Abstract
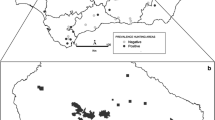
We report an investigation of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in 52 wild birds and 20 wild mammals from northern and central areas of Portugal by using the modified agglutination test. The birds comprised 26 common buzzards (Buteo buteo), five tawny owls (Strix aluco), four white storks (Ceconia ceconia), three Eurasian eagle owls (Bubo bubo), three northern goshawks (Accipiter gentilis), two booted eagles (Hieraaetus pennatus), two common barn owls (Tyto alba), two Eurasian sparrowhawks (Accipiter nisus), two short-toed eagles (Circaetus gallicus), one black kite (Milvus migrans), one Griffin vulture (Gyps fulvus), and one peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus). The mammals were eight wild boars (Sus scrofa), six red foxes (Vulpes vulpes), two common genets (Genetta genetta), two European badgers (Meles meles), one European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus), and one Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus). Fifty percent of the wild birds and 90% of the wild mammals were seropositive; the overall seroprevalence of infection was 61.1%. When comparing the prevalence of antibodies in birds and mammals from northern Portugal, a significant difference was found, but the same was not true for birds and mammals from central Portugal. Seroprevalence levels were 30.0% in juvenile and 62.5% in adult birds (p = 0.046), 0.0% in juvenile and 94.7% in adult mammals (p = 0.100), 80.0% in female and 66.7% in male birds (p = 1.000), and 81.8% in female and 100% in male mammals (p = 0.479). This is the first study performed on T. gondii in birds of prey, white storks, and wild carnivores in Portugal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrzejewska I, Tryjanowski P, Zduniak P, Dolota PT, Ptaszyk J, Cwiertnia P (2004) Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in white stork Ciconia ciconia. Berl Münch Tierärztl Wochenschr 117:274–275
Ajzenberg D, Bañuls AL, Su C, Dumètre A, Demar M, Carme B, Dardé ML (2004) Genetic diversity, clonality and sexuality in Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol 34:1185–1196
Antolová D, Reiterová K, Dubinský P (2007) Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in the Slovak Republic. Ann Agric Environ Med 14:71–73
Anwar A, Knaggs J, Service KM, McLaren GW, Riordan P, Newman C, Delahay RJ, Cheesman C, Macdonald DW (2006) Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in Eurasian badgers. J Wildl Dis 42:179–181
Artois M (1993) Epidemiology of contagious diseases, ecology of mammals, health, management and conservation biology: concluding remarks. Rev Sci Tech OIE 12:203–219
Avelino MM, Campos D, Parada JCB, Castro AM (2003) Pregnancy as a risk factor for acute toxoplasmosis seroconversion. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 108:19–24
Belanger F, Derouin F, Grangeot-Keros L, Meyer L (1999) Incidence and risk factors of toxoplasmosis in a cohort of human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: 1988–1995. HEMOCO and SEROCO Study Groups. Clin Infect Dis 28:575–581
Buxton D, Maley SW, Pastoret PP, Brochier B, Innes EA (1997) Examination of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Belgium for antibody to Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii. Vet Rec 141:308–309
Choi WY, Nam HW, Kwak NH, Huh W, Kim YR, Kang MW, Cho SY, Dubey JP (1997) Foodborne outbreaks of human toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis 175:1280–1282
Davidson MG (2000) Toxoplasmosis. Vet Clin Small Anim 30:1051–1062
Diderrich V, New JC, Noblet GP, Patton S (1996) Serologic survey of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in free-ranging wild hogs (Sus scrofa) from the Great Smoky Mountains National Park and from sites in South Carolina. J Eukaryot Microbiol 43:122S
Dubey JP (1994) Toxoplasmosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc 205:1593–1598
Dubey JP (2002) A review of toxoplasmosis in wild birds. Vet Parasitol 106:121–153
Dubey JP (2004) Toxoplasmosis—a waterborne zoonosis. Vet Parasitol 126:57–72
Dubey JP, Beattie CP (1988) Toxoplasmosis of animals and man. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Dubey JP, Graham DH, de Young RW, Dahl E, Eberhard ML, Nace EK, Won K, Bishop H, Punkosdy G, Sreekumar C, Vianna MCB, Shen SK, Kwok OCH, Sumners JA, Demarais S, Humphreys JG, Lehmann T (2004) Molecular and biologic characteristics of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from wildlife in the United States. J Parasitol 90:67–71
Dubey JP, Jones JL (2008) Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int J Parasitol 38:1257–1278
Dubey JP, Rollor EA, Smith K, Kwok OCH, Thulliez P (1997) Low seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in feral pigs from a remote island lacking cats. J Parasitol 83:839–841
Dubey JP, Storandt ST, Kwok OCH, Thulliez P, Kazacos KR (1999) Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in naturally exposed wild coyotes, red foxes, and gray foxes and serological diagnosis of toxoplasmosis in red foxes fed T. gondii oocysts and tissue cysts. J Parasitol 85:240–243
Dubey JP, Thulliez P, Weigel RM, Andrews CD, Lind P, Powell EC (1995) Sensitivity and specificity of various serologic tests for detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in naturally infected sows. Am J Vet Res 56:1030–1036
Fornazari F, Langoni H, Silva RC, Guazzelli A, Ribeiro MG, Chiacchio SB (2009) Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild boars (Sus scrofa) bred in Brazil. Vet Parasitol 164:333–334
Gaffuri A, Giacometti M, Tranquillo VM, Magnino S, Cordioli P, Lanfranchi P (2006) Serosurvey of roe deer, chamois and domestic sheep in the central Italian Alps. J Wildl Dis 42:685–690
Gamarra JA, Cabezón O, Pabón M, Arnal MC, Luco DF, Dubey JP, Cortázar C, Almería S (2008) Prevalence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in roe deer from Spain. Vet Parasitol 153:152–156
Gauss CBL, Dubey JP, Vidal D, Cabezón O, Ruiz-Fons F, Vicente J, Marco I, Lavin S, Gortazar C, Almería S (2006) Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in red deer (Cervus elaphus) and other wild ruminants from Spain. Vet Parasitol 136:193–200
Gauss CBL, Dubey JP, Vidal D, Ruiz F, Vicente J, Marco I, Lavin S, Gortazar C, Almería S (2005) Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild pigs (Sus scrofa) from Spain. Vet Parasitol 131:151–156
Gennari SM, Cannón-Franco WA, Yai LEO, De Souza SLP, Santos LC, Farias NAR, Ruas J, Rossi FW, Gomes AB (2004) Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies from wild canids from Brazil. Vet Parasitol 121:337–340
Hejlíček K, Literák I, Nezval J (1997) Toxoplasmosis in wild mammals from the Czech Republic. J Wildl Dis 33:480–485
Jakubek EB, Bröjer C, Regnersen C, Uggla A, Schares G, Björkman C (2001) Seroprevalences of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in Swedish red foxes (Vulpes vulpes). Vet Parasitol 102:167–172
Kapperud G, Jenum PA, Stray-Pedersen B, Melby KK, Eskild A, Eng J (1996) Risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnancy: results of a prospective case-control study in Norway. Am J Epidemiol 144:405–412
Lindsay DS, Smith PC, Hoerr FJ, Blagburn BL (1993) Prevalence of encysted Toxoplasma gondii in raptors from Alabama. J Parasitol 79:870–873
Literák I, Hejlíček K, Nezval J, Folk C (1992) Incidence of Toxoplasma gondii in populations of wild birds in the Czech Republic. Avian Pathol 21:659–665
Lopes AP, Cardoso L, Rodrigues M (2008) Serological survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection in domestic cats from northeastern Portugal. Vet Parasitol 155:184–189
Panadero R, Painceira A, López C, Vázquez L, Paz A, Díaz P, Dacal V, Cienfuegos S, Fernández G, Lago N, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P (2010) Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in wild and domestic ruminants sharing pastures in Galicia (Northwest Spain). Res Vet Sci 88:111–115
Petrie A, Watson P (1999) Statistics for veterinary and animal science. Blackwell, Oxford
Richomme C, Aubert D, Gilot-Fromont E, Ajzenberg D, Mercier A, Ducrot C, Ferté H, Delorme D, Villena I (2009) Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from wild boar (Sus scrofa) in France. Vet Parasitol 164:296–300
Ross RD, Stec LA, Werner JC, Blumenkranz MS, Glazer L, Williams GA (2001) Presumed acquired ocular toxoplasmosis in deer hunters. Retina 21:226–229
Ruiz-Fons F, Vicente J, Vidal D, Höfle U, Villanúa D, Gauss C, Segalés J, Almería S, Montoro V, Gortázar CH (2006) Seroprevalence of six reproductive pathogens in European wild boar (Sus scrofa) from Spain: the effect on wild boar female reproductive performance. Theriogenology 65:731–743
Sacks JJ, Delgado DG, Lobel HO, Parker RL (1983) Toxoplasmosis infection associated with eating undercooked venison. Am J Epidemiol 118:833–838
Saénz-de-Buruaga M, Lucio AJ, Purroy J (1991) Reconocimiento de sexo y edad en especies cinegéticas. Diputación Foral de Álava, Vitoria-Gasteiz
Sobrino R, Cabezón O, Millán J, Pabón M, Arnal MC, Luco DF, Gortázar C, Dubey JP, Almería S (2007) Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in wild carnivores from Spain. Vet Parasitol 148:187–192
Tenter AM, Heckeroth AR, Weiss LM (2000) Toxoplasma gondii: from animals to humans. Int J Parasitol 30:1217–1258
Vikøren T, Tharaldsen J, Fredriksen B, Handeland K (2004) Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in wild red deer, roe deer, moose, and reindeer from Norway. Vet Parasitol 120:159–169
Wanha K, Edelhofer R, Gabler-Eduardo C, Prosl H (2005) Prevalence of antibodies against Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii in dogs and foxes in Austria. Vet Parasitol 128:189–193
Williamson JMW, Williams H (1980) Toxoplasmosis in farmed red deer (Cervus elaphus) in Scotland. Res Vet Sci 29:36–40
Zhang SY, Wei MX, Zhou ZY, Yu JY, Shi XK (2000) Prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in the sera of rare wildlife in the Shanghai Zoological Garden, People’s Republic of China. Parasitol Int 49:171–174
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Teresa Coutinho, Susana Veleda, and Fátima Fraga, the interns and staff at CRATAS, and the Board of the Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Department of Veterinary Sciences, University of Trás-os-Montes e Alto Douro for their assistance. A. P. Lopes was supported by a scholarship from FCT-Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, and the European Social Fund (SFRH/44438/2008), Portugal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, A.P., Sargo, R., Rodrigues, M. et al. High seroprevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in wild animals from Portugal. Parasitol Res 108, 1163–1169 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2158-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2158-6