Abstract
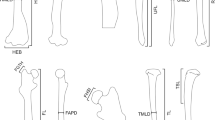
Biomechanical considerations predict that limb proportions should differ between animals with climbing and ground-dwelling lifestyles. Ground-dwellers should have relatively long, parasagittal hind limbs, with high tibia:femur ratios, and relatively short fore limbs. Climbers should have relatively short limbs, with low tibia:femur ratios, and equally long hind and fore limbs. We tested these predictions using gecko species with different locomotion habits (climbing versus ground-dwelling). We measured snout-vent length and lengths of limb segments in 29 species of geckos and analysed them using both non-phylogenetic statistics (nested analysis of variance and principal component analysis) and phylogenetic statistics (analysis of covariance). Neither approach allowed us to find any consistent relationship between habitat use and the morphometric variables. We conclude that either relative limb lengths and limb proportions in geckos have not evolved in response to the physical demands of the microhabitat, or our understanding of those demands is insufficient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 22 February 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaaf, A., Van Damme, R. Limb proportions in climbing and ground-dwelling geckos (Lepidosauria, Gekkonidae): a phylogenetically informed analysis. Zoomorphology 121, 45–53 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004350100044
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004350100044