Abstract
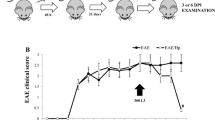
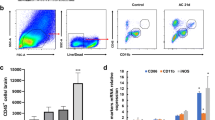
Epidemiological and experimental studies have indicated that helminth infections can ameliorate autoimmune diseases. The present study investigated the amelioration effect of the Trichinella pseudospiralis infection on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease of central nervous system (CNS), and expression kinetics of Th17 and Th1 cytokine which play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of EAE. The results indicated that the infection of helminth T. pseudospiralis obviously ameliorated clinical severity and greatly delayed the onset of EAE induced by myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) immunization. Infection caused much lesser inflammatory infiltration and demyilination in the CNS of infected EAE mice than uninfected EAE mice. The reduced infiltration was also suggested by the expressions of the inflammation cytokines, IL-17, IL-6, IL-1β, IFN-γ, and TNF-α, which were high in the spinal cords of the uninfected EAE mice, but was nearly normal or low in the infected EAE mice. The increased production of MOG-induced IL-17 and IFN-γ and the expression of IL-6, IL-1β, TGF-β in splenocytes after restimulation with MOG was inhibited in the infected EAE mice. On the other hand, the greatly induced Th2 response was observed in the splenocytes of the infected EAE mice. The present study showed that T. pseudospiralis infection can suppresses EAE by reducing the inflammatory infiltration in CNS, likely associated with the suppression of Th17 and Th1 responses by the infection.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelmann M, Wood J, Benzel I, Fiori P, Lassmann H, Matthieu JM, Gardinier MV, Dornmair K, Linington C (1995) The N-terminal domain of the myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) induces acute demyelinating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. J Neuroimmunol 63:17–27
Alford K, Obendorf DL, Fredeking TM, Haehling E, Stewart GL (1998) Comparison of the inflammatory responses of mice infected with American and Australian Trichinella pseudospiralis or Trichinella spiralis. Int J Parasitol 28:343–348
Aranami T, Yamamura T (2008) Th17 Cells and autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE/MS). Allergol Int 57:115–120
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK (2006) Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 441:235–238
Boonmars T, Wu Z, Nagano I, Takahashi Y (2005) Trichinella pseudospiralis infection is characterized by more continuous and diffuse myopathy than T. spiralis infection. Parasitol Res 97:13–20
Bruschi F, Marucci G, Pozio E, Masetti M (2009) Evaluation of inflammatory responses against muscle larvae of different Trichinella species by an image analysis system. Vet Parasitol 159:258–262
Carvalho L, Sun J, Kane C, Marshall F, Krawczyk C, Pearce EJ (2009) Review series on helminths, immune modulation and the hygiene hypothesis: mechanisms underlying helminth modulation of dendritic cell function. Immunol 126:28–34
Del Prete G, Chiumiento L, Amedei A, Piazza M, D'Elios MM, Codolo G, de Bernard M, Masetti M, Bruschi F (2008) Immunosuppression of TH2 responses in Trichinella spiralis infection by Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:908–913
Despommier DD (1983) The biology of Trichinella. In: Campbell WC (ed) Trichinella and Trichinellosis. Plenum, New York, pp 75–151
Duong TT, Finkelman FD, Singh B, Strejan GH (1994) Effect of anti-interferon-gamma monoclonal antibody treatment on the development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in resistant mouse strains. J Neuroimmunol 53:101–107
Elliott DE, Li J, Blum A, Metwali A, Qadir K, Urban JF Jr, Weinstock JV (2003) Exposure to schistosome eggs protects mice from TNBS-induced colitis. Am J Physiol Gasterointest Liver Physiol 284:G385–G391
Elliott DE, Setiawan T, Metwali A, Blum A, Urban JF Jr, Weinstock JV (2004) Heligmosomoides polygyrus inhibits established colitis in IL-10-deficient mice. Eur J Immunol 34:2690–2698
Elliott DE, Summers RW, Weinstock JV (2007) Helminths as governors of immune-mediated inflammation. Int J Parasitol 37:457–464
Elliott DE, Metwali A, Leung J, Setiawan T, Blum AM, Ince MN, Bazzone LE, Stadecker MJ, Urban JF Jr, Weinstock JV (2008) Colonization with Heligmosomoides polygyrus suppresses mucosal IL-17 production. J Immunol 181:2414–2419
Fleming J, Fabry Z (2007) The hygiene hypothesis and multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 61:85–89
Gale EA (2002) The rise of childhood type 1 diabetes in the 20th century. Diabetes 51:3353–3361
Greer JM, Sobel RA, Sette A, Southwood S, Lees MB, Kuchroo VK (1996) Immunogenic and encephalitogenic epitope clusters of myelin proteolipid protein. J Immunol 156:371–379
Gruden-Movsesijan A, Ilic N, Mostarica-Stojkovic M, Stosic-Grujicic S, Milic M, Lj S-M (2008) Trichinella spiralis: modulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in DA rats. Exp Parasitol 118:641–647
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT (2005) Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol 6:1123–1132
Helmby H, Grencis RK (2002) IL-18 regulates intestinal mastocytosis and Th2 cytokine production independently of IFN-gamma during Trichinella spiralis infection. J Immunol 169:2553–2560
Hofstetter HH, Ibrahim SM, Koczan D, Kruse N, Weishaupt A, Toyka KV, Gold R (2005) Therapeutic efficacy of IL-17 neutralization in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Cell Immunol 237:123–130
Hopkin J (2009) Immune and genetic aspects of asthma, allergy and parasitic worm infections: evolutionary links. Parasite Immunol 31:267–273
Hunter MM, McKay DM (2004) Review article: helminths as therapeutic agents for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19:167–177
Irmler IM, Gajda M, Brauer R (2007) Exacerbation of antigeninduced arthritis in IFN-gamma-deficient mice as a result of unrestricted IL-17 response. J Immunol 179:6228–6236
Ishikawa N, Goyal PK, Mahida YR, Li KF, Wakelin D (1998) Early cytokine responses during intestinal parasitic infections. Immunology 93:257–263
Jackson JA, Friberg IM, Little S, Bradley JE (2009) Review series on helminths, immune modulation and the hygiene hypothesis: immunity against helminths and immunological phenomena in modern human populations: coevolutionary legacies? Immunology 126:18–27
Juedes AE, Hjelmström P, Bergman CM, Neild AL, Ruddle NH (2000) Kinetics and cellular origin of cytokines in the central nervous system: insight into mechanisms of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 164:419–426
Karpus WJ, Ransohoff RM (1998) Chemokine regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: temporal and spatial expression patterns govern disease pathogenesis. J Immunol 161:2667–2671
Khan WI, Blennerhasset PA, Varghese AK, Chowdhury SK, Omsted P, Deng Y, Collins SM (2002) Intestinal nematode infection ameliorates experimental colitis in mice. Infect Immun 70:5931–5937
Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Sudo K, Iwakura Y (2006) IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 177:566–573
Lawrence CE, Paterson JC, Higgins LM, MacDonald TT, Kennedy MW, Garside P (1998) IL-4-regulated enteropathy in an intestinal nematode infection. Eur J Immunol 28:2672–2684
Lee KM, Ko RC (2006) Cell-mediated response at the muscle phase of Trichinella pseudospiralis and Trichinella spiralis infections. Parasitol Res 99:70–77
Li CK, Ko RC (2001) Inflammatory response during the muscle phase of Trichinella spiralis and T. pseudospiralis infections. Parasitol Res 87:708–714
Mangan PR, Harrington LE, O’Quinn DB, Helms WS, Bullard DC, Elson CO, Hatton RD, Wahl SM, Schoeb TR, Weaver CT (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature 441:231–234
McInnes IB, Leung BP, Harnett M, Gracie JA, Liew FY, Harnett W (2003) A novel therapeutic approach targeting articular inflammation using the filarial nematode-derived phosphorylcholine-containing glycoprotein ES-62. J Immunol 171:2127–2133
Morales MA, Mele R, Sanchez M, Sacchini D, De Giacomo M, Pozio E (2002) Increased CD8(+)-T-cell expression and a type 2 cytokine pattern during the muscular phase of Trichinella infection in humans. Infect Immun 70:233–239
Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y (2003) Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol 171:6173–6177
Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, Weinshenker BG (2000) Multiple sclerosis. New Eng J Med 343:938–952
Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH, Wang Y, Hood L, Zhu Z, Tian Q, Dong C (2005) A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol 6:1133–1141
Pugliatti M, Sotgiu S, Rosati G (2002) The worldwide prevalence of multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 104:182–191
Reddy A, Fried B (2007) The use of Trichuris suis and other helminth therapies to treat Crohn's disease. Parasitol Res 100:921–927
Salinas-Carmona MC, de la Cruz-Galicia G, Pérez-Rivera I, Solís-Soto JM, Segoviano-Ramirez JC, Vázquez AV, Garza MA (2009) Spontaneous arthritis in MRL/lpr mice is aggravated by Staphylococcus aureus and ameliorated by Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infections. Autoimmunity 42:25–32
Saunders KA, Raine T, Cooke A, Lawrence CE (2007) Inhibition of autoimmune type 1 diabetes by gastrointestinal helminth infection. Infect Immun 75:397–407
Scales HE, Ierna MX, Lawrence CE (2004) The role of IL-4, IL-13 and IL-4Ra in the development of protective and pathological responses to Trichinella spiralis. Parasite Immunol 29:81–91
Sewell D, Qing Z, Reinke E, Elliot D, Weinstock J, Sandor M, Fabry Z (2003) Immunomodulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by helminth ova immunization. Int Immunol 15:59–69
Shaw MK, Kim C, Hao HW, Chen F, Tse HY (1996) Induction of myelin basic protein-specific experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice: mapping of T cell epitopes and T cell receptor V gene segment usage. J Neurosci Res 45:690–699
Shoenfeld Y, Gilburd B, Abu-Shakra M, Amital H, Barzilai O, Berkun Y, Blank M, Zandman-Goddard G, Katz U, Krause I, Langevitz P, Levy Y, Orbach H, Pordeus V, Ram M, Sherer Y, Toubi E, Tomer Y (2008a) The mosaic of autoimmunity: genetic factors involved in autoimmune diseases—2008. Isr Med Assoc J 10:3–7
Shoenfeld Y, Zandman-Goddard G, Stojanovich L, Cutolo M, Amital H, Levy Y, Abu-Shakra M, Barzilai O, Berkun Y, Blank M, de Carvalho JF, Doria A, Gilburd B, Katz U, Krause I, Langevitz P, Orbach H, Pordeus V, Ram M, Toubi E, Sherer Y (2008b) The mosaic of autoimmunity: hormonal and environmental factors involved in autoimmune diseases—2008. Isr Med Assoc J 10:8–12
Smith P, Mangan NE, Walsh CM, Fallon RE, McKenzie AN, van Rooijen N, Fallon PG (2007) Infection with a helminth parasite prevents experimental colitis via a macrophage-mediated mechanism. J Immunol 178:4557–4566
Steinman L (2007) A brief history of T(H)17, the first major revision in the T(H)1/T(H)2 hypothesis of T cell-mediated tissue damage. Nat Med 13:139–145
Steinman L (2010) Mixed results with modulation of TH-17 cells in human autoimmune diseases. Nat Immunol 11:41–44
Stewart GL, Wood B, Boley RB (1985) Modulation of host response by Trichinella pseudospiralis. Parasite Immunol 7:223–233
Stewart GL, Mann MA, Ubelaker JE, McCarthy JL, Wood BG (1988) A role for elevated plasma corticosterone in modulation of host response during infection with Trichinella pseudospiralis. Parasite Immunol 10:139–150
Summers RW, Elliott DE, Weinstock JV (2005) Why Trichuris suis should prove safe for use in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11:783–784
Tran EH, Prince EN, Owens T (2000) IFN-gamma shapes immune invasion of the central nervous system via regulation of chemokines. J Immunol 164:2759–2768
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B (2006) TGF-beta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24:179–189
Voorthuis JA, Uitdehaag BM, De Groot CJ (1990) Suppression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by intraventricular administration of interferon-gamma in Lewis rats. Clin Exp Immunol 81:183–188
Wakelin D, Goyal PK, Dehlawi MS, Hermanek J (1994) Immune responses to Trichinella spiralis and T. pseudospiralis in mice. Immunology 81:475–479
Walsh KP, Brady MT, Finlay CM, Boon L, Mills KH (2009) Infection with a helminth parasite attenuates autoimmunity through TGF-beta-mediated suppression of Th17 and Th1 responses. J Immunol 183:1577–1586
Weinstock JV, Elliott DE (2009) Helminths and the IBD hygiene hypothesis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:128–133
Wilson MS, Maizels RM (2004) Regulation of allergy and autoimmunity in helminth infection. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 26:35–50
Wu Z, Matsuo A, Nakada T, Nagano I, Takahashi Y (2001) Different response of satellite cells in the kinetics of myogenic regulatory factors and ultrastructural pathology after Trichinella spiralis and T. pseudospiralis infection. Parasitology 123:85–94
Wu Z, Nagano I, Boonmars T, Takahashi Y (2007) Thermally induced and developmentally regulated expression of a small heat shock protein in Trichinella spiralis. Parasitol Res 101:201–212
Yazdanbakhsh M, Matricardi PM (2004) Parasites and the hygiene hypothesis: regulating the immune system? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 26:15–24
Zaccone P, Fehervari Z, Jones FM, Sidobre S, Kronenberg M, Dunne DW, Cooke A (2003) Schistosoma mansoni antigens modulate the activity of the innate immune response and prevent onset of type 1 diabetes. Eur J Immunol 33:1439–1449
Zaccone P, Fehervari Z, Phillips JM, Dunne DW, Cooke A (2006) Parasitic worms and inflammatory diseases. Parasite Immunol 28:515–523
Zheng X, Hu X, Zhou G, Lu Z, Qiu W, Bao J, Dai Y (2008) Soluble egg antigen from Schistosoma japonicum modulates the progression of chronic progressive experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via Th2-shift response. J Neuroimmunol 194:107–114
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (20580320) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Nagano, I., Asano, K. et al. Infection of non-encapsulated species of Trichinella ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis involving suppression of Th17 and Th1 response. Parasitol Res 107, 1173–1188 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1985-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1985-9