Abstract
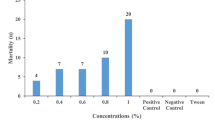
Many natural compounds have low water solubility and need to be dissolved in organic solvents, or surfactant agents must be used before addition into experimental systems. Therefore, it is necessary to determine their toxicity. Experiments were performed aiming to select solvents to be used in the bioassays, searching new acaricide agents from plants. Laboratory tests were carried out on larvae and adults of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus to determine the sensibility of B. microplus female and larvae to different solvents (acetone, methanol, ethanol and 1% dimethyl sulfoxide) and surfactant agents (1% Tween 80 and 5% Triton X-100) using the larval immersion test (LIT) and adult immersion test (AIT). In the AIT, the effect of the treatments on engorged females was assessed by measuring egg production and hatching rate. Acetone was toxic to the adults promoting mortality of 100%. Methanol and ethanol caused 45.3 and 14.2% of mortality, respectively. The other tested substances were not toxic to the engorged females of B. microplus. In the LIT, it was observed that the larvae were more resistant; after 48 h, about 100% of the larvae were alive in all the treatments except with acetone that caused a mortality of 10%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baki MA, Rahman MAA, Khatune NA (2002) Synergic effects of Wedelia calendulacea Less. Plant extracts with lambda cyhalothrin on common housefly Musca domestica L. J Biol Sci 2:686–689
Beadles ML, Drummond RO, Whetstone TM (1973) Tropical horse tick: effects of solvents on oviposition. J Econ Entomol 66:125–127
Borges LM, Ferri PH, Silva WJ, Silva WC, Silva JG (2003) In vitro efficacy of extracts of Melia azedarach against the tick Boophilus microplus. Med Vet Entomol 17:228–231
Castrejón FM, Cruz-Vázquez C, Ruvalcaba MF, Molina-Torres J, Cruz JS, Parra MR (2003) Repellence of Boophilus microplus larvae in Stylosanthes humilis and Stylosanthes hamata plants. Parasitol Latinoam 58:118–121
Chagas ACS, Passos MWM, Prates HT, Leite RC, Furlong J, Fortes ICP (2002) Efeito acaricida de óleos essenciais e concentrados emulsionáveis de Eucalyptus spp. em Boophilus microplus. Braz J Vet Res Anim Sci 3:247–253
Chagas ACS, Leite RC, Furlong J, Prates HT, Passos WM (2003) Sensibilidade do carrapato Boophilus microplus a solventes. Ciência Rural 33:109–114
Chungsamarnyart N, Jansawan W (1996) Acaricidal activity of peel oil of Citrus spp. on Boophilus microplus. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 30:112–117
Chungsamarnyart N, Jiwajinda S (1992) Acaricidal activity of volatile oil from lemon and citronella grasses on tropical cattle ticks. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 26:46–51
Consoli RAGB, Mendes NM, Pereira JP, Santos BS, Lamounier MA (1988) Influência de diversos derivados de vegetais na sobrevida das larvas de Aedes fluviatilis (Lutz) (Diptera: Culicidae) em laboratório. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 83:87–93
Ducornez S, Barré N, Miller RJ, de Garine-Wichatisky M (2005) Diagnosis of amitraz resistance in Boophilus microplus in New Caledonia with modified larval packet test. Vet Parasitol 130:285–292
Fernandes FF, Freitas EPS, da Costa AC, da Silva IG (2005) Larvicidal potential of Sapindus saponaria to control the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 40:1243–1245
Freitas EPS, Fernandes FF (2005) Estudo da bioatividade larvicida das plantas Stryphnodendron adstringens, Qualea grandiflora e Copaifera langsdorffii para o controle de Boophilus microplus (Canestrini, 1887) (Acari, Ixodidae). In: Congresso de Pesquisa, Ensino e Extensão da UFG-CONPEEX. Goiânia. Anais Eletrônicos do XIII Seminário de Iniciação Cientifica. Goiânia: UFG
García M, Sosa ME, Donadel OJ, Giordano OS, Tonn CE (2003) Allelochemical effects of eudesmane and eremophilane sesquiterpenes on Tribolium castaneum larvae. J Chem Ecol 29:175–187
Gorb SN, Keselb A, Bergera J (2000) Microsculpture of the wing surface in Odonata: evidence for cuticular wax covering. Arthropod Struct Dev 29:129–135
Jay AE (1996) Toxic effects of organic solvents on the growth of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Selenastrum capricornutum. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 57:191–198
Ma J, Chen J (2005) How to accurately assay the algal toxicity of pesticides with low water solubility. Environ Pollut 136:267–273
Pereira JR, Famadas KM (2004) Avaliação “in vitro” da eficiência do extrato da raiz do timbó (Dahlstedtia pentaphylla) (Leguminosae, Papilionoidae, Millettiedae) sobre Boophilus microplus (Canestrini 1887) na Região do Vale do Paraíba, São Paulo, Brasil. Arq Inst Biol 71:443–450
Porter RBR, Reese PB, Williams LAD (1995) Acaricidal and insecticidal activities of Candina-4,10(15)-dien-3-one. Phytochemistry 40:735–738
Prates HT, Oliveira AB, Leite RC, Craveiro AA (1993) Atividade carrapaticida e composição química do óleo essencial do capim-gordura. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 28:621–625
Sabatini GA, Kemp DH, Hughes S, Nari A, Hansen J (2001) Tests to determine LC50 and discriminating doses for macrocyclic lactones against the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. Vet Parasitol 95:53–62
Sobbhy H, Aggour MG, Sonenshine DE, Burridge MJ (1994) Cholesteryl esters on the body surfaces of the camel tick, Hyalomma dromedarii (Koch, 1844) and the brown dog tick, Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille 1806). Exp Appl Acarol 18:265–280
Stratton GW (1989) Effect of the solvent acetone on membrane integrity in green alga Chlorella pyrenoidesa. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 42:754–760
Tadros MG, Philips J, Patel H, Pandiripally V (1994) Differential response of green algal species to solvents. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 52:332–337
Yoder JA, Selim ME, Needham GR (1997) Impact of feeding, molting and relative humidity on cuticular wax deposition and water loss in the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum. J Insect Physiol 43:547–551
Williams LAD (1993) Adverse effects of extracts of Artocarpus altilis Park. and Azadirachta indica (A. Juss) on the reproductive physiology of the adult female tick, Boophilus microplus (Canest.). Invertebr Reprod Develop 23:159–164
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to CNPq, Fapergs and Propesq/UFRGS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, K., Toigo, E., Ascoli, B. et al. Effects of solvents and surfactant agents on the female and larvae of cattle tick Boophilus microplus . Parasitol Res 100, 1267–1270 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0418-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0418-2