Abstract
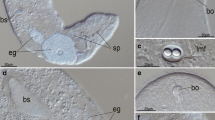
The musculature of larvae of Gordius aquaticus was investigated by laser-scanning microscopy and compared to transmission electron microscopic data for the larva of Paragordius varius. In the anterior portion of the body, the preseptum, four different muscle groups can be distinguished: (1) 12 anterior parietal muscles in the body wall, (2) six oblique muscles that function as retractors of the introvert, (3) six proboscideal muscles, which function as retractors for the proboscis, and (4) six muscles associated with spines of the outermost of the three rings of spines. The posterior portion of the body, the postseptum, possesses four pairs of longitudinal muscle strands in G. aquaticus, the postseptal parietal muscles, that are located dorsolaterally and ventrolaterally. These are not clearly visible in P. varius, where instead three pairs of parietal muscles are present. Additional small muscles are associated with the terminal spines and with the duct running from the pseudointestine to the body wall. All fibers show a cross-striated pattern although this striation is less obvious at the ends of the fibers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bresciani J (1991) Nematomorpha. In: Harrison FW, Ruppert EE (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 4. Aschelminthes. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 197–218
Dorier A (1930) Recherches biologiques et systematiques sur les gordiaces. Trav Lab Hydrobiol Piscicult Grenoble 22:1–183
Hanelt B, Janovy J (2002) Morphometric analysis of nonadult characters of common species of American gordiids (Nematomorpha: Gordioidea). J Parasitol 88:557–562
Inoue I (1958) Studies on the life history of Chordodes japonensis a species of Gordiacea. I. The development and structure of the larva. Jap J Zool 12:203–218
Lanzavecchia G (1977) Morphological modulations in helical muscles (Aschelminthes and Annelida). Int Rev Cytol 51:133–186
Lanzavecchia G, Valvassori R, de Eguileor M, Lanzavecchia P (1979) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the contractile system of the Nematomorpha muscle fiber. J Ultrastruct Res 66: 201–223
May HG (1919) Contributions to the life histories of Gordius robustus Leidy and Paragordius varius (Leidy). Illinois Biol Monogr 5:7–119
Müller MCM, Schmidt-Rhaesa A (2003) Reconstruction of the muscle system in Antygomonas sp. (Kinorhyncha, Cyclorhagida) by phalloidin labeling and cLSM. J Morphol 256:103–110. DOI 10.1002/jmor.10058
Ruppert EE (1991) Gastrotricha. In: Harrison FW, Ruppert EE (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 4. Aschelminthes. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 41–109
Schmidt-Rhaesa A (1997) Nematomorpha. In: Schwoerbel J, Zwick P (eds) Süßwasserfauna Mitteleuropas. Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 1–124
Schmidt-Rhaesa A (1998) Muscular ultrastructure in Nectonema munidae and Gordius aquaticus (Nematomorpha). Invert Biol 117:38–45
Storch V (1991) Priapulida. In: Harrison FW, Ruppert EE (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 4. Aschelminthes. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 333–350
Zapotosky JE (1974) Fine structure of the larval stage of Paragordius varius (Leidy, 1851) (Gordiodea: Paragordidae). I. The preseptum. Proc Helm Soc Wash 41:209–221
Zapotosky JE (1975) Fine structure of the larval stage of Paragordius varius (Leidy, 1851) (Gordioidea: Paragordidae). II. The postseptum. Proc Helm Soc Wash 42:103–111
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ben Hanelt for his permission to use larvae of Paragordius varius from his laboratory life cycle at the University of Nebraska at Lincoln and Fernanda Zanca for her help in collecting and culturing specimens of Gordius aquaticus. We are grateful to Eward E. Ruppert and an anonymous reviewer for valuable comments, and to Mechthild Krabusch for rearranging the TEM plates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, M.C.M., Jochmann, R. & Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. The musculature of horsehair worm larvae (Gordius aquaticus, Paragordius varius, Nematomorpha): F-actin staining and reconstruction by cLSM and TEM. Zoomorphology 123, 45–54 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-003-0088-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-003-0088-x