Abstract
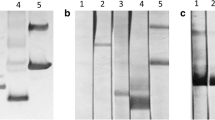
Paramyosin, a vaccine candidate in different helminthiases, was purified from the adult liver fluke Fasciola hepatica using two different procedures. The first started with a crude extraction of paramyosin in high-salt buffer followed by gel filtration chromatography and two precipitation-solubilization cycles; in the second, anion exchange chromatography replaced the gel filtration step. In both cases, the apparent molecular weight of the purified protein determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis under reducing and non-reducing conditions was 97 kDa and 200 kDa, respectively. The molecular weights were consistent with the presence of a dimeric protein linked by disulfide bridges. Western blot analysis showed that the dimeric and monomeric forms were both recognized by an antiserum raised against the F. hepatica 97 kDa band (α-FhPmy), and by an anti-Schistosoma mansoni paramyosin immune serum. Immunohistochemistry using α-FhPmy demonstrated the localization of paramyosin within the subtegumental muscle and in muscle cells surrounding the gut of adult parasites. We also observed labeling of extramuscular structures like testes, surface lamellae of the gut and the tegument of adult flukes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–54
Bullard B, Luke B, Winkelman L (1973) The paramyosin of insect flight muscle. J Mol Biol 75:359–367
Epstein HF, Miller DM, Oriz I, Berliner GC (1985) Myosin and paramyosin are organized about a newly identified core structure. J Cell Biol 100:904–915
Flanigan TP, King CH, Lett RR, Nanduri J, Majmoud AAF (1989) Induction of resistance to Schistosoma mansoni infection in mice by purified parasite paramyosin. J Clin Inv 83:1010–1014
Gaassenbeek CP, Moll L, Cornelissen JB, Vellema P, Borgsteede FH (2001) An experimental study on triclabendazole resistance of Fasciola hepatica in sheep. Vet Parasitol 95:37–43
Gobert GN, Stenzel DJ, Jones MK, Allen DE, McManus DP (1997) Schistosoma japonicum: immunolocalization of paramyosin during development. Parasitology 114:45–52
Harlow E, Lane D (1988) Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Harris HE, Epstein HF (1977) Myosin and paramyosin of Caenorhabditis elegans: biochemical and structural properties of wild type and mutant proteins. Cell 10:709–719
Heukeshoven J, Dernick R (1985) Simplified method for silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels and the mechanism of silver staining. Electrophoresis 6:103–112
Kalinna BH, McManus DP (1993) An IgG (Fcγ)-binding protein of Taenia crassiceps (Cestoda) exhibits sequence homology and antigenic similarity with schistosome paramyosin. Parasitology 106:289–296
Kalinna BH, Becker MM, McManus DP (1997) Engineering and expression of a full length cDNA encoding Schistosoma japonicum paramyosin: purification of the recombinant protein and its recognition by infected patient sera. Acta Trop 65:111–115
Kawaga H, Gengyo K, McLachlan AD, Brenner S, Karn J (1989) Paramyosin gene (unc-15) of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence and models for thick filament structure. J Mol Biol 207:311–333
Kyhse-Andersen J (1984) Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods 10:203–209
Laclette JP, Alagón A, Willms K, Torre-Blanco A (1990) Purification of antigen B from Taenia solium cysticerci by affinity to mammalian collagen. J Parasitol 76:273–275
Laclette JP, Shoemaker CB, Richter D, Arcos L, Pante N, Cohen C, Bing D, Nicholson-Weller A (1992) Paramyosin inhibits complement C1. J Immunol 148:124–128
Laclette JP, Skelly PJ, Merchant MT, Shoemaker CB (1995) Aldehyde fixation dramatically alters the immunolocalization pattern of paramyosin in platyhelminth parasites. Exp Parasitol 81:140–143
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lanar D, Pearce EJ, James SL, Sher A (1986) Identification of paramyosin as the schistosome antigen recognized by intradermally vaccinated mice. Science 234:593–596
Liu F, Bauer CC, Ortiz I, Cook RG, Schmid MF, Epstein HF (1998). β-filagenin, a newly identified protein coassembling with myosin and paramyosin in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Cell Biol 28:1229–1233
Loukas A, Jones MK, King LT, Brindley PJ, McManus DP (2001) Receptor for Fc on the surface of schistosomes. Infect Immunol 69:3646–3651
Mas-Coma MS, Esteban JG, Bargues MD (1999) Epidemiology of human fasciolosis: a review and proposed new classification. Bull World Health Organ 77:340–346
Matsumoto Y, Perry G, Levine RJ, Blanton R, Mahmoud AAF, Aikawa M (1988) Paramyosin and actin in schistosomal teguments. Nature 333:76–78
McNicol AM, Richmond JA (1998) Optimizing immunohistochemistry: antigen retrieval and signal amplification. Histopathology 32:97–103
Nanduri J, Kazura JW (1989) Paramyosin-enhaced clearance of Brugia malayi microfilaremia in mice. J Immunol 143:3359–3363
Overend DJ, Bowen FL (1995) Resistance of Fasciola hepatica to triclabendazole. Aust Vet J 72:275–276
Pearce EJ, James SL, Hieny S, Lanar D, Sher A (1988) Induction of protective immunity against Schistosoma mansoni by vaccination with schistosome paramyosin (Sm 97), a non-surface parasite antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:5678–5682
Plaut AG, Tomasi TB (1970) Immunoglobulin M: pentameric Fcμ fragments released by trypsin at higher temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 65:318–322
Ramirez BL, Kurtis JD, Wiest PM, Arias P, Aligui F, Acosta L, Peters P, Olds GR (1996) Paramyosin: a candidate vaccine against Schistosoma japonicum. Parasite Immunol 18:49–52
Schmidt J, Bodor O, Gohr L, Kunz W (1996) Paramyosin isoforms of Schistosoma mansoni are phosphorylated and localized in a large variety of muscle types. Parasitology 112:459–467
Spithill TW, Dalton JP (1998) Progress in development of liver fluke vaccines. Parasitol Today 14:224–228
Vinos J, Domingo A, Marco R, Cervera M (1991) Identification and characterization of Drosophila melanogaster paramyosin. J Mol Biol 220:687–700
Wisnewski AV, Kresina TF (1995) Induction of protective immunity to schistomiasis with immunologically cross-reactive Lumbricus molecules. Int J Parasitol 25:503–510
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Edward Pearce from Cornell University, USA for kindly supplying the anti-SmPmy hyper-immune serum. This work was supported by grants from IFS (International Foundation for Science) and SIDA (Swedish International Development Agency). Patricia Berasain was the recipient of a PEDECIBA doctoral fellowship. The experiments described in this study comply with the current laws of Uruguay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cancela, M., Carmona, C., Rossi, S. et al. Purification, characterization, and immunolocalization of paramyosin from the adult stage of Fasciola hepatica . Parasitol Res 92, 441–448 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-1059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-1059-3