Abstract
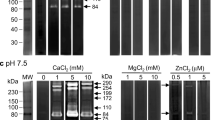
Parasite-derived proteases are important for the parasite life cycle and the pathogenesis of the disease they produce. Proteases of intestinal protozoan parasite Blastocystis hominis were studied for the first time with azocasein assays and gelatin SDS-PAGE analysis. Parasitic lysates were found to have high protease activity and nine protease bands of low (20–33 kDa) and high (44–75 kDa) molecular weights were reported. Proteases were found to be pH-dependent and highest proteolytic activity was observed at neutral pH. Inhibition studies showed that B. hominis isolate B, like many other protozoan parasites, contains mainly cysteine proteases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Tawil YS, Gilger MA, Gopalakrishna GS, Langston C, Bommer KE (1994) Invasive Blastocystis hominis infection in a child. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 148:882–885
Dagci H, Ustun S, Taner MS, Ersoz G, Karacasu F, Budak S (2002) Protozoon infections and intestinal permeability. Acta Trop 81:1–5
Ho LC, Singh M, Suresh G, Ng GC, Yap EH (1993) Axenic culture of Blastocystis hominis in Iscove’s modified Dulbecco’s medium. Parasitol Res 79:614–616
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lockwood BC, North MJ, Scott KI, Bremner AF, Coombs GH (1987) The use of a highly sensitive electrophoretic method to compare the proteinases of trichomonads. Mol Biochem Parasitol 24:89–95
McKerrow JH, Sun E, Rosenthal PJ, Bouvier J (1993) The proteases and pathogenicity of parasitic protozoa. Annu Rev Microbiol 47:821–853
Noel C, Dufernez F, Gerbod D, Edgcomb VP, Viscogliosi PD, Ho LC, Singh M, Wintjens R, Sogin ML, Capron M, Pierce R, Zenner L, Viscogliosi E (2005) Molecular phylogenies of Blastocystis isolates from different hosts: implications for genetic diversity, identification of species, and zoonosis. J Clin Microbiol 43:348–355
North MJ (1982) Comparative biochemistry of the proteinases of eucaryotic microorganisms. Microbiol Rev 46:308–340
North MJ (1994) Cysteine endopeptidases of parasitic protozoa. In: Barrett AJ (ed) Methods in enzymology (vol. 244) Proteolytic enzymes: serine and cysteine peptidases. Academic, pp 523–537
Puthia MK, Vaithilingam A, Lu J, Tan KSW (2005) Degradation of human secretory immunoglobulin A by Blastocystis. Parasitol Res 97:286–389
Sajid M, McKerrow JH (2002) Cysteine proteases of parasitic organisms. Mol Biochem Parasitol 120:1–21
Scholze H, Tannich E (1994) Cysteine endopeptidases of Entamoeba histolytica. In: Barrett AJ (ed) Methods in enzymology. Proteolytic enzymes: serine and cysteine peptidases, vol 244. Academic, p 513–523
Stenzel DJ, Boreham PFL (1996) Blastocystis hominis revisited. Clin Microbiol Rev 9:563–584
Tan KSW (2004) Blastocystis in humans and animals: new insights using modern methodologies. Vet Parasitol 126:121–144
Williams AG, Coombs GH (1995) Multiple protease activities in Giardia intestinalis trophozoites. Int J Parasitol 25:771–778
Yoshikawa H, Morimoto K, Wu Z, Singh M, Hashimoto T (2004) Problems in speciation in the genus Blastocystis. Trends Parasitol 20:251–255
Zhang Z, Yan L, Wang L, Seydel KB, Li E, Ankri S, Mirelman D, Stanley SL Jr (2000) Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteinases with interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme (ICE) activity cause intestinal inflammation and tissue damage in amoebiasis. Mol Microbiol 37:542–548
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by generous grants from the National Medical Research Council (R-182-000-058-213) and from the School of Medicine, National University of Singapore. We express appreciation to Ms. Geok Choo Ng and Mr. Ramachandran for technical support. Thanks are also due to Dr. Punam Dahiya, Ms. Tan Mui Hong, and Ms. Tan Li Li for their generous contributions. The present experiments were carried out in compliance with the laws and regulations of Singapore.
Selena W. S. Sio and Manoj K. Puthia contributed equally to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sio, S.W.S., Puthia, M.K., Lee, A.S.Y. et al. Protease activity of Blastocystis hominis . Parasitol Res 99, 126–130 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0131-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0131-1