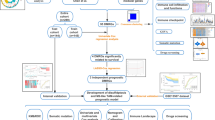
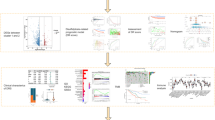
Abstract
Purpose
Disulfidptosis is a novel type of cell death induced by disulphide stress that depends on the accumulation of cystine disulphide, causing cytotoxicity and triggering cell death. However, the direct prognostic effect and regulatory mechanism of disulfidptosis-related genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma (BLCA) remain unclear.
Methods
To explore the role of 10 disulfidptosis-related genes, the multiomic data of 10 genes were comprehensively analysed. Next, based on seven disulfidptosis-related differentially expressed genes, a novel disulfidptosis-related gene score was developed to help predict the prognosis of BLCA. Immunohistochemistry, EDU, Real-time PCR and western blot were used to verify the model.
Results
Significant functional differences were found between the high- and low-risk score groups, and samples with a higher risk score were more malignant. Furthermore, the tumour exclusion and Tumour Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion scores of the high-risk score group were higher than those of the low-risk score group. The risk score was positively correlated with the expression of immune checkpoints. Drug sensitivity analyses revealed that the low-risk score group had a higher sensitivity to cisplatin, doxorubicin, docetaxel and gemcitabine than the high-risk score group. Moreover, the expression of the TM4SF1 was positively correlated with the malignancy degree of BLCA, and the proliferation ability of BLCA cells was reduced after knockdown TM4SF1.
Conclusion
The present study results suggest that disulfidptosis-related genes influence the prognosis of BLCA through their involvement in immune cell infiltration. Thus, these findings indicate the role of disulfidptosis in BLCA and its potential regulatory mechanisms.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
References
Battaglia AM, Chirillo R, Aversa I, Sacco A, Costanzo F, Biamonte F (2020) Ferroptosis and cancer: mitochondria meet the “Iron Maiden” cell death. Cells 9(6):1505. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061505
Cambier S, Sylvester RJ, Collette L et al (2016) EORTC nomograms and risk groups for predicting recurrence, progression, and disease-specific and overall survival in non-muscle-invasive stage Ta-T1 urothelial bladder cancer patients treated with 1–3 years of maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guérin. Eur Urol 69(1):60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.06.045
Cao J, Yang J, Ramachandran V et al (2015) TM4SF1 promotes gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 10(12):e0144969. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144969
Cao R, Wang G, Qian K et al (2018) TM4SF1 regulates apoptosis, cell cycle and ROS metabolism via the PPARγ-SIRT1 feedback loop in human bladder cancer cells [published correction appears in Cancer Lett. 2022 Jan 28;525:198-199]. Cancer Lett 414:278–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.11.015
Chen M, Zhang S, Wen X, Cao H, Gao Y (2020) Prognostic value of CLIC3 mRNA overexpression in bladder cancer. PeerJ 8:e8348. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8348
Chung YT, Matkowskyj KA, Li H et al (2012) Overexpression and oncogenic function of aldo-keto reductase family 1B10 (AKR1B10) in pancreatic carcinoma. Mod Pathol 25(5):758–766. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2011.191
Dehmelt L, Halpain S (2005) The MAP2/Tau family of microtubule-associated proteins. Genome Biol 6(1):204. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-6-1-204
Freidman N, Chen I, Wu Q et al (2020) Amino acid transporters and exchangers from the SLC1A family: structure, mechanism and roles in physiology and cancer. Neurochem Res 45(6):1268–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02934-x
Fukumoto S, Yamauchi N, Moriguchi H et al (2005) Overexpression of the aldo-keto reductase family protein AKR1B10 is highly correlated with smokers’ non-small cell lung carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 11(5):1776–1785. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1238
Gao Y, Church G (2005) Improving molecular cancer class discovery through sparse non-negative matrix factorization. Bioinformatics 21(21):3970–3975. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti653
Glasner A, Plitas G (2021) Tumor resident regulatory T cells. Semin Immunol 52:101476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2021.101476
Guo Z, Song J, Hao J et al (2019) M2 macrophages promote NSCLC metastasis by upregulating CRYAB. Cell Death Dis 10(6):377. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1618-x
Hanahan D (2022) Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov 12(1):31–46. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J (2013) GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform 14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-7
Hao W, Wu L, Cao L et al (2021) Radioresistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells exhibited decreased cisplatin sensitivity by inducing SLC1A6 expression. Front Pharmacol 12:629264. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.629264
Huang YK, Fan XG, Qiu F (2016) TM4SF1 promotes proliferation, invasion, and metastasis in human liver cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 17(5):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050661
Huang LJ, Shen Y, Bai J et al (2020) High expression levels of long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 18 and semaphorin 5A indicate poor prognosis in multiple myeloma. Acta Haematol 143(3):279–288. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502404
Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D et al (2018) Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 24(10):1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M (2021) Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(4):266–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
Jin L, Mei W, Liu X et al (2022) Identification of cuproptosis -related subtypes, the development of a prognosis model, and characterization of tumor microenvironment infiltration in prostate cancer. Front Immunol 13:974034. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.974034
Jordan B, Meeks JJ (2019) T1 bladder cancer: current considerations for diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Urol 16(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-018-0105-y
Kalluri R (2016) The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 16(9):582–598. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.73
Ke M, Sun N, Lin Z et al (2023) SNHG18 inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation by increasing p21 transcription through destabilizing c-Myc protein. Cancer Cell Int 23(1):48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-023-02887-w
Kim JH, Kim BS, Lee SK (2020) Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment and approach for anticancer immunotherapy. Immune Netw. 20(1):e4. https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2020.20.e4
Li C, Jiang P, Wei S, Xu X, Wang J (2020) Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: new mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol Cancer 19(1):116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01234-1
Liu XF, Thin KZ, Ming XL et al (2018) Small nucleolar RNA host gene 18 acts as a tumor suppressor and a diagnostic indicator in hepatocellular carcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat 17:1533033818794494. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533033818794494
Liu J, Hong M, Li Y, Chen D, Wu Y, Hu Y (2022) Programmed Cell death tunes tumor immunity. Front Immunol 13:847345. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.847345
Liu X, Nie L, Zhang Y et al (2023) Actin cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates disulfidptosis. Nat Cell Biol 25(3):404–414. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-023-01091-2
Macpherson IR, Rainero E, Mitchell LE et al (2014) CLIC3 controls recycling of late endosomal MT1-MMP and dictates invasion and metastasis in breast cancer. J Cell Sci 127(Pt 18):3893–3901. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.135947
Maeser D, Gruener RF, Huang RS (2021) oncoPredict: an R package for predicting in vivo or cancer patient drug response and biomarkers from cell line screening data. Brief Bioinform 22(6):260. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbab260
Martínez VG, Rubio C, Martínez-Fernández M et al (2017) BMP4 induces M2 macrophage polarization and favors tumor progression in bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23(23):7388–7399. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1004
Nishikawa H, Koyama S (2021) Mechanisms of regulatory T cell infiltration in tumors: implications for innovative immune precision therapies [published correction appears in J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Sep;9(9):]. J Immunother Cancer 9(7):e002591. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2021-002591
Park SY (2018) Nomogram: An analogue tool to deliver digital knowledge. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 155(4):1793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.12.107
Peyrottes A, Ouzaid I, Califano G, Hermieu JF, Xylinas E (2021) Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Medicina (kaunas) 57(8):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080769
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C, Garufi A, D’Orazi G (2016) Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging (albany NY) 8(4):603–619. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100934
Qin J, Zhang X, Tan B et al (2020) Blocking P2X7-mediated macrophage polarization overcomes treatment resistance in lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 8(11):1426–1439. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-20-0123
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D et al (2015) limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43(7):e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Salmaninejad A, Valilou SF, Soltani A et al (2019) Tumor-associated macrophages: role in cancer development and therapeutic implications. Cell Oncol (dordr) 42(5):591–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00453-z
Schneider AK, Chevalier MF, Derré L (2019) The multifaceted immune regulation of bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol 16(10):613–630. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-019-0226-y
Seo H, González-Avalos E, Zhang W et al (2021) BATF and IRF4 cooperate to counter exhaustion in tumor-infiltrating CAR T cells. Nat Immunol 22(8):983–995. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-021-00964-8
Sharifi L, Nowroozi MR, Amini E, Arami MK, Ayati M, Mohsenzadegan M (2019) A review on the role of M2 macrophages in bladder cancer; pathophysiology and targeting. Int Immunopharmacol 76:105880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105880
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A (2023) Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 73(1):17–48. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21763
Tang D, Kang R, Berghe TV, Vandenabeele P, Kroemer G (2019) The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res 29(5):347–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0164-5
Tang Q, Chen J, Di Z et al (2020) TM4SF1 promotes EMT and cancer stemness via the Wnt/β-catenin/SOX2 pathway in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):232. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01690-z
Tian Z, Cao S, Li C et al (2019) LncRNA PVT1 regulates growth, migration, and invasion of bladder cancer by miR-31/ CDK1. J Cell Physiol 234(4):4799–4811. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27279
Tsuzura H, Genda T, Sato S et al (2014) Expression of aldo-keto reductase family 1 member b10 in the early stages of human hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 15(4):6556–6568. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046556
Uhlen M, Zhang C, Lee S, Sjöstedt E, Fagerberg L, Bidkhori G et al (2017) A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science 357(6352):eaan2507
van der Leun AM, Thommen DS, Schumacher TN (2020) CD8+ T cell states in human cancer: insights from single-cell analysis. Nat Rev Cancer 20(4):218–232. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0235-4
van Rhijn BW, Burger M, Lotan Y et al (2009) Recurrence and progression of disease in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: from epidemiology to treatment strategy. Eur Urol 56(3):430–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2009.06.028
Wang J, Qin D, Tao Z et al (2022) Identification of cuproptosis-related subtypes, construction of a prognosis model, and tumor microenvironment landscape in gastric cancer. Front Immunol 13:1056932. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1056932
Wilkerson MD, Hayes DN (2010) ConsensusClusterPlus: a class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 26(12):1572–1573. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq170
Winerdal ME, Krantz D, Hartana CA et al (2018) Urinary bladder cancer Tregs suppress MMP2 and potentially regulate invasiveness. Cancer Immunol Res 6(5):528–538. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0466
Wohlhieter CA, Richards AL, Uddin F et al (2020) Concurrent mutations in STK11 and KEAP1 promote ferroptosis protection and SCD1 dependence in lung cancer. Cell Rep 33(9):108444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108444
Yuan C, Yuan M, Chen M et al (2021) Prognostic implication of a novel metabolism-related gene signature in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:666199. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.666199
Zhang Z, Lin M, Wang J et al (2021) Calycosin inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion by suppressing EMT via BATF/TGF-β1. Aging (albany NY) 13(12):16009–16023. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203093
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Doctor Haojie Wang, Qiong Cao and Zhihao Wei for their help with the experimental verification process. We are particularly grateful to the MogoEdit (http://www.mogoedit.com/login) for the language polishing.
Funding
This work was supported by the Medical Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (No. LHGJ20190567) and (No. LHGJ20200582).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SX designed the research methods. RL performed the analysis; SX and RL drafted the manuscript. QC and ZW performed the IHC. HW performed the western blot, EDU and others experiments. All authors approved the version of the manuscript to be released and agreed to be responsible for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study complied with the principles set forth in the Declaration of Helsinki. Access to the de-identified linked dataset was obtained from the TCGA databases in accordance with the database policy. For analyses of de-identified data from the TCGA databases, institutional review board approval and informed consent were not required.
Consent for publication
All authors have read the final version of the manuscript and agree.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2023_5235_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 2. (A-B). GO and KEGG enriched analysis for the DEGs associated with the Disulfidptosis. (C). PPI network exhibiting the connection between the DEGs associated with the Disulfidptosis
432_2023_5235_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure 3. (A)Univariate COX regression analysis for the DEGs associated with the Disulfidptosis. (B). Multivariate COX regression analysis for the DEGs associated with the Disulfidptosis. (C-F) KM survival analysis indicated the difference between low- and high-expression of SLC1A6, CLIC3, SNHG18 and AKR1B15
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, S., Li, R., Su, J. et al. A novel model based on disulfidptosis-related genes to predict prognosis and therapy of bladder urothelial carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 13925–13942 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05235-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05235-7