Abstract
Purpose
Early death (ED) is the main cause of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) treatment failure, and the ED rate is higher for elderly patients than that for young ones. To date, no studies have been found focusing on ED in elderly patients with APL.
Methods
This study retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 409 consecutive patients with APL (139 patients ≥ 50 years old, 270 patients < 50 years old). All patients received arsenic trioxide alone as induction therapy. The baseline clinical characteristics and ED occurrence and predictors between elderly and young patients with APL were compared and analyzed.
Results
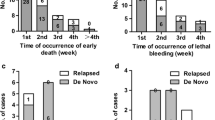
The clinical features of elderly patients at admission were not significantly different from those of young ones. The ED rate of elderly patients was significantly greater than that of young patients (23.74% vs 11.85%, P = 0.0018). Hemorrhage is the main cause of ED in elderly patients, followed by infection and differentiation syndrome. From the 15th to 30th days of treatment, elderly patients had a higher mortality rate than that of young patients (7.83% vs 2.06%, P = 0.009). Male, white blood cell (WBC) count > 10 × 109/L, fibrinogen < 1.0 g/L and low albumin levels were independent risk factors for ED in elderly patients, while ED was only correlated with WBC count, fibrinogen and creatinine levels in young patients.
Conclusion
The results of this study may help design more rational treatment plans for elderly patients with APL based on early mortality risk to reduce the ED rate.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APL:
-
Acute promyelocytic leukemia
- ED:
-
Early death
- ATO:
-
Arsenic trioxide
- FIB:
-
Fibrinogen
- WBC:
-
White blood cell
- PLT:
-
Platelet
- DD:
-
D-dimer
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ALB:
-
Albumin
- Cr:
-
Creatinine
- UA:
-
Uric acid
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- DS:
-
Differentiation syndrome
- DIC:
-
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- ATRA:
-
All-trans retinoic acid
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- ECOG-PS:
-
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
References
Ades L, Chevret S, De Botton S, Thomas X, Dombret H, Beve B et al (2005) Outcome of acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all trans retinoic acid and chemotherapy in elderly patients: the European group experience. Leukemia 19:230–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403597
Chamoun K, Kantarjian HM, Wang X, Naqvi K, Aung F, Garcia-Manero G et al (2019) Unrecognized fluid overload during induction therapy increases morbidity in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer 125:3219–3224. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32196
de la Serna J, Montesinos P, Vellenga E, Rayón C, Parody R, León A et al (2008) Causes and prognostic factors of remission induction failure in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all-trans retinoic acid and idarubicin. Blood 111:3395–3402. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-07-100669
Di Bona E, Avvisati G, Castaman G, Luce Vegna M, De Sanctis V, Rodeghiero F, Mandelli F (2000) Early haemorrhagic morbidity and mortality during remission induction with or without all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 108:689–695. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.01936.x
Ghavamzadeh A, Alimoghaddam K, Rostami S, Ghaffari SH, Jahani M, Iravani M et al (2011) Phase II study of single-agent arsenic trioxide for the front-line therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 29:2753–2757. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.32.2107
Hassan IB, Zaabi MRA, Alam A, Hashim MJ, Tallman MS, Kristensen J (2017) Characteristics features and factors influencing early death in Acute promyelocytic leukemia; Experience from United Arab Emirates (UAE). Int J Hematol 106:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-017-2211-7
Iland HJ, Collins M, Bradstock K, Supple SG, Catalano A, Hertzberg M et al (2015) Use of arsenic trioxide in remission induction and consolidation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukaemia in the Australasian Leukaemia and Lymphoma Group (ALLG) APML4 study: a non-randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol 2:e357–e366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00115-5
Jácomo RH, Melo RA, Souto FR, de Mattos ER, de Oliveira CT, Fagundes EM et al (2007) Clinical features and outcomes of 134 Brazilians with acute promyelocytic leukemia who received ATRA and anthracyclines. Haematologica 92:1431–1432. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.10874
Jeddi R, Ghédira H, Menif S, Ben Neji H, Ben Amor R, Kacem K et al (2010) Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with PETHEMA LPA 99 protocol: a Tunisian single center experience. Hematology 15:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1179/102453309X12583347114176
Jeddi R, Ghédira H, Ben Amor R, Ben Abdennebi Y, Karima K, Mohamed Z et al (2011) Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with AIDA based regimen. Update of a Tunisian Single Center Study. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 3:e2011033. https://doi.org/10.4084/MJHID.2011.033
Kim DY, Lee JH, Lee JH, Kim SD, Lim SN, Choi Y et al (2011) Significance of fibrinogen, D-dimer, and LDH levels in predicting the risk of bleeding in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Leuk Res 35:152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2010.05.022
Lehmann S, Ravn A, Carlsson L, Antunovic P, Deneberg S, Möllgård L et al (2011) Continuing high early death rate in acute promyelocytic leukemia: a population-based report from the Swedish Adult Acute Leukemia Registry. Leukemia 25:1128–1134. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.78
Lou Y, Ma Y, Suo S, Ni W, Wang Y, Pan H et al (2015) Prognostic factors of patients with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with arsenic trioxide-based frontline therapy. Leuk Res 39:938–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2015.05.016
Lou Y, Ma Y, Sun J, Suo S, Tong H, Qian W et al (2017) Effectivity of a modified Sanz risk model for early death prediction in patients with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol 96:1793–1800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3096-5
Mandelli F, Latagliata R, Avvisati G, Fazi P, Rodeghiero F, Leoni F et al (2003) Treatment of elderly patients (> or = 60 years) with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Results of the Italian multicenter group GIMEMA with ATRA and idarubicin (AIDA) protocols. Leukemia 17:1085–1090. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402932
Martínez-Cuadrón D, Montesinos P, Vellenga E, Bernal T, Salamero O, Holowiecka A et al (2018) Long-term outcome of older patients with newly diagnosed de novo acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with ATRA plus anthracycline-based therapy. Leukemia 32:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.178
Park JH, Qiao B, Panageas KS, Schymura MJ, Jurcic JG, Rosenblat TL et al (2011) Early death rate in acute promyelocytic leukemia remains high despite all-trans retinoic acid. Blood 118:1248–1254. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-04-346437
Paulson K, Serebrin A, Lambert P, Bergeron J, Everett J, Kew A et al (2014) Acute promyelocytic leukaemia is characterized by stable incidence and improved survival that is restricted to patients managed in leukaemia referral centres: a pan-Canadian epidemiological study. Br J Haematol 166:660–666. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12931
Rashidi A, Riley M, Goldin TA, Sayedian F, Bayerl MG, Aguilera NS et al (2014) Delay in the administration of all-trans retinoic acid and its effects on early mortality in acute promyelocytic leukemia: final results of a multicentric study in the United States. Leuk Res 38:1036–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2014.06.011
Sanz MA, Martín G, Rayón C, Esteve J, González M, Díaz-Mediavilla J et al (1999) A modified AIDA protocol with anthracycline-based consolidation results in high antileukemic efficacy and reduced toxicity in newly diagnosed PML/RARalpha-positive acute promyelocytic leukemia. PETHEMA group. Blood 94:3015–3021
Sanz MA, Lo Coco F, Martín G, Avvisati G, Rayón C, Barbui T et al (2000) Definition of relapse risk and role of nonanthracycline drugs for consolidation in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia: a joint study of the PETHEMA and GIMEMA cooperative groups. Blood 96:1247–1253
Sanz MA, Vellenga E, Rayón C, Díaz-Mediavilla J, Rivas C, Amutio E et al (2004) All-trans retinoic acid and anthracycline monochemotherapy for the treatment of elderly patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 104:3490–3493. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-04-1642
Sun J, Zhu J, Zhou D, Zhu L, Yang X, Xie M et al (2019) Factors affecting early death and survival of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with ATRA-based therapy regimens. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 19:e63–e70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2018.08.001
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Li J, Li L, Han X, Han L et al (2013) Long-term efficacy and safety of arsenic trioxide for first-line treatment of elderly patients with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer 119:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.27650
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81270589), and Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. H2017032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BJ conceived, designed, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. YZ conceived, designed, and participated in data analysis. JZ analyzed data and is the corresponding author. WH, FC and ML analyzed the data. HY, XT, YW, JH, JF and HL participated in data collection. All authors reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study protocol was discussed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University who waived the need for patient informed consent for this retrospective analysis.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, B., Zhang, Y., Hou, W. et al. Comparative analysis of causes and predictors of early death in elderly and young patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with arsenic trioxide. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 485–492 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-03076-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-03076-x