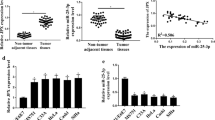
Abstract
Purpose
The abnormal regulation of lncRNA CARMN has been proved to be a tumor suppressor gene of cervical cancer (CC). However, its role in CC is still elusive. The regulation of CARMN post-transcriptional level by m6A modification and miRNA has not been studied. This study aims to analyze the molecular mechanism of m6A modification and miRNA on the abnormal expression of CARMN in CC cells, so as to provide a new theoretical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of CC.
Methods
MeRIP-seq was used to identify the differential m6A-modified genes between tumor and normal cervical tissues. RT-qPCR assay was used to detect gene expression levels in tissues or cells. The m6A modification sites of CARMN was predicted by bioinformatics, and the modification of m6A and its regulatory effect on CARMN were analyzed by MeRIP-qPCR, Actinomycin D assay and RIP assay. RIP-microarray combined with bioinformatics methods to screen miRNAs that may target CARMN. The regulation mechanism between miRNA and CARMN was verified by RT-qPCR, nucleo-plasmic separation assay, mRNA stability assay, dual-luciferase reporter assay, and in vivo experiments.
Results
MeRIP-seq found that CARMN is a significant different gene in the abundance of m6A in CC, and the modification level of m6A in CC tissues was higher than that in normal cervical tissues. Further, this study verified that m6A reader YTHDF2 could recognize m6A-modified CARMN and promote its degradation in CC cells. miR-21-5p was proved to be the downstream target gene of CARMN, and miR-21-5p could negatively regulate the expression of CARMN. Further experiments showed that miR-21-5p could directly bind to CARMN and lead to the degradation of CARMN. The in vivo experimental results indicated that the level of miR-21-5p in the overexpressed CARMN group was significantly lower than that in the control group.
Conclusion
m6A modification and miR-21-5p play important roles in promoting the occurrence and development of tumors by regulating CARMN, provide new potential targets for the treatment of CC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analysed during the current study are available in the TCGA GDC repository (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/).
References
Bhandari M, Dahal T, Kc J (2022) Professionalism among nurses working at different government and private hospitals of province 1. J Nepal Health Res Counc 20:419–425. https://doi.org/10.33314/jnhrc.v20i02.4071
Braconi C et al (2011) microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene 30:4750–4756. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.193
Brogna S, Wen J (2009) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) mechanisms. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1550
Chen M et al (2018) RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology 67:2254–2270. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29683
Di Gesualdo F, Capaccioli S, Lulli M (2014) A pathophysiological view of the long non-coding RNA world. Oncotarget 5:10976–10996. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2770
Ding J et al (2022) Identification of a dysregulated ceRNA network modulated by copy number variation-driven lncRNAs in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Environ Mol Mutagen 63:351–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.22509
Ding YX et al (2023) Exosomes secreted from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth by transferring miRNAs. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 45:50–55. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200622-00586
Du R, Bai Y, Li L (2022) Biological networks in gestational diabetes mellitus: insights into the mechanism of crosstalk between long non-coding RNA and N(6)-methyladenine modification. BMC Pregnancy Childb 22:384. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-022-04716-w
Gan L, Zhao Y, Fu Y, Chen Q (2023) The potential role of m6A modifications on immune cells and immunotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother 160:114343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114343
Ghafouri-Fard S, Azimi T, Taheri M (2021) Cervical carcinoma high expressed 1 (CCHE1): an oncogenic lncRNA in diverse neoplasms. Biomed Pharmacother 142:112003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112003
Han X, Li B, Zhang S (2023) MIR503HG: a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target in human diseases. Biomed Pharmacother 160:114314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114314
Hao C, Lin S, Liu P, Liang W, Li Z, Li Y (2023) Potential serum metabolites and long-chain noncoding RNA biomarkers for endometrial cancer tissue. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 49:725–743. https://doi.org/10.1111/jog.15494
He RZ, Luo DX, Mo YY (2019) Emerging roles of lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Genes Dis 6:6–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2019.01.003
He Y, Wang W, Xu X, Yang B, Yu X, Wu Y, Wang J (2022) Mettl3 inhibits the apoptosis and autophagy of chondrocytes in inflammation through mediating Bcl2 stability via Ythdf1-mediated m(6)A modification. Bone 154:116182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2021.116182
Ji F, Lu Y, Chen S, Lin X, Yu Y, Zhu Y, Luo X (2021) m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3-mediated lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 promotes the tumorigenesis of cervical cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics 22:574–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2021.07.004
Lan Y, Liu B, Guo H (2021) The role of M(6)A modification in the regulation of tumor-related lncRNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 24:768–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2021.04.002
Ledesma-Pacheco SJ et al (2023) Regulatory mechanisms of microRNAs in endocrine disorders and their therapeutic potential. Front Genet 14:1137017. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2023.1137017
Liu JL et al (1988) Changes in thyroid, cerebral cortex and bones of therapeutically aborted fetuses from endemic goiter region supplied with iodized salt for 5 years. Chin Med J (engl) 101:133–136
Marquez-Molins J, Juarez-Gonzalez VT, Gomez G, Pallas V, Martinez G (2022) Occurrence of RNA post-transcriptional modifications in plant viruses and viroids and their correlation with structural and functional features. Virus Res 323:198958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198958
Mehterov N et al (2022) A novel panel of clinically relevant miRNAs signature accurately differentiates oral cancer from normal mucosa. Front Oncol 12:1072579. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.1072579
Meng X, Deng Y, He S, Niu L, Zhu H (2021) m(6)A-mediated upregulation of LINC00857 promotes pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis by regulating the miR-150–5p/E2F3 Axis. Front Oncol 11:629947. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.629947
Patamsyte V, Zukovas G, Gecys D, Zaliaduonyte D, Jakuska P, Benetis R, Lesauskaite V (2020) Long Noncoding RNAs CARMN, LUCAT1, SMILR, and MALAT1 in thoracic aortic aneurysm: validation of biomarkers in clinical samples. Dis Mark 2020:8521899. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8521899
Pilleron S, Cabasag CJ, Ferlay J, Bray F, Luciani S, Almonte M, Pineros M (2020) Cervical cancer burden in Latin America and the Caribbean: where are we? Int J Cancer 147:1638–1648. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32956
Shen J, Feng XP, Hu RB, Wang H, Wang YL, Qian JH, Zhou YX (2021) N-methyladenosine reader YTHDF2-mediated long noncoding RNA FENDRR degradation promotes cell proliferation in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Lab Investig 101:775–784. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-021-00543-3
Sheng X et al (2021) LncRNA CARMN overexpression promotes prognosis and chemosensitivity of triple negative breast cancer via acting as miR143-3p host gene and inhibiting DNA replication. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40:205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-02015-4
Singh D et al (2023) Global estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2020: a baseline analysis of the WHO Global Cervical Cancer Elimination Initiative. Lancet Glob Health 11:e197–e206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00501-0
Statello L, Guo CJ, Chen LL, Huarte M (2021) Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22:96–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00315-9
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tao Z, Zhao Y, Chen X (2020) Role of methyltransferase-like enzyme 3 and methyltransferase-like enzyme 14 in urological cancers. PeerJ 8:e9589. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9589
Wang P, Doxtader KA, Nam Y (2016) Structural basis for cooperative function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 methyltransferases. Mol Cell 63:306–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.041
Wang J, Tan L, Yu X, Cao X, Jia B, Chen R, Li J (2022a) lncRNA ZNRD1-AS1 promotes malignant lung cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis via the miR-942/TNS1 axis and is positively regulated by the m(6)A reader YTHDC2. Mol Cancer 21:229. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-022-01705-7
Wang X, Wu S, Yang Y, Zhao J (2022b) LncRNA CARMN affects hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis by regulating the miR-192-5p/LOXL2 axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:9277360. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9277360
Wang L, Zhao H, Fang Y, Yuan B, Guo Y, Wang W (2023) LncRNA CARMN inhibits cervical cancer cell growth via the miR-92a-3p/BTG2/Wnt/beta-catenin axis. Physiol Genom 55:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00088.2022
Wu M, Chen G, Liao X, Xiao L, Zheng J (2022) YTHDF2 interference suppresses the EMT of cervical cancer cells and enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity by regulating AXIN1. Drug Dev Res 83:1190–1200. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21942
Wu Y, Cao F, Xie L, Wu F, Zhu S, Qiu C (2023) Comparative transcriptome profiling reveals key microRNAs and regulatory mechanisms for aluminum tolerance in olive. Plants (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12050978
Xie M et al (2022a) Cuproptosis-related MiR-21–5p/FDX1 axis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its potential impact on tumor microenvironment. Cells 12:1–52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010173
Xie Q et al (2022b) piRNA-14633 promotes cervical cancer cell malignancy in a METTL14-dependent m6A RNA methylation manner. J Transl Med 20:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03257-2
Xu J, Zhang W, Lv Q, Zhu D (2015) Overexpression of miR-21 promotes the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells via the inhibition of PTEN. Oncol Rep 33:3108–3116. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3931
Xue L, Li J, Lin Y, Liu D, Yang Q, Jian J, Peng J (2021) m(6) A transferase METTL3-induced lncRNA ABHD11-AS1 promotes the Warburg effect of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Cell Physiol 236:2649–2658. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30023
Xun W, Cen W, Dahai Y, Huaqing W, Jiping S, Mengzhu G, Ning M (2020) LncRNA miR143HG suppresses miR-21 through methylation to inhibit cell invasion and migration. Laryngoscope 130:E640–E645. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28474
Yang Z et al (2019) GRSF1-mediated MIR-G-1 promotes malignant behavior and nuclear autophagy by directly upregulating TMED5 and LMNB1 in cervical cancer cells. Autophagy 15:668–685. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1539590
Zhang G, Hou J, Mei C, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang K (2023) Effect of circular RNAs and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification on cancer biology. Biomed Pharmacother 159:114260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114260
Funding
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (81872684), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2242023K40023), Southeast University “Zhongying Young Scholars” Project, Opening Foundation of Jiangsu Provincial Health Development Research Center (JSHD2022056), Natural Science Foundation for Colleges and Universities of Jiangsu Province (22KJB330004), Major Project of Jiangsu Health Vocational College, Scientific Research Project of Jiangsu Provincial Health Commission (Z2019009), Major Project of Jiangsu Health Vocational College (JKA202202), Foundation for Shihezi University School of Medicine (ZZZC2022016), and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX21_0162 and KYCX22_0301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bingjia Yu conceived the study, performed data analysis and wrote the article. Xiuting Li and Wenjing Yan downloaded gene expression data of CC. Bo Ding, Xing Zhang, Siyuan Shen, Shuqian Xie, Jing Hu, Haohan Liuundertook data analysis and interpretation. Xue Chen, Yamei Nie, Fengying Liu performed manuscript review. Yan Zhang and Shizhi Wang critically revised the article for research content and administrative support. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
The study was conducted according to guidelines approved by the Institutional Review Board of Southeast University. All participants signed informed consent.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, B., Li, X., Yan, W. et al. Post-transcriptional regulation of tumor suppressor gene lncRNA CARMN via m6A modification and miRNA regulation in cervical cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 10307–10318 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04893-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04893-x