Abstract
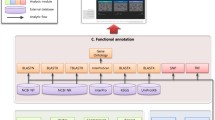
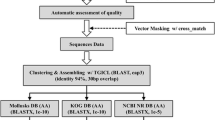
Expressed sequence tag (EST) pools represent partial profiles of the gene expressions of organisms. In an effort to construct a Clonorchis sinensis EST pool, 2,387 ESTs were collected from an adult C. sinensis cDNA library and assembled into 1,573 clusters. Of these clusters, 1,225 ESTs (51%) were singletons and 348 clusters consisted of more than two ESTs. There were 848 clusters (54%) that shared significant identity with previously reported proteins, and of these, 401 clusters were categorized into 11 major functional protein classes. Three cDNA clones of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) aldolase were selected from the C. sinensis EST pool and analyzed for phylogenic clustering. FBP clones encoded a complete polypeptide, which shared significant identity to those of vertebrate and invertebrate animals and clustered with those of trematodes. We believe that the EST pool described can be confidently used as a platform in multigene researches on C. sinensis gene expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Fleischmann RD, Fuldner RA, Bult CJ, Lee NH, Kirkness EF, Weinstock KG, Gocayne JD, White O et al (1995) Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence. Nature 377(Suppl 6547):3–174
Brehm K, Jensen K, Frosch M (2000) mRNA trans-splicing in the human parasitic cestode Echinococcus multilocularis. J Biol Chem 275:38311–38318
Crompton DWT (1999) How much human helminthiasis is there in the world? J Parasitol 85:397–403
El-Dabaa E, Mei H, El-Sayed A, Karim AM, Eldesoky HM, Fahim FA, LoVerde PT, Saber MA (1998) Cloning and characterization of Schistosoma mansoni fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase isoenzyme. J Parasitol 84:954–960
Gamblin S, Davies GJ, Grimes JM, Sackson RM, Lottlechild JA, Watson HC (1991) Activity and specificities of human aldolases. J Mol Biol 219:573–576
Hasegawa M, Kishino H (1994) Accuracies of the simple methods for estimating the bootstrap tree. Mol Biol Evol 11:142–145
Hikasa H, Hori K, Shiokawa K (1997) Structure of aldolase A (muscle-type) cDNA and its regulated expression in oocytes, embryos and adult tissues of Xenopus laevis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1354:189–203
Hong SJ, Seong KY, Sohn WM, Song KY (2000) Molecular cloning and immunological characterization of phosphoglycerate kinase from Clonorchis sinensis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 108:207–216
Hong SJ, Lee JY, Lee DH, Sohn WM, Cho SY (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a mu-class glutathione S-transferase from Clonorchis sinensis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 115:69–75
Horecher BL, Tsalas O, Lai CY (1972) Aldolases. In: Boyer PD (ed) Enzyme, vol. 7. Academic, New York, pp 158–213
Inoue T, Yatsuki H, Kusakabe T, Joh K, Takasaki Y, Nikoh N, Miyata T, Hori K (1997) Caenorhabditis elegans has two isozymic forms, CE-1 and CE-2, of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase which are encoded by different genes. Arch Biochem Biophys 339:226–234
Junqueira-de-Azevedo Ide L, Ho PL (2002) A survey of gene expression and diversity in the venom glands of the pit viper snake Bothrops insularis through the generation of expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Gene 299:279–291
Kai T, Sugimoto Y, Kusakabe T, Zhang R, Koga K, Hori K (1992) Gene structure and multiple mRNA species of Drosophila melanogaster aldolase generating three isozymes with different enzymatic properties. J Biochem (Tokyo) 112:677–688
Kang TH, Yun DH, Lee EH, Chung YB, Bae YA, Chung JY, Kang I, Kim J, Cho SY, Kong Y (2004) A cathepsin F of adult Clonorchis sinensis and its phylogenetic conservation in trematodes. Parasitology 128:195–207
Kitajima Y, Takasaki Y, Takahashi I, Hori K (1990) Construction and properties of active chimeric enzymes between human aldolases A and B. J Biol Chem 265:17493–17498
Kuba M, Yatsuki H, Kusakabe T, Takasaki Y, Nikoh N, Miyata T, Yamaguchi T, Hori K (1997) Molecular evolution of amphioxus fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Arch Biochem Biophys 348:329–336
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobson IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Kwon YD, Cho PY, Hong SJ (2005) Clonorchis sinensis: molecular cloning and localization of myosin regulatory light chain. Parasitol Res 97:21–26
Lee JS, Lee JW, Park SJ, Yong TS (2003) Analysis of the genes expressed in Clonorchis sinensis adults using the expressed sequence tag approach. Parasitol Res 91:283–289
McCarthy JS, Wieseman M, Tropea J, Kaslow D, Abraham D, Lustigman S, Tuan R, Guderian RH, Nutman TB (2002) Onchocerca volvulus glycolytic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase as a target for a protective immune response in humans. Infect Immun 70:851–858
Nagano I, Pei F, Wu Z, Wu J, Cui H, Boonmars T, Takahashi Y (2004) Molecular expression of a cysteine proteinase of Clonorchis sinensis and its application to an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunodiagnosis of clonorchiasis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11:411–416
Park H, Ko MY, Paik MK, Soh CT, Seo JH, Im KI (1995) Cytotoxicity of a cysteine proteinase of adult Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol 33:211–218
Rice-Ficht AC, Dusek KA, Kochevar GJ, Waite JH (1992) Eggshell precursor proteins of Fasciola hepatica, I. Structure and expression of vitelline protein B. Mol Biochem Parasitol 54:129–141
Santos TM, Johnston DA, Azevedo V, Ridgers IL, Martinez MF, Marotta GB, Santos RL, Fonseca SJ, Ortega JM, Rabelo EML, Saber M, Ahmed HM, Romeih MH, Franco GR, Rollinson D, Pena SDJ (1999) Analysis of the gene expression profile of Schistosoma mansoni cercariae using the expressed sequence tag approach. Mol Biochem Parasitol 103:79–97
Sakakibara M, Mukai T, Hori K (1985) Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human aldolase: a messenger RNA in the liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 131:413–420
Shiokawa K, Kajitawa E, Hara H, Yatsuki H, Hori K (2002) A developmental biological study of aldolase gene expression in Xenopus laevis. Cell Res 12:85–96
Tang Y, Cho PY, Kim BS, Hong SJ (2005) Molecular cloning and Characterization of vitelline precursor protein B1 from Clonorchis sinensis. J Parasitol 91:1374–1378
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Zhang R, Yatsuki H, Kusakabe T, Iwabe N, Miyata T, Imai T, Yoshida M, Hori K (1995) Structures of cDNAs encoding the muscle-type and non-muscle-type isozymes of lamprey fructose bisphosphate aldolases and the evolution of aldolase genes. J Biochem (Tokyo) 117:545–553
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2002-041-E20086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, P.Y., Lee, M.J., Kim, T.I. et al. Expressed sequence tag analysis of adult Clonorchis sinensis, the Chinese liver fluke. Parasitol Res 99, 602–608 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0204-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0204-1