Abstract
Purpose
The role of estrogen receptor beta (ER-β) expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is largely unknown. Ligand-independent phosphorylation and activation of ER-β may play a relevant role in the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway and, as a result, in tumor progression. Here, we examined the effect of ER-β, phosphorylated ER-β (pER-β), STAT3, phosphorylated STAT3 (pSTAT3) and IL-6 expression on the overall and recurrence-free survival in a cohort of patients with resected PDAC.
Methods
We identified 175 patients who underwent pancreatic resection for PDAC. Tissue microarrays were constructed from the archival tumor specimens. These were stained with specific antibodies for the above molecules. The expression of the markers was then correlated with clinicopathological parameters and survival analysis was performed.
Results
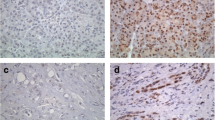
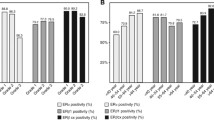
High nuclear expression of ER-β was found in 61.7% and pER-β in 80.6% of the tumors. STAT3 was expressed in 54.3% of the tumor samples, pSTAT3 in 68% and IL-6 in 76.6%. The median overall survival for patients with low pER-β expression was 29 months, whereas for patients with high pER-β expression was 15.1 months (p = 0.016). Multivariate analysis revealed that pER-β expression was an independent factor correlating with shorter overall survival (hazard ratio 1.9; p = 0.013) and disease-free survival (hazard ratio 1.9; p = 0.029).
Conclusions
Expression of pER-β constitutes an independent prognostic marker for PDAC and is correlated with poor prognosis. These data may help in identifying novel drug targets in PDAC and patients who could benefit from additional therapeutic regimens, including selective estrogen receptor modulators.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam N, Rabe B, Suthaus J, Grötzinger J, Rose-John S, Scheller J (2009) Unraveling viral interleukin-6 binding to Gp130 and activation of STAT-signaling pathways independently of the interleukin-6 receptor. J Virol 83(10):5117–5126. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01601-08
Andrén-Sandberg Å, Hoem D, Bäckman PL (1999) Other risk factors for pancreatic cancer: hormonal aspects. Ann Oncol 10(suppl 4):S131–S135. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/10.suppl_4.S131
Atmaca A, Al-Batran SE, Wirtz RM, Werner D, Zirlik S, Wiest G, Eschbach C, Claas S, Hartmann A, Ficker JH, Jäger E, Brueckl WM (2014) The validation of estrogen receptor 1 mRNA expression as a predictor of outcome in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 134(10):2314–2321. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28571
Barillé S, Bataille R, Amiot M (2000) The role of interleukin-6 and interleukin-6/interleukin-6 receptor-Alpha complex in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Eur Cytokine Netw 11(4):546–551
Bellone G, Smirne C, Mauri FA, Tonel E, Carbone A, Buffolino A, Dughera L, Robecchi A, Pirisi M, Emanuelli G (2005) Cytokine expression profile in human pancreatic carcinoma cells and in surgical specimens: implications for survival. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55(6):684–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0047-0
Block KM, Hanke NT, Maine EA, Baker AF (2012) IL-6 stimulates STAT3 and Pim-1 kinase in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas 41(5):773–781. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e31823cdd10
Bryant HU, Glasebrook AL, Yang NN, Sato M (1999) An estrogen receptor basis for raloxifene action in bone. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 69(1–6):37–44
Cheskis BJ, Greger JG, Nagpal S, Freedman LP (2007) Signaling by estrogens. J Cell Physiol 213(3):610–617. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.21253
Coutts AS, Murphy LC (1998) Elevated mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in estrogen-nonresponsive human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 58(18):4071–4074
Denley SM, Jamieson NB, McCall P, Oien KA, Morton JP, Carter CR, Edwards J, McKay CJ (2013) Activation of the IL-6R/Jak/Stat pathway is associated with a poor outcome in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 17(5):887–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2168-7
Dong J, Jiang SW, Niu Y, Chen L, Liu S, Ma T, Chen X, Xu L, Su Z, Chen H (2013) Expression of estrogen receptor α and β in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 30(6):2771–2776. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2013.2770
Ellmann S, Sticht H, Thiel F, Beckmann MW, Strick R, Strissel PL (2009) Estrogen and progesterone receptors: from molecular structures to clinical targets. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(15):2405–2426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0017-3
Falconer JS, Fearon KC, Plester CE, Ross JA, Carter DC (1994) Cytokines, the acute-phase response, and resting energy expenditure in cachectic patients with pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 219(4):325–331
Fang Y-J, Lu Z-H, Wang F, Wu X-J, Li L-R, Zhang L-Y, Pan Z-Z, Wan D-S (2010) Prognostic impact of ERβ and MMP7 expression on overall survival in colon cancer. Tumor Biol 31(6):651–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0082-0
Greene FL (2003) TNM staging for malignancies of the digestive tract: 2003 changes and beyond. Semin Surg Oncol 21(1):23–29. https://doi.org/10.1002/ssu.10018
Greenway B, Iqbal MJ, Johnson PJ, Williams R (1981) Oestrogen receptor proteins in malignant and fetal pancreas. BMJ 283(6294):751–753
Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M et al (2007) Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev 87(3):905–931. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00026.2006
Hirono S, Yamaue H, Hoshikawa Y, Ina S, Tani M, Kawai M, Ushijima M et al (2010) Molecular markers associated with lymph node metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by genome-wide expression profiling. Cancer Sci 101(1):259–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01359.x
Horvath LG, Henshall SM, Lee CS, Head DR, Quinn DI, Makela S, Delprado W et al (2001) Frequent loss of estrogen receptor-beta expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 61(14):5331–5335
Huang C, Yang G, Jiang T, Huang K, Cao J, Qiu Z (2010) Effects of IL-6 and AG490 on regulation of Stat3 signaling pathway and invasion of human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29(1):51. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-29-51
Imamura Y, Mizuno S (2005) Comparison of pancreatic cancer mortality in five countries: France, Italy, Japan, UK and USA from WHO Mortality Database (1960–2000). Jpn J Clin Oncol 35(5):283–286. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyi082
Iwao K, Miyoshi Y, Ooka M, Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H, Kasugai T, Egawa C, Noguchi S (2001) Quantitative analysis of estrogen receptor-α and -β messenger RNA expression in human pancreatic cancers by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Lett 170(1):91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3835(01)00563-8
Jilka RL, Hangoc G, Girasole G, Passeri G, Williams DC, Abrams JS, Boyce B, Broxmeyer H, Manolagas SC (1992) Increased osteoclast development after estrogen loss: mediation by interleukin-6. Science 257(5066):88–91. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1621100
Knösel T, Emde A, Schlüns K, Chen Y, Jürchott K, Krause M, Dietel M, Petersen I (2005) Immunoprofiles of 11 biomarkers using tissue microarrays identify prognostic subgroups in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia 7(8):741–747. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.05178
Knösel T, Emde V, Schlüns K, Schlag PM, Dietel M, Petersen I (2006) Cytokeratin profiles identify diagnostic signatures in colorectal cancer using multiplex analysis of tissue microarrays. Cell Oncol 28(4):167–175
Konduri S, Schwarz RE (2007) Estrogen receptor/ ratio predicts response of pancreatic cancer cells to estrogens and phytoestrogens. J Surg Res 140(1):55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2006.10.015
Lange CA, Gioeli D, Hammes SR, Marker PC (2007) Integration of rapid signaling events with steroid hormone receptor action in breast and prostate cancer. Annu Rev Physiol 69(1):171–199. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.69.031905.160319
Lannigan DA (2003) Estrogen receptor phosphorylation. Steroids 68(1):1–9
Le R, Poulard MC, Cohen P, Sentis S, Renoir J-M, Corbo L (2011) Cracking the estrogen receptor’s posttranslational code in breast tumors. Endocr Rev 32(5):597–622. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2010-0016
Lee AV, Cui X, Oesterreich S (2001) Cross-talk among estrogen receptor, epidermal growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7(12):4429s–4435s
Lesina M, Kurkowski MU, Ludes K, Rose-John S, Treiber M, Klöppel G, Yoshimura A et al (2011) Stat3/Socs3 activation by IL-6 trans signaling promotes progression of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia and development of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell 19(4):456–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.03.009
Lesina M, Wörmann SM, Neuhöfer P, Song L, Algül H (2014) Interleukin-6 in inflammatory and malignant diseases of the pancreas. Semin Immunol 26(1):80–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2014.01.002
Lou W, Ni Z, Dyer K, Tweardy DJ, Gao AC (2000) Interleukin-6 induces prostate cancer cell growth accompanied by activation of Stat3 signaling pathway. Prostate 42(3):239–242
Mæhle BO, Collett K, Tretli S, Akslen LA, Grotmol T (2009) Estrogen receptor—an independent prognostic marker in estrogen receptor α and progesterone receptor-positive breast cancer?. APMIS 117(9):644–650. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0463.2009.02510.x
Millikan KW, Deziel DJ, Silverstein JC, Kanjo TM, Christein JD, Doolas A, Prinz RA (1999) Prognostic factors associated with resectable adenocarcinoma of the head of the pancreas. Am Surg 65(7):618–623 (discussion 623–624)
Nacusi LP, Debes JD (2008) Primers on molecular pathways: nuclear receptors in pancreatic cancer: the ligand-independent way. Pancreatology 8(4–5):422–424. https://doi.org/10.1159/000151479
Nakao A, Fujii T, Sugimoto H, Kanazumi N, Nomoto S, Kodera Y, Inoue S, Takeda S (2006) Oncological problems in pancreatic cancer surgery. World J Gastroenterol 12(28):4466–4472. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4466
Okada S, Okusaka T, Ishii H, Kyogoku A, Yoshimori M, Kajimura N, Yamaguchi K, Kakizoe T (1998) Elevated serum interleukin-6 levels in patients with pancreatic cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 28(1):12–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/28.1.12
Ollayos CW, Riordan GP, Rushin JM (1994) Estrogen receptor detection in paraffin sections of adenocarcinoma of the colon, pancreas, and lung. Arch Pathol Lab Med 118(6):630–632
Remmele W, Stegner HE (1987) Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe 8(3):138–140
Roshani R, McCarthy F, Hagemann T (2014) Inflammatory cytokines in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 345(2):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.07.014
Sareddy GR, Nair BC, Gonugunta VK, Zhang QG, Brenner A, Brann DW, Tekmal RR, Vadlamudi RK (2012) Therapeutic significance of estrogen receptor β agonists in gliomas. Mol Cancer Ther 11(5):1174–1182. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0960
Satake M, Sawai H, Go VLW, Satake K, Reber HA, Hines OJ, Eibl G (2006) Estrogen receptors in pancreatic tumors. Pancreas 33(2):119–127. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mpa.0000226893.09194.ec
Shim WS, Conaway M, Masamura S, Yue W, Wang JP, Kmar R, Santen RJ (2000) Estradiol hypersensitivity and mitogen-activated protein kinase expression in long-term estrogen deprived human breast cancer cells in vivo. Endocrinology 141(1):396–405. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.141.1.7270
Simpkins F, Garcia-Soto A, Slingerland J (2013) New insights on the role of hormonal therapy in ovarian cancer. Steroids 78(6):530–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2013.01.008
Singh S, Baker PR, Poulsom R, Wright NA, Sheppard MC, Langman MJ, Neoptolemos JP (1997) Expression of oestrogen receptor and oestrogen-inducible genes in pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg 84(8):1085–1089
Syed V, Ulinski G, Mok SC, Ho S-M (2002) Reproductive hormone-induced, STAT3-mediated interleukin 6 action in normal and malignant human ovarian surface epithelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 94(8):617–629. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/94.8.617
Taylor OM, Benson EA, McMahon MJ (1993) Clinical trial of tamoxifen in patients with irresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg 80(3):384–386. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.1800800341
Tremblay A, Tremblay GB, Labrie F, Giguère V (1999) Ligand-independent recruitment of SRC-1 to estrogen receptor β through phosphorylation of activation function AF-1. Mol Cell 3(4):513–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80479-7
Yamamoto T, Matsuda T, Junicho A, Kishi H, Saatcioglu F, Muraguchi A (2000) Cross-talk between signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and estrogen receptor signaling. FEBS Lett 486(2):143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02296-1
Yeh T-S, Jan Y-Y, Chiu C-T, Ho Y-B, Chen T-C, Lee K-F, Chan K-M, Hsu J-C, Hwang T-L, Chen M-F (2002) Characterisation of oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, trefoil factor 1, and epidermal growth factor and its receptor in pancreatic cystic neoplasms and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gut 51(5):712–716
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, Sitzmann JV, Hruban RH, Goodman SN, Dooley WC, Coleman J, Pitt HA (1995) Pancreaticoduodenectomy for cancer of the head of the pancreas. 201 patients. Ann Surg 221(6):721–731 (discussion 731–733)
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Sohn TA, Lillemoe KD, Pitt HA, Talamini MA, Hruban RH et al (1997) Six hundred fifty consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies in the 1990s: pathology, complications, and outcomes. Ann Surg 226(3):248–257 (discussion 257–260)
Yu JH, Kim H (2012) Role of Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gut Liver 6(4):417. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl.2012.6.4.417
Zhang J, Dhakal I, Ning B, Kesteloot H (2008) Patterns and trends of pancreatic cancer mortality rates in Arkansas, 1969–2002: a comparison with the US population. Eur J Cancer Prev 17(1):18–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/CEJ.0b013e32809b4ccd
Acknowledgements
We thank Mrs. Andrea Sendelhofert (Institute of Pathology, Ludwig-Maximilians-University, Munich) for her expertise and technical assistance in tissue microarray immunohistochemistry staining and Dipl.-Math. Andrea Stroux (Institute of Biometry und Clinical Epidemiology, Charité—Universitätsmedizin Berlin) for her valuable advice on statistical analysis. This work was conducted in the framework of a PhD programme at Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin and has been published as a part of a full thesis in the library of the Freie Universität Berlin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital of the University of Munich.
Additional information
This work was conducted in the framework of a PhD programme at Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany and has been published as a part of a full thesis in the library of the Freie Universität Berlin (http://www.diss.fu-berlin.de/diss/receive/FUDISS_thesis_000000105618).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pozios, I., Knösel, T., Zhao, Y. et al. Expression of phosphorylated estrogen receptor beta is an independent negative prognostic factor for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 1887–1897 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2717-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2717-2