Abstract
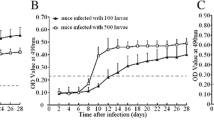
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method is recommended for farm surveillance programs and may be useful for epidemiological studies in wildlife or for establishing Trichinella-free areas. In this study, our interest was to compare the specificity and the time of seroconversion of excretory–secretory (E/S) antigens prepared from Trichinella spiralis. A group of eight pigs was inoculated with 500 T. spiralis larvae per animal, and blood sampling was performed at 3 and 4-day intervals during all experiments. The numbers of muscle larvae were determined in four different muscles groups. The larvae per gram burden shows that the most heavily parasitized muscles were the diaphragm [mean = 43.7 larvae per gram (lpg)] and the tongue (mean = 16.9 lpg). Antibody responses were detected by any of eight infected pigs of T. spiralis. Using the ELISA method with E/S antigen, antibodies to T. spiralis were first found on the day 21st p.i. The initial detection of antibodies varied from 21st to 31st day p.i., and the peak was reported 42nd day p.i. Dynamic of antibodies was stable or increased slightly throughout the experimental period (60 days post-inoculation). Our results represent important data for validation of a serological test, especially if blood samples are taken during early stages of infection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arriaga C, Yépez-Mulia L, Morilla A, Ortega-Pierres G (1995) Detection of circulating Trichinella spiralis muscle larva antigens in serum samples of experimentally and naturally infected swine. Vet Parasitol 58:319–326
Bruschi F, Moretti A, Wassom D, Piergili-Fioretti D (2001) The use of a synthetic antigen for the serological diagnosis of human trichinellosis. Parasite 8:141–143
Gamble HR (1996) Detection of trichinellosis in pigs by artificial digestion and enzyme immunoassay. J Food Prot 59:295–298
Gamble HR (1998) Sensitivity of artificial digestion and enzyme immunoassay methods of inspection for trichinae in pigs. J Food Prot 61:339–343
Gamble HR, Anderson WR, Graham CE, Murrell KD (1983) Diagnosis of swine trichinosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using an excretory/secretory antigen. Vet Parasitol 13:349–361
Gamble HR, Rapic D, Marinculic A, Murrell KD (1988) Evaluation of excretory–secretory antigens for the serodiagnosis of swine trichinellosis. Vet Parasitol 30:131–137
Kapel CMO, Gamble HR (2000) Infectivity, persistence, and antibody response to domestic and sylvatic Trichinella spp. in experimentally infected pigs. Int J Parasitol 30:215–221
Kapel CMO, Webster P, Lind P, Pozio E, Henriksen SA, Murrell KD, Nansen P (1998) Trichinella spiralis, T. britovi and T. nativa: infectivity, larval distribution in muscle, and antibody response after experimental infection of pigs. Parasitol Res 84:264–271
Murrell KD, Anderson WR, Schad GA, Hanbury RD, Kazacos KR, Gamble HR, Brown J (1986) Field evaluation of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for swine trichinosis: efficacy of the excretory–secretory antigen. Am J Vet Res 47(5):1046–1049
Nöckler K, Voigt WP, Protz D, Miko A, Ziedler K (1995) Intravitale Diagnostik der Trichinellose beim Schwein mit dem indirekten ELISA [indirect ELISA for the diagnosis of trichinellosis in living pigs]. Berl Münch Tierärztl Wochenschr 108:167–174
Nöckler K, Pozio E, Voigt WP, Heidrich J (2000) Detection of Trichinella infection in food animals. Vet Parasitol 93:335–350
Nöckler K, Hamidi A, Fries R, Heidrich J, Beck R, Marinculic A (2004) Influence of methods for Trichinella detection in pigs from endemic and non-endemic European region. J Vet Med B 51:297–301
Reiterová K, Dubinský P, Klimenko VV, Tomašovičová O, Dvorožňáková E (1999) Comparison of Trichinella spiralis larva antigens for the detection of specific antibodies in pigs. VET MED - CZECH 44:1–5
Ribicich M, Miguez M, Franco A, Basso N, Gamble HR, Santillan G, Molina V, Guarnera E (2000) Evaluation of ELISA test for the diagnosis of porcine trichinellosis. Pig J 46:24–34
Van der Leek ML, Dame JB, Adams CL, Gillis KD, Littel RC (1992) Evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of trichinellosis in swine. Am J Vet Res 53(6):877–882
Van Knapen F, Franchimont JM, Verdonk AR, Stumpf J, Udeutsch K (1982) Detection of specific immunoglobulins IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE) and total IgE levels in human trichinosis by means of the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Am J Trop Med and Hyg 31:973–976
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grant no. 524/03H 133 from the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic.
This research was partially supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Physical Training of the Czech Republic–Project no. FR 141 232 1495 G3.
These experiments comply with the current law of the Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kořínková, K., Kovařčík, K., Pavlíčková, Z. et al. Serological detection of Trichinella spiralis in swine by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) using an excretory–secretory (E/S) antigen. Parasitol Res 102, 1317–1320 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-0911-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-0911-x