Abstract
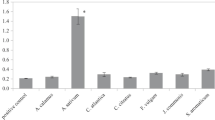
The insecticidal activity of nine essential oils (EOs) against the house fly (Musca domestica) was evaluated by placing flies in a screw-cap glass jar holding a piece of EO-treated cotton yarn. The dose necessary to kill 50% of flies (LC50) in 30 min was determined at 26 ± 1°C. The EOs showed LC50 values ranging from 0.5 to 46.9 mg/dm3. The EO from Minthostachys verticillata was the most potent insecticide (LC50 = 0.5 mg/dm3) followed by EOs from Hedeoma multiflora (LC50 = 1.3 mg/dm3) and Artemisia annua (LC50 = 6.5 mg/dm3). The compositions of the nine EOs, obtained by hydrodistillation of medicinal herbs, were analyzed by gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy. These analyses showed that (4R)(+)-pulegone (69.70%), menthone (12.17%), and limonene (2.75%) were the principal components of M. verticillata EO. (4R)(+)-pulegone was also the main constituent (52.80%) of H. multiflora, while artemisia ketone (22.36%) and 1,8-cineole (16.67%) were the major constituents of A. annua EO. The terpene (4R)(+)-pulegone showed a lower toxicity (LC50 = 1.7 mg/dm3) than M. verticillata or H. multiflora EOs. Dimethyl 2,2-dichlorovinyl phosphate, selected as a positive control, showed an LC50 of 0.5 mg/dm3. EOs from M. verticillata and H. multiflora show promise as natural insecticides against houseflies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo GR, Zapater M, Toloza AC (2009) Insecticide resistance of house fly, Musca domestica (L.) from Argentina. Parasitol Res 105:489–493
Bakkali F, Averbeck S, Averbeck D, Idaomar M (2008) Biological effects of essential oils - a review. Food Chem Toxicol 46:446–475
Batish RB, Harminder PS, Ravinder KK, Shalinder K (2008) Eucalyptus essential oil as a natural pesticide. Forest Ecol Manage 256:2166–2174
Bidawid SP, Edeson JFB, Ibrahim J, Matossian RM (1978) The role of non-biting flies in the transmission of enteric pathogens (Salmonella species and Shigella species) in Beirut, Lebanon. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 72:117–121
Bustos JA, Bonino EE (2005) Cosecha silvestre de peperina (Minthosthachys mollis) en Córdoba, Argentina: implicancias socioeconómicas. Rev Iberoam Econ Ecol 2:45–55
Carvajal G, Thilly W (1988) Mutagenic activity of Minthostachys mollis in AHH1 lymphoblast cells. Plant Food Hum Nutr 38:105–114
Coats J, Karr L, Drewes C (1991) Toxicity and neurotoxic effects of monoterpenoids in insects and earthworms. In: Hedin PA (ed) Naturally occurring pest bioregulators. ACS, Washington, D.C., pp 306–316 Symposium Series no. 449
Dorman HJD, Deans SG (2000) Antimicrobial agents from plants: antibacterial activity of plant volatile oils. J Appl Microbiol 88:308–316
Echeverria P, Harrison BA, Tirapat C, McFarland A (1983) Flies as a source of enteric pathogens in a rural village in Thailand. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:32–36
Enan E (2001) Insecticidal activity of essential oils: octopaminergic sites of action. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 130:325–337
Ferrer A (2003) Pesticide poisoning. Anal Sis San Navarra 26:155–171
Förster M, Klimpel S, Mehlhorn H, Sievert K, Messler S, Pfeffer K (2007) Pilot studies on synantropic flies (e.g. Musca, Sarcophaga, Calliphora, Fania, Lucilia, Stomoxys) as vectors of pathogenic microorganisms. Parasitol Res 101:243–246
Fukushima H, Ito Y, Saito K, Tsubokura M, Otsuki K (1979) Role of the fly in the transport of Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:1009–1010
Goleniowski ME, Bongiovanni GA, Palacio L, Nuñez CO, Cantero JJ (2006) Medicinal plants from the “Sierra de Comechingones”, Argentina. J Ethnopharm 107:324–341
Graczyk T, Knight R, Gilman R, Cranfield M (2001) The role of non-biting flies in the epidemiology of human infectious diseases. Microbes Infect 3:231–235
Graham JP, Price LB, Evans SL, Graczyk TK, Silbergeld EK (2009) Antibiotic resistant enterococci and staphylococci isolated from flies collected near confined poultry feeding operations. Sci Total Environ 407:2701–2710
Grundy DL, Still CC (1985) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterases by pulegone-1, 2-epoxide. Pest Biochem Physiol 23:383–388
Hammond G, Fernández I, Villegas L, Vaisberg A (1998) A survey of traditional medicinal plants from the Callejón de Huaylas, Department of Ancash, Perú. J Ethnopharm 61:17–30
Isman MB (1999) Pesticides based on plant essential oils. Pestic Pest Outlook 10:68–72
Isman MB (2000) Plant essential oils for pest and disease management. Crop Protect 19:603–608
Isman MB (2006) Botanical Insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu Rev Entomol 51:45–6
Isman MB, Machial CM (2006) Pesticides based on plant essential oils: from traditional practice to commercialization. In: Rai M, Carpinella MC (eds) Naturally occurring bioactive compounds, vol 3, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 29–44
Keane S, Ryan MF (1999) Purification, characterization, and inhibition by monoterpenes of acetylcholinsterase from the waxmoth, Galleria mellonella (L). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 29:1097–1104
Khan AR, Huq F (1978) Disease agents carried by flies in Dacca city. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull 4:86–93
Kostyukovsky M, Rafaeli A, Gileadi C, Demchenko N, Shaaya E (2002) Activation of octopaminergic receptors by essential oil constituents isolated from aromatic plants: possible mode of action against insect pests. Pest Manag Sci 58:1101–1106
Lee S, Tsao R, Peterson C, Coats JR (1997) Insecticidal activity of monoterpenoids to western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), twospotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae), and housefly (Diptera: Muscidae). J Econ Entomol 90:883–892
Maggi ME, Mangeaud A, Carpinella MC, Ferrayoli CG, Valladares GR, Palacios SM (2005) Laboratory evaluation of Artemisia annua L. extract and artemisinin activity against Epilachna paenulata and Spodoptera eridania. J Chem Ecol 31:1527–1536
Malik A, Singh N, Satya S (2007) House Fly (Musca domestica): a review of control strategies for a challenging pest. J Environ Sci Health Part B 42:453–469
Mills C, Cleary BJ, Gilmer JF, Walsh JJ (2004) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by Tea Tree oil. J Pharm Pharmacol 56:375–379
Misra G, Pavlostathis SG (1997) Biodegradation kinetics of monoterpenes in liquid and in soil-slurry system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:572–577
Miyazawa M, Watanabe H, Kameoka H (1997) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity by monoterpenoids with a p-menthane skeleton. J Agric Food Chem 45:677–679
Olsen AR (1998) Regulatory action criteria for filth and other extraneous materials. III. Review of flies and foodborne enteric diseases. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 28:199–211
Ozden S, Catalgol B, Gezginci-Oktayoglu S, Arda-Pirincci P, Bolkent S, Alpertunga B (2009) Methiocarb-induced oxidative damage following subacute exposure and the protective effects of vitamin E and taurine in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 47:1676–1684
Palacios SM, Bertoni A, Rossi Y, Santander R, Urzúa A (2009) Efficacy of essential oils from edible plants as insecticides against the house fly, Musca domestica L. Molecules 14:1938–1947
Pavela (2008) Insecticidal properties of several essential oils to the House Fly (Musca domestica L.). Phytother Res 22:274–278
Picollo MI, Toloza AC, Cueto GM, Zygadlo J, Zerba E (2008) Anticholinesterase and pediculicidal activities of monoterpenoids. Fitoterapia 79:271–278
Priestley CM, Williamson EM, Wafford K, Satelle D (2003) Thymol, a constituent of thyme essential oil, is a positive allosteric modulator of human GABAA receptors and a homo-oligomeric GABA receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Br J Pharmacol 140:1363–1372
Regnault-Roger C (1997) The potential of botanical essential oils for insect pest control. Integr Pest Manag Rev 2:25–34
Rice PJ, Coats JR (1994a) Insecticidal properties of several monoterpenoids to the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae), red flour beetle (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) and southern corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J Econ Entomol 87:1172–1179
Rice PJ, Coats JR (1994b) Insecticidal properties of monoterpenoids derivatives to the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae), and red flour beetle (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Pestic Sci 41:195–202
Ryan MF, Byrne O (1988) Plant insect coevolution and inhibition of acetylcolinesterase. J Chem Ecol 14:1965–1975
Schmidt-Lebuhn AN (2008) Ethnobotany, biochemistry and pharmacology of Minthostachys (Lamiaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 118:343–353
Scott JG, Alefantis TG, Kaufman PE, Rutz DA (2000) Insecticide resistance in houseflies from caged-layer poultry facilities. Pest Manag Sci 56:147–153
Stroh J, Wan MT, Isman MB, Moul DJ (1998) Evaluation of the acute toxicity to juvenile Pacific coho salmon and rainbow trout of some plant essential oils, a formulated product, and the carrier. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 60:923–930
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Técnica, FONCYT, PICT 33593. We thank Joss Heywood for revising the English language.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palacios, S.M., Bertoni, A., Rossi, Y. et al. Insecticidal activity of essential oils from native medicinal plants of Central Argentina against the house fly, Musca domestica (L.). Parasitol Res 106, 207–212 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1651-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1651-2