriguez M, Rubiera R, Penichet M, Montesions R, Cremata J, Falcon V, Sanchez G, Bringas R, Cordoves C, Valdes M, Lleonart R, Herrera L, de la Fuente J (1994) High level expression of the Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Bm86 antigen in the yeast Pichia pastoris forming highly immunogenic particles for cattle. J Biotec 33:135–146
Wambura PN, Gwakisa PS, Silayo RS, Rugaimukamu EA (1998) Breed-associated resistance to tick infestation in Bos indicus and their crosses with Bos taurus. Vet Parasitol 77:63–70
Willadsen P (2004) Anti-tick vaccines. Parasitol 129:S367–S387
Willadsen P, Riding G, Mckenna RV, Kemp DH, Tellam RL, Nielsen JN, Lahnstein J, Cobon GS, Gough JM (1989) Immunological control of the parasitic arthropod. Identification of a protective antigen from Boophilus microplus. J Immunol 143:1346–1351
Acknowledgments
Sincere thanks are due to the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for the funding. Senior author is highly thankful to the Indian Council of Agriculture Research (ICAR) for providing Senior Research fellowship. The technical support provided by the laboratory staff (Mr. Laxmi Lal and Naresh Kumar) of the entomology laboratory is highly acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, B., Murugan, K., Ray, D.D. et al. Efficacy of rBm86 against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (IVRI-I line) and Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum (IVRI-II line) infestations on bovine calves. Parasitol Res 111, 629–635 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2879-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-2879-9