Abstract
Lymphatic filariasis is mainly caused by the filarial nematodes Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi. Wolbachia, intracellular symbiotic bacteria in filarial parasite, is known to induce immune response predominantly through Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2). This study was performed to investigate the association between polymorphisms of the TLR2 gene and susceptibility to asymptomatic bancroftian filariasis. A total of 142 unrelated asymptomatic bancroftian filariasis patients and 151 endemic normal controls in Tak province, Thailand were recruited into this study. The −196 to −173 deletion (del) polymorphism in the 5′ untranslated region was investigated by allele-specific polymerase chain reaction. Two single nucleotide polymorphisms, +597 T>C and +1350 T>C, in exon 3 were identified by polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Furthermore, we analyzed the functional difference between the TLR2 −196 to −173 del and wild-type (wt) alleles using the luciferase reporter assay. All three polymorphisms were associated with a higher risk of asymptomatic bancroftian filariasis and were in strong linkage disequilibrium with each other. The TLR2 haplotype −196 to −173del/+597C/+1350C was strongly associated with an increased risk of asymptomatic bancroftian filariasis. The TLR2 −196 to −173 del allele had a significantly lower transcriptional activity than wt allele. The results of our study indicate that TLR2 −196 to −173 del, +597 T>C and +1350 T>C polymorphisms are associated with asymptomatic bancroftian filariasis in Thailand. Our functional study also supports this finding with respect to differential TLR2 gene expression by −196 to −173 del polymorphism.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babu S, Blauvelt CP, Kumaraswami V, Nutman TB (2005) Diminished expression and function of TLR in lymphatic filariasis: a novel mechanism of immune dysregulation. J Immunol 175:1170–1176
Babu S, Blauvelt CP, Kumaraswami V, Nutman TB (2006) Cutting edge: diminished T cell TLR expression and function modulates the immune response in human filarial infection. J Immunol 176:3885–3889
Babu S, Bhat SQ, Kumar NP, Anuradha R, Kumaran P, Gopi PG, Kolappan C, Kumaraswami V, Nutman TB (2009) Attenuation of Toll-like receptor expression and function in latent tuberculosis by coexistent filarial infection with restoration following antifilarial chemotherapy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3:e489
Bandi C, Trees AJ, Brattig NW (2001) Wolbachia in filarial nematodes: evolutionary aspects and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of filarial diseases. Vet Parasitol 98:215–238
Bazzocchi C, Jamnongluk W, O’Neill SL, Anderson TJ, Genchi C, Bandi C (2000) wsp gene sequences from the Wolbachia of filarial nematodes. Curr Microbiol 41:96–100
Behbehani K (1998) Candidate parasitic diseases. Bull World Health Organ 76(Suppl 2):64–67
Ben-Ali M, Barbouche MR, Bousnina S, Chabbou A, Dellagi K (2004) Toll-like receptor 2 Arg677Trp polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis in Tunisian patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11:625–626
Brabin L (1990) Sex differentials in susceptibility to lymphatic filariasis and implications for maternal child immunity. Epidemiol Infect 105:335–353
Brattig NW, Buttner DW, Hoerauf A (2001) Neutrophil accumulation around Onchocerca worms and chemotaxis of neutrophils are dependent on Wolbachia endobacteria. Microbes Infect 3:439–446
Brattig NW, Bazzocchi C, Kirschning CJ, Reiling N, Buttner DW, Ceciliani F, Geisinger F, Hochrein H, Ernst M, Wagner H, Bandi C, Hoerauf A (2004) The major surface protein of Wolbachia endosymbionts in filarial nematodes elicits immune responses through TLR2 and TLR4. J Immunol 173:437–445
Capon F, Allen MH, Ameen M, Burden AD, Tillman D, Barker JN, Trembath RC (2004) A synonymous SNP of the corneodesmosin gene leads to increased mRNA stability and demonstrates association with psoriasis across diverse ethnic groups. Hum Mol Genet 13:2361–2368
Carter KW, McCaskie PA, Palmer LJ (2006) JLIN: a Java based linkage disequilibrium plotter. BMC Bioinform 7:60
Chan SH, Dissanayake S, Mak JW, Ismail MM, Wee GB, Srinivasan N, Soo BH, Zaman V (1984) HLA and filariasis in Sri Lankans and Indians. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 15:281–286
Chanock SJ, Foster CB (1999) SNPing away at innate immunity. J Clin Invest 104:369–370
Chen GL, Vallender EJ, Miller GM (2008) Functional characterization of the human TPH2 5′ regulatory region: untranslated region and polymorphisms modulate gene expression in vitro. Hum Genet 122:645–657
Choi EH, Zimmerman PA, Foster CB, Zhu S, Kumaraswami V, Nutman TB, Chanock SJ (2001) Genetic polymorphisms in molecules of innate immunity and susceptibility to infection with Wuchereria bancrofti in South India. Genes Immun 2:248–253
Das PK, Manoharan A, Srividya A, Grenfell BT, Bundy DA, Vanamail P (1990) Frequency distribution of Wuchereria bancrofti microfilariae in human populations and its relationships with age and sex. Parasitology 101(Pt 3):429–434
Debrah AY, Mand S, Toliat MR, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Batsa L, Nurnberg P, Lawson B, Adjei O, Hoerauf A, Pfarr K (2007) Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) and VEGF-A gene polymorphism are associated with hydrocele development in lymphatic filariasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 77:601–608
Derrigo M, Cestelli A, Savettieri G, Di Liegro I (2000) RNA–protein interactions in the control of stability and localization of messenger RNA (review). Int J Mol Med 5:111–123
Duan J, Wainwright MS, Comeron JM, Saitou N, Sanders AR, Gelernter J, Gejman PV (2003) Synonymous mutations in the human dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) affect mRNA stability and synthesis of the receptor. Hum Mol Genet 12:205–216
Guilbert JJ (2003) The World Health Report 2002—reducing risks, promoting healthy life. Educ Health (Abingdon) 16:230
Haddix AC, Kestler A (2000) Lymphatic filariasis: economic aspects of the disease and programmes for its elimination. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 94:592–593
Haehnel V, Schwarzfischer L, Fenton MJ, Rehli M (2002) Transcriptional regulation of the human Toll-like receptor 2 gene in monocytes and macrophages. J Immunol 168:5629–5637
Hise AG, Daehnel K, Gillette-Ferguson I, Cho E, McGarry HF, Taylor MJ, Golenbock DT, Fitzgerald KA, Kazura JW, Pearlman E (2007) Innate immune responses to endosymbiotic Wolbachia bacteria in Brugia malayi and Onchocerca volvulus are dependent on TLR2, TLR6, MyD88, and Mal, but not TLR4, TRIF, or TRAM. J Immunol 178:1068–1076
Hoerauf A, Volkmann L, Hamelmann C, Adjei O, Autenrieth IB, Fleischer B, Buttner DW (2000) Endosymbiotic bacteria in worms as targets for a novel chemotherapy in filariasis. Lancet 355:1242–1243
Johnson CM, Tapping RI (2007) Microbial products stimulate human Toll-like receptor 2 expression through histone modification surrounding a proximal NF-kappaB-binding site. J Biol Chem 282:31197–31205
Lamb TJ, Le Goff L, Kurniawan A, Guiliano DB, Fenn K, Blaxter ML, Read AF, Allen JE (2004) Most of the response elicited against Wolbachia surface protein in filarial nematode infection is due to the infective larval stage. J Infect Dis 189:120–127
Medzhitov R (2001) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 1:135–145
Meyrowitsch DW, Simonsen PE, Garred P, Dalgaard M, Magesa SM, Alifrangis M (2010) Association between mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms and Wuchereria bancrofti infection in two communities in north-eastern Tanzania. Am J Trop Med Hyg 82:115–120
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Noguchi E, Nishimura F, Fukai H, Kim J, Ichikawa K, Shibasaki M, Arinami T (2004) An association study of asthma and total serum immunoglobin E levels for Toll-like receptor polymorphisms in a Japanese population. Clin Exp Allergy 34:177–183
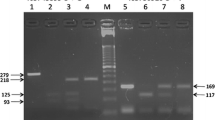
Nuchprayoon S, Junpee A, Poovorawan Y, Scott AL (2005) Detection and differentiation of filarial parasites by universal primers and polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 73:895–900
Ogus AC, Yoldas B, Ozdemir T, Uguz A, Olcen S, Keser I, Coskun M, Cilli A, Yegin O (2004) The Arg753GLn polymorphism of the human Toll-like receptor 2 gene in tuberculosis disease. Eur Respir J 23:219–223
Punkosdy GA, Addiss DG, Lammie PJ (2003) Characterization of antibody responses to Wolbachia surface protein in humans with lymphatic filariasis. Infect Immun 71:5104–5114
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Sauna ZE, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Ambudkar SV, Gottesman MM (2007) Silent polymorphisms speak: how they affect pharmacogenomics and the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res 67:9609–9612
Schroder NW, Schumann RR (2005) Single nucleotide polymorphisms of Toll-like receptors and susceptibility to infectious disease. Lancet Infect Dis 5:156–164
Subrahmanyam D, Mehta K, Nelson DS, Rao YV, Rao CK (1978) Immune reactions in human filariasis. J Clin Microbiol 8:228–232
Tahara T, Arisawa T, Wang F, Shibata T, Nakamura M, Sakata M, Hirata I, Nakano H (2007) Toll-like receptor 2-196 to 174del polymorphism influences the susceptibility of Japanese people to gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 98:1790–1794
Takeda K, Takeuchi O, Akira S (2002) Recognition of lipopeptides by Toll-like receptors. J Endotoxin Res 8:459–463
World Health Organization (1995) The World Health Report 1995—bridging the gaps. World Health Forum 16:377–385
Thuong NT, Hawn TR, Thwaites GE, Chau TT, Lan NT, Quy HT, Hieu NT, Aderem A, Hien TT, Farrar JJ, Dunstan SJ (2007) A polymorphism in human TLR2 is associated with increased susceptibility to tuberculous meningitis. Genes Immun 8:422–428
Tisch DJ, Hazlett FE, Kastens W, Alpers MP, Bockarie MJ, Kazura JW (2001) Ecologic and biologic determinants of filarial antigenemia in bancroftian filariasis in Papua New Guinea. J Infect Dis 184:898–904
Triteeraprapab S, Kanjanopas K, Suwannadabba S, Sangprakarn S, Poovorawan Y, Scott AL (2000) Transmission of the nocturnal periodic strain of Wuchereria bancrofti by Culex quinquefasciatus: establishing the potential for urban filariasis in Thailand. Epidemiol Infect 125:207–212
Triteeraprapab S, Nuchprayoon I, Porksakorn C, Poovorawan Y, Scott AL (2001) High prevalence of Wuchereria bancrofti infection among Myanmar migrants in Thailand. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 95:535–538
Turner JD, Langley RS, Johnston KL, Gentil K, Ford L, Wu B, Graham M, Sharpley F, Slatko B, Pearlman E, Taylor MJ (2009) Wolbachia lipoprotein stimulates innate and adaptive immunity through Toll-like receptors 2 and 6 to induce disease manifestations of filariasis. J Biol Chem 284:22364–22378
van der Stoep N, Quinten E, van den Elsen PJ (2002) Transcriptional regulation of the MHC class II trans-activator (CIITA) promoter III: identification of a novel regulatory region in the 5′-untranslated region and an important role for cAMP-responsive element binding protein 1 and activating transcription factor-1 in CIITA-promoter III transcriptional activation in B lymphocytes. J Immunol 169:5061–5071
Velez DR, Wejse C, Stryjewski ME, Abbate E, Hulme WF, Myers JL, Estevan R, Patillo SG, Olesen R, Tacconelli A, Sirugo G, Gilbert JR, Hamilton CD, Scott WK (2010) Variants in Toll-like receptors 2 and 9 influence susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in Caucasians, African-Americans, and West Africans. Hum Genet 127:65–73
Venugopal PG, Nutman TB, Semnani RT (2009) Activation and regulation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) by helminth parasites. Immunol Res 43:252–263
Wang F, Tahara T, Arisawa T, Shibata T, Nakamura M, Fujita H, Iwata M, Kamiya Y, Nagasaka M, Takahama K, Watanabe M, Hirata I, Nakano H (2007) Genetic polymorphisms of CD14 and Toll-like receptor-2 (TLR2) in patients with ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22:925–929
Yazdanbakhsh M, Abadi K, de Roo M, van Wouwe L, Denham D, Medeiros F, Verduijn W, Schreuder GM, Schipper R, Giphart MJ, de Vries RR (1997) HLA and elephantiasis revisited. Eur J Immunogenet 24:439–442
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by Ratchadapiseksompotch Fund, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University and the National Research Council of Thailand. AJ and VS are supported by The Royal Golden Jubilee PhD Program, The Thailand Research Fund. We would like to thank Dr. Saravudh Suvannadabba, Dr. Anupong Chitvarakorn, and the entire staff of the Filariasis Division and regional officers for their assistance in specimen collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junpee, A., Tencomnao, T., Sanprasert, V. et al. Association between Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) polymorphisms and asymptomatic bancroftian filariasis. Parasitol Res 107, 807–816 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1932-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1932-9