Abstract
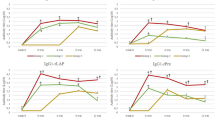
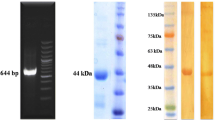
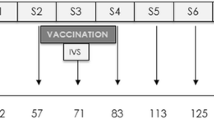
Fasciola gigantica, causative agent of tropical fasciolosis, inflicts substantial economic losses on the livestock industry, affecting severely buffalo productivity in the tropical countries. Very few vaccination trials with different target antigens against F. gigantica infection have been conducted in this host. Present study describes a vaccination trial in buffaloes with F. gigantica recombinant glutathione S-transferase and fatty acid binding protein. The two recombinant proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli and evaluated for their immunoprophylactic potential in buffalo calves, using montanide 70 M-VG, a mineral oil-based adjuvant, for delivering the antigens. Buffalo calves were distributed in three groups, with group I, II and III calves immunized with recombinant glutathione S-transferase, fatty acid binding protein and a cocktail of these two antigens, respectively. Immunization of the calves evoked a mixed IgG1 and IgG2 antibody response. Present vaccination trial in these animals achieved a maximum protection level of 35%, when the two antigens were used in combination. Eosinophils were measured in both immunized and non-immunized challenge control animals, which showed a steady increase in their count in response to immunization with both the antigens and infection with F. gigantica, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agricultural Research Data Book (2002) Indian agricultural statistics. Research Institute, New Delhi, p 28
Aiello SE, Mays A (1998) The Merck veterinary manual, 8th edn. Merck & Co Inc, New Jersey, pp 1196–1198
Brophy PM, Pritchard DI (1994) Parasitic helminth glutathione S-transferases: an update on their potential as targets for immuno and chemotherapy. Exp Parasitol 79:89–96
Butterworth AE (1984) Cell-mediated damage to helminthes. Adv Parasitol 23:143–235
Chunchob S, Grams R, Viyanant V, Smooker PM, Vichasri-Grams S (2010) Comparative analysis of two fatty acid binding proteins from Fasciola gigantica. Parasitology 137:1805–1817
Edith R, Godara R, Sharma RL, Thilagar MB (2010) Serum enzyme and hematological profile of Fasciola gigantica immunized and experimentally infected riverine buffaloes. Parasitol Res 106:947–956
Estuningsih ES, Smooker PM, Wiedosari E, Widjajanti S, Vaiano A, Partotomo S, Spithill TW (1997) Evaluation of antigens of Fasciola gigantica as vaccine against tropical fasciolosis. Int J Parasitol 11:1419–1428
FAO (1994) Diseases of domestic animals caused by flukes. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, p 49
Hansen DS, Clery DG, Estuningsih SE, Widjajanti S, Partoutomo S, Spithill TW (1999) Immune responses in Indonesian thin tail and Merino sheep during a primary infection with Fasciola gigantica: lack of a specific IgG2 antibody response is associated with increased resistance to infection in Indonesian sheep. Int J Parasitol 29:1027–1035
Hillyer GV (1985) Induction of immunity in mice to Fasciola hepatica with a Fasciola/Schistosoma cross-reactive defined antigen. Am J Trop Med Hyg 34:1127–1131
Hillyer GV, Haroun EM, Hermandez A, De Galanes MS (1987) Acquired resistance to Fasciola hepatica in cattle using a purified adult worm antigen. Am J Trop Med Hyg 37:363–369
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:630–684
López-Abán J, Nogal-Ruiz JJ, Vicente B, Morrondo P, Diez-Baños P, Hillyer GV, Martínez-Fernández AR, Feliciano AS, Muro A (2008) The addition of a new immunomodulator with the adjuvant adaptation ADAD system using fatty acid binding proteins increases the protection against Fasciola hepatica. Vet Parasitol 153:176–181
McTigue MA, Williams DR, Tainer JA (1995) Crystal structures of a schistosomal drug and vaccine target: glutathione S-transferase from Schistosoma japonicum and its complex with the leading antischistosomal drug praziquantel. J Mol Biol 246:21–27
Mehra UR, Dass RS, Verma AK, Sharma RL, Yadav SC (1999) Effect of Fasciola gigantica infection on growth and nutrient utilization in buffalo calves. Vet Rec 145:699–702
Mendes RE, Pérez-Ecija RA, Zafra R, Buffoni L, Martínez-Moreno A, Dalton JP, Mulcahy G, Pérez J (2010) Evaluation of hepatic changes and local and systemic immune responses in goats immunized with recombinant peroxiredoxin and challenged with Fasciola hepatica. Vaccine 28:2832–2840
Meyer F, Meyer H, Bueding E (1970) Lipid metabolism in the parasitic and free living flatworms. Schistosoma mansoni and Dugesia dorotocephala. Biochim Biophys Acta 210:257–266
Mitchell GF (1989) Glutathione S-transferase: potential component of antischistosomal vaccines. Parasitol Today 5:34–57
Morrison CA, Colin T, Sexton JL, Bowen F, Wicker J, Friedel T, Spithill TW (1996) Protection of cattle against Fasciola hepatica infection by vaccination with glutathione S-transferase. Vaccine 14:1603–1612
Mulcahy G, O'Connor G, Clery D, Hogan SF, Dowd AJ, Andrews SJ, Dalton JP (1999) Immune responses to cattle to experimental anti-Fasciola hepatica vaccines. Res Vet Sci 67:27–33
Muro A, Ramajo V, Lopez J, Simon F, Hillyer GV (1997) Fasciola hepatica: vaccination of rabbits with recombinant and native antigens related to fatty acid binding proteins. Vet Parasitol 69:219–229
Muro A, Casanueva P, López-Abán J, Ramajo V, Martínez-Fernández AR, Hillyer GV (2007) Identification of Fasciola hepatica recombinant 15-kDa fatty acid-binding protein T-cell epitopes that protect against experimental fascioliasis in rabbits and mice. J Parasitol 93:817–823
Nambi PA, Yadav SC, Raina OK, Sriveny D, Saini M (2005) Vaccination of buffaloes with Fasciola gigantica recombinant fatty acid binding protein. Parasitol Res 97:129–135
Ockner RK (1990) Historic overviews of the studies on fatty acid binding proteins. Mol Cell Biochem 98:3–9
Piedrafita D, Estuningsih E, Pleasance J, Prowse R, Raadsma HW, Meeusen Els NT, Spithill TW (2007) Peritoneal lavage cells of Indonesian thin-tail sheep mediate antibody-dependent superoxide radical cytotoxicity in vitro against newly excysted juvenile Fasciola gigantica but not juvenile Fasciola hepatica. Infect Immun 75:1954–1963
Preyavichyapugdee N, Sahaphong S, Riengrojpitak S, Grams R, Viyanant V, Sobhon P (2008) Fasciola gigantica and Schistosoma mansoni: vaccine potential of recombinant glutathione S-transferase (rFgGST26) against infections in mice. Exp Parasitol 119:229–237
Radostits OM, Blood DC, Gay CC (1994) Veterinary medicine-a text book of the diseases of cattle, sheep, pigs, goats and horses, 8th edn. Bailliere Tindall, London, pp 1230–1236
Ramajo V, Oleaga A, Casanueva P, Hillyer GV, Muro A (2001) Vaccination of sheep against Fasciola hepatica with homologous fatty acid binding proteins. Vet Parasitol 97:35–46
Rossjohn J, Feil SC, Wilee MCL, Sexton JL, Spithill TW, Parker MW (1997) Crystallization structural determination and analysis of a novel parasite vaccine candidate Fasciola hepatica GST. J Mol Biol 273:857–872
Sanyal PK (2001) Control of tropical fasciolosis in cattle and buffaloes in India at the backdrop of its integrated management. J Vet Parasitol 15:13–16
Sexton JL, Milner AR, Panaccio M, Waddington J, Wijffels G, Chandler D, Thompson C, Wilson L, Spithill TW, Mitchell GF, Campbell NJ (1990) Glutathione S-transferase. novel vaccine against Fasciola hepatica infection in sheep. J Immunol 145:3905–3910
Sexton JL, Wilce M, Colin T, Wijffels GL, Salvatore L, Feil S, Parker MW, Spithill TW, Morrison CA (1994) Vaccination of sheep against Fasciola hepatica with glutathione S-transferase: identification and mapping of antibody epitopes on a three dimensional model of the antigen. J Immunol 152:1861–1872
Tendler M, Brito CA, Vilar MM, Serra-Freire N, Diogo CM, Almeida MS, Delbem AC, De Silva JF, Sanivo W, Garratt RC, Simpson AJ (1996) A Schistosoma mansoni fatty acid binding protein Sm14 is the potential basis of dual purpose anti-helminth vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:269–273
Wijffels GL, Salvatore L, Dosen M, Waddington J, Wilson L, Thompson C, Campbell N, Sexton JL, Wicker J, Bowen F, Spithill TW (1994) Vaccination of sheep with purified cysteine proteinases of Fasciola hepatica decreases worm fecundity. Exp Parasitol 78:132–148
Yadav SC, Sharma RL, Kalicharan A, Mehra UR, Das RS, Verma AK (1999) Primary experimental infection of riverine buffaloes with Fasciola gigantica. Vet Parasitol 82:285–296
Zhang WY, Moreau E, Yang BZ, Li ZQ, Hope JC, Howard CJ, Huang WY, Chauvin A (2006) Humoral and cellular immune responses to Fasciola gigantica experimental infection in buffaloes. Res Vet Sci 80:299–307
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, New Delhi for providing grants to this research project. We are also thankful to the Director, Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Izatnagar for providing necessary facilities for completion of this reserach work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Anju, V., Gaurav, N. et al. Vaccination of buffaloes with Fasciola gigantica recombinant glutathione S-transferase and fatty acid binding protein. Parasitol Res 110, 419–426 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2507-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-011-2507-0