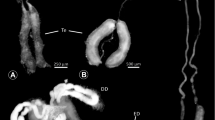
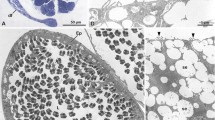
Abstract
The wolf spider Schizocosa malitiosa is a well-known model system for studies on sexual selection in spiders. Despite this, little is known about the morphology of the reproductive system and spermatozoa in this species. In the present study, we investigate the male genital system and sperm cells of S. malitiosa using electron microscopy and provide a computer-based 3D reconstruction of the spermatozoa for the first time for arthropods. In general, the male genital system consists of two long, tube-like testes that lead into convoluted deferent ducts. The ejaculatory duct is enlarged and contains a large quantity of sperm and secretion. As revealed by transmission electron microscopy, only one type of secretion droplet is present in the seminal fluid. The spermatozoa of S. malitiosa resemble an organization known for members of the RTA clade, i.e., with an arrow-shaped acrosomal vacuole partly sunk into the nucleus and a chambered centriolar adjunct (a newly introduced character). This organization provides further support for these characters as potential synapomorphies for the RTA clade. By the end of the spermiogenesis, the nucleus and axoneme coils within the cell and a multi-layered secretion sheath are formed representing cleistospermia. The function of the thick secretion sheath is still unknown, but might be correlated either with the residency time in the female (insemination until oviposition) since female S. malitiosa do not lay eggs before the fourth month after copulation or with the receptivity-inhibiting substances suggested for this species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aire TA, Ozegbe PC (2012) Components and development of the centriolar complex during and beyond spermiogenesis in a passeridan bird, the masked weaver (Ploceus velatus). Tissue Cell 44:63–67
Aisenberg A, Costa FG (2005) Females mated without sperm transfer maintain high sexual receptivity level in the wolf spider Schizocosa malitiosa. Ethology 111:545–558
Alberti G (1990) Comparative spermatology of Araneae. Acta Zool Fenn 190:17–34
Alberti G (2000) Chelicerata. In: Adiyodi KG, Adiyodi RG (eds) Reproductive biology of invertebrates, vol IX B. Wiley, Chichester, pp 311–388
Alberti G, Coyle FA (1991) Ultrastructure of the primary male genital system, spermatozoa and spermiogenesis of Hypochilus pococki (Araneae, Hypochilidae). J Arachnol 19:136–149
Alberti G, Weinmann C (1985) Fine structure of spermatozoa of some labidognath spiders (Filistatidae, Segestriidae, Dysderidae, Oonopidae, Scytodidae, Pholcidae; Araneae; Arachnida) with remarks on spermiogenesis. J Morphol 185:1–35
Alberti G, Afzelius BA, Lucas SM (1986) Ultrastructure of spermatozoa and spermatogenesis in bird spiders (Theraphosidae, Mygalomorphae, Araneae). J Submicr Cytol 18:739–753
Baruffaldi L, Costa FG, Rodríguez A, González A (2010) Chemical communication in Schizocosa malitiosa: evidence of a female contact sex pheromone and persistence in the field. J Chem Ecol 36:759–767
Bertkau P (1875) Über den Generationsapparat der Araneiden. Arch Naturgesch 41:235–262
Bertkau P (1877) Über die Übertragungsorgane und die Spermatozoen der Spinnen. Verh Naturh Ver Preuss Rheinl 34:28–32
Breed WG (2005) Evolution of the spermatozoon in muroid rodents. J Morphol 265:271–290
Burger M, Michalik P (2010) The male genital system of goblin spiders: evidence for the monophyly of Oonopidae (Araneae, Arachnida). Am Mus Novit 3675:1–13
Coddington JA, Levi HW (1991) Systematics and evolution of spiders (Araneae). Annu Rev Ecol Syst 22:565–592
Coelho L, Aisenberg A, Costa FG (2010) Testing female receptiveness to novel or previous mating partners in a wolf spider. Behaviour 147:383–395
Costa FG (1975) El comportamiento precopulatorio de Lycosa malitiosa Tullgren (Araneae: Lycosidae). Rev Brasil Biol 35:359–368
Costa FG (1979) Análisis de la cópula y de la actividad postcopulatoria de Lycosa malitiosa Tullgren (Araneae, Lycosidae). Rev Brasil Biol 39:361–376
Costa (1991) Fenología de Lycosa malitiosa Tullgren (Araneae, Lycosidae) como componente del criptozoos en Marindia, localidad costera del sur del Uruguay. Bol Soc Zool Uruguay 6:8–21
Costa FG, Capocasale RM (1985) La producción de ootecas de Lycosa malitiosa Tullgren (Araneae, Lycosidae). III. Distribución temporal de las oviposiciones. Aracnología 5:1–14
Costa-Ayub CLS, Faraco CD (2007) Ultrastructural aspects of spermiogenesis and synspermia in the brown spider Loxosceles intermedia (Araneae: Sicariidae). Arthropod Struct Dev 36:41–51
Crome W (1951) Die grobe Morphologie des männlichen Genitalapparates einiger Araneen. Deut Zool Z 1:169–186
Estramil N, Costa FG (2007) Female sexual receptivity after partial copulations in the wolf spider Schizocosa malitiosa. J Zool 271:148–153
Fouquet JP, Kann ML, Combeau C, Melki R (1998) γ-tubulin during the differentiation of spermatozoa in various mammals and man. Mol Hum Reprod 12:1122–1129
Fouquet JP, Kann ML, Souès S, Melki R (2000) ARP1 in Golgi organisation and attachment of manchette microtubules to the nucleus during mammalian spermatogenesis. J Cell Sci 113:877–886
González M, Costa FG (2008) Persistence of sexual reluctance in mated females and importance of regular copulations in a wolf spider. Ethol Ecol Evol 20:115–124
Griswold CE, Ramírez MJ, Coddington JA, Platnick NI (2005) Atlas of phylogenetic data for entelegyne spiders (Araneae: Araneomorphae: Entelegynae) with comments on their phylogeny. Proc Calif Acad Sci 56:1–325
Higginson DM, Pitnick S (2011) Intra-ejaculate sperm interactions: do sperm cooperate? Biol Rev 86:249–270
Jamieson BGM (1987) Ultrastructure and phylogeny of insect spermatozoa. Cambridge University Press, London
Jamieson BGM (2007) Avian spermatozoa: structure and phylogeny. In: Jamieson BGM (ed) Reproductive biology and phylogeny of birds. Science Publishers, Enfield New Hampshire, pp 349–511
Jamieson BGM, Dallai R, Afzelius BA (1999) Insects: their spermatozoa and phylogeny. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire
Jörger KM, Heß M, Neusser TP, Schrödl M (2009) Sex in the beach: spermatophores, dermal insemination and 3D sperm ultrastructure of the aphallic mesopsammic Pontohedyle milaschewitchii (Acochlidia, Opisthobranchia, Gastropoda). Mar Biol 156:1159–1170
Kim JK, Kim TH, Moon MJ (1993) Ultrastructure of the testis in the spider Pardosa astrigera L. Koch. Korean Arachnol 9:43–53
Lopez A, Bonaric JC, Boissin L (1983) Etude ultrastructurale de la spermiogenese chez l’araignée Pisaura mirabilis (Clerck, 1858) (Pisauridae). Rev Arachnol 5:55–64
Marotta R, Ferraguti M, Erséus C, Gustavsson LM (2008) Combined-data phylogenetics and character evolution of Clitellata (Annelida) using 18S rDNA and morphology. Zool J Linn Soc 154:1–26
Michalik P (2007) Spermatozoa and spermiogenesis of Liphistius cf phuketensis (Mesothelae, Araneae, Arachnida) with notes on phylogenetic implications. Arthropod Struct Dev 36:327–335
Michalik P (2009) The male genital system of spiders (Arachnida, Araneae) with notes on the fine structure of seminal secretions. In: Kropf C, Horak O (eds) Towards a natural history of arthropods and other organisms. In memoriam Konrad Thaler. Contributions to Natural History, Bern, pp 959–972
Michalik P, Alberti G (2005) On the occurence of the 9+0 axonemal pattern in the spermatozoa of sheetweb spiders (Linyphiidae, Araneae). J Arachnol 33:569–572
Michalik P, Hormiga G (2010) Ultrastructure of the spermatozoa in the spider genus Pimoa: new evidence for the monophyly of Pimoidae plus Linyphiidae (Arachnida: Araneae). Am Mus Novit 3682:1–17
Michalik P, Huber BA (2006) Spermiogenesis in Psilochorus simoni (Berland, 1911) (Pholcidae, Araneae): evidence for considerable within-family variation in sperm structure and development. Zoology 109:14–25
Michalik P, Uhl G (2005) The male genital system of the cellar spider Pholcus phalangioides (Fuesslin, 1775) (Pholcidae, Araneae): development of spermatozoa and seminal secretion. Front Zool 2:1–12
Michalik P, Dallai R, Giusti F, Alberti G (2004a) The ultrastructure of the peculiar synspermia of some Dysderidae (Araneae, Arachnida). Tissue Cell 36:447–460
Michalik P, Haupt J, Alberti G (2004b) On the occurence of coenospermia in mesothelid spiders (Araneae: Heptathelidae). Arthropod Struct Dev 33:173–181
Michalik P, Sacher P, Alberti G (2006) Ultrastructural observations of spermatozoa of several tetragnathid spiders with phylogenetic implications (Araneae, Tetragnathidae). J Morphol 267:129–151
Miller JA, Carmichael A, Ramírez MJ, Spagna JC, Haddad CR, Řezáč M, Johannesen J, Král J, Wang XP, Griswold CE (2010) Phylogeny of entelegyne spiders: affinities of the family Penestomidae (NEW RANK), generic phylogeny of Eresidae, and asymmetric rates of change in spinning organ evolution (Araneae, Araneoidea, Entelegynae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 55:786–804
Mottier-Pavie V, Megraw TL (2009) Drosophila bld10 is a centriolar protein that regulates centriole, basal body, and motile cilium assembly. Mol Biol Cell 20:2605–2614
Ōsaki H (1969) Electron microscope study on the spermatozoon of the liphistiid spider Heptathela kimurai. Acta Arachnol 22:1–12
Ōsaki H (1972) Electron microscope study on spermiogenesis in the spider Oxyopes sertatus. Jap J Zool 16:184–199
Platnick NI (2012) The World Spider Catalog, Version 13.0, American Museum of Natural History. http://research.amnh.org/iz/spiders/catalog
Platnick NI, Abrahim N, Álvarez-Padilla F, Andriamalala D, Baehr B, Baert L, Bonaldo AB, Brescovit AD, Chousou-Polydouri N, Dupérré N, Eichenberger B, Fannes W, Gaublomme E, Gillespie RG, Grismado CJ, Griswold CE, Harvey MS, Henrard A, Hormiga G, Izquierdo MA, Jocqué R, Kranz-Baltensperger Y, Kropf C, Ott R, Ramírez MJ, Raven RI, Rheims C, Ruiz GRS, Santos AJ, Saucedo A, Sierwald P, Szüts T, Ubick D, Wang X-P (2012) Tarsal organ morphology and the phylogeny of goblin spiders (Araneae, Oonopidae), with notes on basal genera. Am Mus Novit 3736:1–52
Reger JF (1970) Spermiogenesis in the spider Pisaurina sp.: a fine structure study. J Morphol 130:421–433
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Simmons LW (2001) Sperm competition and its evolutionary consequences in the insects. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Useta G, Huber BA, Costa FG (2007) Spermathecal morphology and sperm dynamics in the female Schizocosa malitiosa (Araneae: Lycosidae). Eur J Entomol 104:777–785
Wang Z, Zhong X (1993) Origin and function of the centriole adjunct in spermatids of insects. Acta Entomol Sinica 36:419–422
Wu XM, Song DX, Chen DY (1997) Ultrastructure of spermatozoa and spermatogenesis in wolf spider Pardosa astrigera (Araneae: Lycosidae). Acta Zool Sinica 43:17–26
Acknowledgments
We are deeply indebted to Christian Wirkner (Universität Rostock, Germany) for help with the implementation of the 3D pdf. We thank Steffen Harzsch (Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald, Germany) who gave us the possibility to use the Amira 5.3 workstation. The first author thanks Gerd Alberti (Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald, Germany) for helpful discussion on the sperm structures of the RTA clade. The authors wish to thank Jason Dunlop (Museum für Naturkunde, Berlin, Germany) for improving the English and the anonymous reviewers for the helpful comments on the manuscript. Funding for this research was provided by the German Research Foundation to PM (DFG Mi 1255/5-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Schmidt-Rhaesa.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
435_2012_166_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Computer-based 3D reconstruction visualizing the different cell components in a coiled sperm cell in the lumen of the testis. To be able to actively rotate and study the 3D-reconstruction, click on the picture. Use the mouse for navigation. To hide/show different structures, click the tree icon and select from the list. The image stack used for the 3D reconstruction is stored in MorphDBase (https://www.morphdbase.de?P_Michalik_20120706-M-2.1) (PDF 3614 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michalik, P., Aisenberg, A., Postiglioni, R. et al. Spermatozoa and spermiogenesis of the wolf spider Schizocosa malitiosa (Lycosidae, Araneae) and its functional and phylogenetic implications. Zoomorphology 132, 11–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-012-0166-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-012-0166-z