Abstract
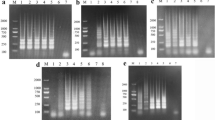
The fish-borne clonorchiasis caused by the oriental liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis is endemic in a number of countries with over 35 million people being infected globally. Rapid and accurate detection of C. sinensis in its intermediate host fish is important for the control and prevention of clonorchiasis in areas where the disease is endemic. In the present study, we established a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) approach for the sensitive and rapid detection of C. sinensis metacercariae in fish. The specificity and sensitivity of primers designed from the C. sinensis cathepsins B3 gene were evaluated, and specific amplification products were obtained with C. sinensis, while no amplification products were detected with DNA of related trematodes, demonstrating the specificity of the assay. The LAMP assay was proved to be 100 times more sensitive than a conventional polymerase chain reaction for detection of C. sinensis. The established LAMP assay provides a useful tool for the rapid and sensitive detection of C. sinensis in fish, which has important implications for the effective control of human clonorchiasis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP (1992) Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 54:165–173
Karanis P, Thekisoe O, Kiouptsi K, Ongerth J, Igarashi I, Inoue N (2007) Development and preliminary evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification procedure for sensitive detection of cryptosporidium oocysts in fecal and water samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5660–5662
Kim EM, Verweij JJ, Jalili A, van Lieshout L, Choi MH, Bae YM, Lim MK, Hong ST (2009) Detection of Clonorchis sinensis in stool samples using real-time PCR. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 103:513–518
Kuboki N, Inoue N, Sakurai T, Di Cello F, Grab DJ, Suzuki H, Sugimoto C, Igarashi I (2003) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of African trypanosomes. J Clin Microbiol 41:5517–5524
Le TH, Van De N, Blair D, Sithithaworn P, McManus DP (2006) Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini: development of a mitochondrial-based multiplex PCR for their identification and discrimination. Exp Parasitol 112:109–114
Lun ZR, Gasser RB, Lai DH, Li AX, Zhu XQ, Yu XB, Fang YY (2005) Clonorchiasis: a key foodborne zoonosis in China. Lancet Infect Dis 5:31–41
Müller B, Schmidt J, Mehlhorn H (2007) Sensitive and species-specific detection of Clonorchis sinensis by PCR in infected snails and fishes. Parasitol Res 100:911–914
Nagamine K, Hase T, Notomi T (2002) Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol Cell Probes 16:223–229
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:E63
Parvathi A, Sanath Kumar H, Kenchanna Prakasha B, Lu J, Xu X, Hu W, Feng Z, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I (2007) Clonorchis sinensis: development and evaluation of a nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. Exp Parasitol 115:291–295
Poon LL, Wong BW, Ma EH, Chan KH, Chow LM, Abeyewickreme W, Tangpukdee N, Yuen KY, Guan Y, Looareesuwan S, Peiris JS (2006) Sensitive and inexpensive molecular test for Falciparum malaria: detecting Plasmodium falciparum DNA directly from heat-treated blood by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Clin Chem 52:303–306
Rim HJ (2005) Clonorchiasis: an update. J Helminthol 79:269–281
Tinga N, De N, Vien HV, Chau L, Toan ND, Kager PA, Vries PJ (1999) Little effect of praziquantel or artemisinin on clonorchiasis in Northern Vietnam. A pilot study. Trop Med Int Health 4:814–818
Xu J, Rong R, Zhang HQ, Shi CJ, Zhu XQ, Xia CM (2010) Sensitive and rapid detection of Schistosoma japonicum DNA by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Int J Parasitol 40(3):327–331
Yong TS, Im K, Chung PR (1991) Analysis of Clonorchis sinensis antigens and diagnosis of clonorchiasis using monoclonal antibodies. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 29:293–310
Zhang R, Gao S, Geng Y, Huang D, Yu L, Zhang S, Cheng J, Fu Y (2007) Epidemiological study on Clonorchis sinensis infection in Shenzhen area of Zhujiang delta in China. Parasitol Res 101:179–183
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant No. IRT0723) and the State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology, Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, CAAS. Dr X. C. Hu of Zhongshan Medical College, Sun Yat-Sen University was thanked for providing Paracanthopoma parva fish muscles infected with metacercariae of Clonorchis sinensis. Prof. S. J. Hong of the College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Republic of Korea was thanked for providing O. viverrini adult worms. The experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which the experiments were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
X. Q. Cai and M. J. Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, X.Q., Xu, M.J., Wang, Y.H. et al. Sensitive and rapid detection of Clonorchis sinensis infection in fish by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Parasitol Res 106, 1379–1383 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1812-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1812-3