Abstract
Background
Previous researches have indicated physical activity (PA) may be associated with lower risk of lung cancer. However, causal relationship between PA and risk of lung cancer is not clear. We aimed to inspect the causal effect of PA on lung cancer.
Methods
We analyzed summary data of accelerator-measured PA and lung cancer from the genome-wide association study (GWAS) using two‐sample Mendelian randomization (MR) method. We obtained summary data of accelerator-measured PA from UK Biobank, data of lung cancer patients from Consortium and International Lung Cancer Consortium (ILCCO) to investigate possible causal effect of PA on lung cancer.
Results
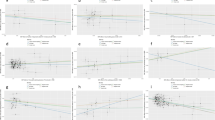
According to result of MR using inverse variance weighted method (IVW), we found that genetically predicted higher PA level did not causally decrease risk of lung cancer (OR 0.95, 95% CI 0.88–1.03, p = 0.238). Results of MR-Egger and weighted median method were consistent with IVW method.
Conclusion
Our mendelian randomization study showed that genetically higher PA is not causally associated with risk of lung cancer. More researches are needed to investigate relationship between PA and lung cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in [UK Biobank] at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0120-3, [ILCCO] at https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3002, reference number [9,10].
Abbreviations
- PA:
-
Physical activity
- MR:
-
Mendelian randomization
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association study
- IVW:
-
Inverse variance weighted
References
Avancini A et al (2019) Physical activity and exercise in lung cancer care: will promises be fulfilled? Oncologist. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0463
Bade BC, Thomas DD, Scott JB, Silvestri GA (2015) Increasing physical activity and exercise in lung cancer: reviewing safety, benefits, and application. J Thorac Oncol 10:861–871. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000536
Boef AGC, Dekkers OM, le Cessie S (2015) Mendelian randomization studies: a review of the approaches used and the quality of reporting. Int J Epidemiol 44:496–511. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv071
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Brenner DR, Yannitsos DH, Farris MS, Johansson M, Friedenreich CM (2016) Leisure-time physical activity and lung cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 95:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.01.021
Brion MJ, Shakhbazov K, Visscher PM (2013) Calculating statistical power in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol 42:1497–1501. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyt179
Burgess S, Thompson SG (2017) Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol 32:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x
Clarke MA, Joshu CE (2017) Early life exposures and adult cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 39:11–27. https://doi.org/10.1093/epirev/mxx004
Dhillon HM et al (2017) Impact of physical activity on fatigue and quality of life in people with advanced lung cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Oncol 28:1889–1897. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx205
Doherty A et al (2017) Large scale population assessment of physical activity using wrist worn accelerometers: the UK Biobank study. PLoS ONE 12:e0169649. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169649
Emaus A, Thune I (2010) Physical activity and lung cancer prevention. Phys Act Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04231-7_5
Hemani G et al (2018) The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34408
Ho V et al (2017) Physical activity and lung cancer risk in men and women. Cancer Causes Control 28:309–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-017-0872-4
Hojman P (2017) Exercise protects from cancer through regulation of immune function and inflammation. Biochem Soc Trans 45:905–911. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160466
Jones LW (2011) Physical activity and lung cancer survivorship. Recent Results Cancer Res 186:255–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04231-7_11
Kazmi N, Haycock P, Tsilidis K, Lynch BM, Truong T, Martin RM, Lewis SJ (2020) Appraising causal relationships of dietary, nutritional and physical-activity exposures with overall and aggressive prostate cancer: two-sample Mendelian-randomization study based on 79148 prostate-cancer cases and 61106 controls. Int J Epidemiol 49:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyz235
Klimentidis YC et al (2018) Genome-wide association study of habitual physical activity in over 377,000 UK Biobank participants identifies multiple variants including CADM2 and APOE. Int J Obes 42:1161–1176. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0120-3
Lawlor DA, Harbord RM, Sterne JAC, Timpson N, Davey Smith G (2008) Mendelian randomization: using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat Med 27:1133–1163. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.3034
Lugo D et al (2019) The effects of physical activity on cancer prevention, treatment and prognosis: a review of the literature. Complement Ther Med 44:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2019.03.013
Moore SC et al (2016) Association of leisure-time physical activity with risk of 26 types of cancer in 1.44 million adults. JAMA Intern Med 176:816–825. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.1548
Papadimitriou N et al (2020) Physical activity and risks of breast and colorectal cancer: a Mendelian randomisation analysis. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14389-8
Physical activity (2018) World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity. Accessed 3 Sept 2020
Rezende LFM et al (2018) Physical activity and cancer: an umbrella review of the literature including 22 major anatomical sites and 770000 cancer cases. Br J Sports Med 52:826–833. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-098391
Schmid D, Ricci C, Behrens G, Leitzmann MF (2016) Does smoking influence the physical activity and lung cancer relation? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol 31:1173–1190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-016-0186-y
Smith GD, Ebrahim S (2004) Mendelian randomization: prospects, potentials, and limitations. Int J Epidemiol 33:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyh132
Wang Y et al (2014) Rare variants of large effect in BRCA2 and CHEK2 affect risk of lung cancer. Nat Genet 46:736–741. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3002
Zhong S, Ma T, Chen L, Chen W, Lv M, Zhang X, Zhao J (2016) Physical activity and risk of lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin J Sport Med 26:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1097/jsm.0000000000000219
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC0905500, 2016YFC0905503), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong (2017B020227001) and the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (201704020072). The funders had no role in the design of the study; the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data; the writing of the manuscript; and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WX, JYS, HQZ and LZ designed the study. WX, JYS analysed the data and interpreted the results with the help of JQL, YXZ and ZHZ. WX and JYS drafted the paper. TZ, SDH, YPY, WFF, HYZ and YH critically revised the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval and consent to participants
Patient consent and ethical approval were waived in our research because they were obtained from the previous original studies.
Code availability statement
The R code for analysis is not publicly available, but is available from corresponding author if required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xian, W., Shen, J., Zhou, H. et al. Mendelian randomization study indicates lack of causal relationship between physical activity and lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 177–181 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03409-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03409-1