Abstract
Purpose
Since combination of Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands could boost antitumor immunity, we evaluated the efficacy of dendritic cell (DC) vaccines upon dual activation of TLR9 and TLR7 in breast cancer models.
Methods
DCs were generated from mouse bone marrow or peripheral blood from healthy human donors and stimulated with CpG1826 (mouse TLR9 agonist), CpG2006 or IMT504 (human TLR9 agonists) and R848 (TLR7 agonist). Efficacy of antitumor vaccines was evaluated in BALB/c mice bearing metastatic mammary adenocarcinomas.
Results
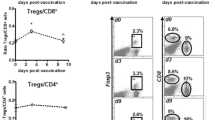
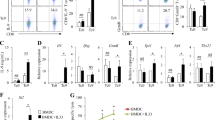
CpG-DCs improved the survival of tumor-bearing mice, reduced the development of lung metastases and generated immunological memory. However, dual activation of TLRs impaired the efficacy of DC vaccines. In vitro, we found that R848 inhibited CpG-mediated maturation of murine DCs. A positive feedback loop in TLR9 mRNA expression was observed upon CpG stimulation that was inhibited in the presence of R848. Impaired activation of NF-κB was detected when TLR9 and TLR7 were simultaneously activated. Blockade of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and indoleamine-pyrrole-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) improved the activation of CpG-DCs. When we evaluated the effect of combined activation of TLR9 and TLR7 in human DCs, we found that R848 induced robust DC activation that was inhibited by TLR9 agonists.
Conclusions
These observations provide insight in the biology of TLR9 and TLR7 crosstalk and suggest caution in the selection of agonists for multiple TLR stimulation. Blockade of NOS and IDO could improve the maturation of antitumor DC vaccines. R848 could prove a useful adjuvant for DC vaccines in human patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Cader MS, Amarasinghe A, Abdul-Careem MF (2016) Activation of toll-like receptor signaling pathways leading to nitric oxide-mediated antiviral responses. Adv Virol 161:2075–2086. doi:10.1007/s00705-016-2904-x
Adler HS et al (2010) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase modulates maturation of human dendritic cells. J Immunol 184:6025–6034. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0901327
Ahn MY et al (2012) Toll-like receptor 7 agonist, imiquimod, inhibits oral squamous carcinoma cells through apoptosis and necrosis. J Oral Pathol Med 41:540–546. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.2012.01158.x
Akazawa T, Shingai M, Sasai M, Ebihara T, Inoue N, Matsumoto M, Seya T (2007) Tumor immunotherapy using bone marrow-derived dendritic cells overexpressing Toll-like receptor adaptors. FEBS Lett 581:3334–3340. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.06.019
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511. doi:10.1038/nri1391
Aktan F (2004) iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci 75:639–653. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2003.10.042
An H et al (2002) Involvement of ERK, p38 and NF-κB signal transduction in regulation of TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 gene expression induced by lipopolysaccharide in mouse dendritic cells. Immunology 106:38–45
Aslakson CJ, Miller FR (1992) Selective events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the sequential dissemination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary tumor. Cancer Res 52:1399–1405
Athie-Morales V, Smits HH, Cantrell DA, Hilkens CM (2004) Sustained IL-12 signaling is required for Th1 development. J Immunol 172:61–69
Baban B et al (2011) Physiologic control of IDO competence in splenic dendritic cells. J Immunol 187:2329–2335. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100276
Bagchi A, Herrup EA, Warren HS, Trigilio J, Shin HS, Valentine C, Hellman J (2007) MyD88-dependent and MyD88-independent pathways in synergy, priming, and tolerance between TLR agonists. J Immunol 178:1164–1171
Bauer S et al (2001) Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9237–9242. doi:10.1073/pnas.161293498
Behboudi S, Chao D, Klenerman P, Austyn J (2000) The effects of DNA containing CpG motif on dendritic cells. Immunology 99:361–366
Berghofer B, Haley G, Frommer T, Bein G, Hackstein H (2007) Natural and synthetic TLR7 ligands inhibit CpG-A- and CpG-C-oligodeoxynucleotide-induced IFN-alpha production. J Immunol 178:4072–4079
Bode C, Zhao G, Steinhagen F, Kinjo T, Klinman DM (2011) CpG DNA as a vaccine adjuvant. Expert Rev Vaccines 10:499–511. doi:10.1586/erv.10.174
Bogdan C (2001) Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat Immunol 2:907–916. doi:10.1038/ni1001-907
Booth JS, Buza JJ, Potter A, Babiuk LA, Mutwiri GK (2010) Co-stimulation with TLR7/8 and TLR9 agonists induce down-regulation of innate immune responses in sheep blood mononuclear and B cells. Dev Comp Immunol 34:572–578. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2009.12.018
Bourquin C et al (2011) Systemic cancer therapy with a small molecule agonist of toll-like receptor 7 can be improved by circumventing TLR tolerance. Can Res 71:5123–5133. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3903
Broad A, Kirby JA, Jones DE, Applied I, Transplantation Research G (2007) Toll-like receptor interactions: tolerance of MyD88-dependent cytokines but enhancement of MyD88-independent interferon-β production. Immunology 120:103–111. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02485.x
Butchi NB, Du M, Peterson KE (2010) Interactions between TLR7 and TLR9 agonists and receptors regulate innate immune responses by astrocytes and microglia. Glia 58:650–664. doi:10.1002/glia.20952
Candolfi M et al (2012) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the tumor microenvironment: immune targets for glioma therapeutics. Neoplasia 14:757–770
Ciorba MA, Bettonville EE, McDonald KG, Metz R, Prendergast GC, Newberry RD, Stenson WF (2010) Induction of IDO-1 by immunostimulatory DNA limits severity of experimental colitis. J Immunol 184:3907–3916. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900291
Couzin-Frankel J (2013) Breakthrough of the year 2013. Cancer Immunother Sci 342:1432–1433. doi:10.1126/science.342.6165.1432
Degli-Esposti MA, Smyth MJ (2005) Close encounters of different kinds: dendritic cells and NK cells take centre stage. Nat Rev Immunol 5:112–124. doi:10.1038/nri1549
Dey M et al (2015) Dendritic cell-based vaccines that utilize myeloid rather than plasmacytoid cells offer a superior survival advantage in malignant glioma. J Immunol 195:367–376. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1401607
Fallarino F, Puccetti P (2006) Toll-like receptor 9-mediated induction of the immunosuppressive pathway of tryptophan catabolism. Eur J Immunol 36:8–11. doi:10.1002/eji.200535667
Finn OJ (2014) Vaccines for cancer prevention: a practical and feasible approach to the cancer epidemic. Cancer Immunol Res 2:708–713. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0110
Flores RR, Diggs KA, Tait LM, Morel PA (2007) IFN-gamma negatively regulates CpG-induced IL-10 in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol 178:211–218
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2011) NF-κB in immunobiology. Cell Res 21:223–244. doi:10.1038/cr.2011.13
Hellman P, Eriksson H (2007) Early activation markers of human peripheral dendritic cells. Hum Immunol 68:324–333. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2007.01.018
Hemmi H et al (2002) Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 3:196–200. doi:10.1038/ni758
Hemmi H, Kaisho T, Takeda K, Akira S (2003) The roles of Toll-like receptor 9, MyD88, and DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit in the effects of two distinct CpG DNAs on dendritic cell subsets. J Immunol 170:3059–3064
Hemont C, Neel A, Heslan M, Braudeau C, Josien R (2013) Human blood mDC subsets exhibit distinct TLR repertoire and responsiveness. J Leukoc Biol 93:599–609. doi:10.1189/jlb.0912452
Hernandez A et al (2007) Inhibition of NF-kappa B during human dendritic cell differentiation generates anergy and regulatory T-cell activity for one but not two human leukocyte antigen DR mismatches. Hum Immunol 68:715–729. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2007.05.010
Hirsch I, Caux C, Hasan U, Bendriss-Vermare N, Olive D (2010) Impaired Toll-like receptor 7 and 9 signaling: from chronic viral infections to cancer. Trends Immunol 31:391–397. doi:10.1016/j.it.2010.07.004
Hoene V, Peiser M, Wanner R (2006) Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells express TLR9 and react directly to the CpG-A oligonucleotide D19. J Leukoc Biol 80:1328–1336. doi:10.1189/jlb.0106011
Hoesel B, Schmid JA (2013) The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 12:86. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-86
Hontelez S, Ansems M, Karthaus N, Zuidscherwoude M, Looman MW, Triantis V, Adema GJ (2012) Dendritic cell-specific transcript: dendritic cell marker and regulator of TLR-induced cytokine production. J Immunol 189:138–145. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1103709
Hornung V et al (2002) Quantitative expression of toll-like receptor 1-10 mRNA in cellular subsets of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and sensitivity to CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. J Immunol 168:4531–4537
Hou DY et al (2007) Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells by stereoisomers of 1-methyl-tryptophan correlates with antitumor responses. Cancer Res 67:792–801. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2925
Huang B, Zhao J, Unkeless JC, Feng ZH, Xiong H (2008) TLR signaling by tumor and immune cells: a double-edged sword. Oncogene 27:218–224. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210904
Itakura E, Huang RR, Wen DR, Paul E, Wunsch PH, Cochran AJ (2011) IL-10 expression by primary tumor cells correlates with melanoma progression from radial to vertical growth phase and development of metastatic competence. Mod Pathol 24:801–809. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.5
Ito T et al (2002) Interferon-alpha and interleukin-12 are induced differentially by Toll-like receptor 7 ligands in human blood dendritic cell subsets. J Exp Med 195:1507–1512
Ito H, Ando T, Arioka Y, Saito K, Seishima M (2015) Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity enhances the anti-tumour effects of a Toll-like receptor 7 agonist in an established cancer model. Immunology 144:621–630. doi:10.1111/imm.12413
Jarrossay D, Napolitani G, Colonna M, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A (2001) Specialization and complementarity in microbial molecule recognition by human myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol 31:3388–3393. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200111)31:11<3388:AID-IMMU3388>3.0.CO;2-Q
Kaczanowska S, Joseph AM, Davila E (2013) TLR agonists: our best frenemy in cancer immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol 93:847–863. doi:10.1189/jlb.1012501
Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Signaling to NF-κB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med 13:460–469. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2007.09.002
Klinman DM (2004) Immunotherapeutic uses of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Nat Rev Immunol 4:249–258. doi:10.1038/nri1329
Krieg AM (2008) Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) agonists in the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 27:161–167. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210911
Krug A et al (2003) CpG-A oligonucleotides induce a monocyte-derived dendritic cell-like phenotype that preferentially activates CD8 T cells. J Immunol 170:3468–3477
Lang TJ, Nguyen P, Peach R, Gause WC, Via CS (2002) In vivo CD86 blockade inhibits CD4+ T cell activation, whereas CD80 blockade potentiates CD8+ T cell activation and CTL effector function. J Immunol 168:3786–3792
Larange A, Antonios D, Pallardy M, Kerdine-Romer S (2009) TLR7 and TLR8 agonists trigger different signaling pathways for human dendritic cell maturation. J Leukoc Biol 85:673–683. doi:10.1189/jlb.0808504
Ligtenberg MA, Rojas-Colonelli N, Kiessling R, Lladser A (2013) NF-κB activation during intradermal DNA vaccination is essential for eliciting tumor protective antigen-specific CTL responses. Hum Vaccin Immunother 9:2189–2195. doi:10.4161/hv.25699
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lombardi V, Van Overtvelt L, Horiot S, Moingeon P (2009) Human dendritic cells stimulated via TLR7 and/or TLR8 induce the sequential production of Il-10, IFN-gamma, and IL-17A by naive CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 182:3372–3379. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0801969
Mac Keon S, Ruiz MS, Gazzaniga S, Wainstok R (2015) Dendritic cell-based vaccination in cancer: therapeutic implications emerging from murine models. Front Immunol 6:243. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00243
Markov OV, Mironova NL, Sennikov SV, Vlassov VV, Zenkova MA (2015) Prophylactic dendritic cell-based vaccines efficiently inhibit metastases in murine metastatic melanoma. PLoS One 10:e0136911. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0136911
Marshall JD, Heeke DS, Gesner ML, Livingston B, Van Nest G (2007) Negative regulation of TLR9-mediated IFN-α induction by a small-molecule, synthetic TLR7 ligand. J Leukoc Biol 82:497–508. doi:10.1189/jlb.0906575
Meixlsperger S et al (2013) CD141+ dendritic cells produce prominent amounts of IFN-alpha after dsRNA recognition and can be targeted via DEC-205 in humanized mice. Blood 121:5034–5044. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-12-473413
Mellor AL, Baban B, Chandler PR, Manlapat A, Kahler DJ, Munn DH (2005) Cutting edge: CpG oligonucleotides induce splenic CD19+ dendritic cells to acquire potent indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-dependent T cell regulatory functions via IFN Type 1 signaling. J Immunol 175:5601–5605
Mitchell D, Yong M, Schroder W, Black M, Tirrell M, Olive C (2010) Dual stimulation of MyD88-dependent Toll-like receptors induces synergistically enhanced production of inflammatory cytokines in murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. J Infect Dis 202:318–329. doi:10.1086/653499
Mogensen TH (2009) Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:240–273. doi:10.1128/CMR.00046-08 (Table of Contents)
Montoya CJ et al (2006) Activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells with TLR9 agonists initiates invariant NKT cell-mediated cross-talk with myeloid dendritic cells. J Immunol 177:1028–1039
Napolitani G, Rinaldi A, Bertoni F, Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A (2005) Selected Toll-like receptor agonist combinations synergistically trigger a T helper type 1-polarizing program in dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 6:769–776. doi:10.1038/ni1223
Narayanan P, Lapteva N, Seethammagari M, Levitt JM, Slawin KM, Spencer DM (2011) A composite MyD88/CD40 switch synergistically activates mouse and human dendritic cells for enhanced antitumor efficacy. J Clin Invest 121:1524–1534. doi:10.1172/JCI44327
Obregon C, Graf L, Chung KF, Cesson V, Nicod LP (2015) Nitric oxide sustains IL-1β expression in human dendritic cells enhancing their capacity to induce IL-17-producing T-cells. PLoS One 10:e0120134. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120134
Palucka K, Banchereau J (2012) Cancer immunotherapy via dendritic cells. Nat Rev Cancer 12:265–277. doi:10.1038/nrc3258
Pan J et al (2004) Interferon-gamma is an autocrine mediator for dendritic cell maturation. Immunol Lett 94:141–151. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2004.05.003
Paolucci C et al (2003) Synergism of nitric oxide and maturation signals on human dendritic cells occurs through a cyclic GMP-dependent pathway. J Leukoc Biol 73:253–262
Paone A et al (2008) Toll-like receptor 3 triggers apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells through a PKC-α-dependent mechanism. Carcinogenesis 29:1334–1342. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn149
Park MJ et al (2012) A distinct tolerogenic subset of splenic IDO+ CD11b+ dendritic cells from orally tolerized mice is responsible for induction of systemic immune tolerance and suppression of collagen-induced arthritis. Cell Immunol 278:45–54. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.06.009
Platt CD et al (2010) Mature dendritic cells use endocytic receptors to capture and present antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:4287–4292. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910609107
Platten M, von Knebel Doeberitz N, Oezen I, Wick W, Ochs K (2014) Cancer immunotherapy by targeting IDO1/TDO and their downstream effectors. Front Immunol 5:673. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00673
Puccetti P, Grohmann U (2007) IDO and regulatory T cells: a role for reverse signalling and non-canonical NF-κB activation. Nat Rev Immunol 7:817–823
Pufnock JS, Cigal M, Rolczynski LS, Andersen-Nissen E, Wolfl M, McElrath MJ, Greenberg PD (2011) Priming CD8+ T cells with dendritic cells matured using TLR4 and TLR7/8 ligands together enhances generation of CD8+ T cells retaining CD28. Blood 117:6542–6551. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-11-317966
Pulendran B, Ahmed R (2006) Translating innate immunity into immunological memory: implications for vaccine development. Cell 124:849–863. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.019
Ramirez D, Saba J, Carniglia L, Durand D, Lasaga M, Caruso C (2015) Melanocortin 4 receptor activates ERK-cFos pathway to increase brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in rat astrocytes and hypothalamus. Mol Cell Endocrinol 411:28–37. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2015.04.008
Ridnour LA et al (2013) Molecular pathways: toll-like receptors in the tumor microenvironment–poor prognosis or new therapeutic opportunity. Clin Cancer Res 19:1340–1346. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0408
Rodriguez JM et al (2015) PyNTTTTGT and CpG immunostimulatory oligonucleotides: effect on granulocyte/monocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) secretion by human CD56+ (NK and NKT) cells. PLoS One 10:e0117484. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0117484
Rosenberger K, Derkow K, Dembny P, Kruger C, Schott E, Lehnardt S (2014) The impact of single and pairwise Toll-like receptor activation on neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflamm 11:166. doi:10.1186/s12974-014-0166-7
Sabado RL, Bhardwaj N (2015) Cancer immunotherapy: dendritic-cell vaccines on the move. Nature 519:300–301. doi:10.1038/nature14211
Saikh KU, Kissner TL, Sultana A, Ruthel G, Ulrich RG (2004) Human monocytes infected with Yersinia pestis express cell surface TLR9 and differentiate into dendritic cells. J Immunol 173:7426–7434
Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A (1994) Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 179:1109–1118
Samarasinghe R, Tailor P, Tamura T, Kaisho T, Akira S, Ozato K (2006) Induction of an anti-inflammatory cytokine, IL-10, in dendritic cells after toll-like receptor signaling. J Interferon Cytokine Res Off J Int Soc Interferon Cytokine Res 26:893–900. doi:10.1089/jir.2006.26.893
Saraiva M, O’Garra A (2010) The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 10:170–181. doi:10.1038/nri2711
Scheiermann J, Klinman DM (2014) Clinical evaluation of CpG oligonucleotides as adjuvants for vaccines targeting infectious diseases and cancer. Vaccine 32:6377–6389. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.06.065
Schon MP, Schon M (2008) TLR7 and TLR8 as targets in cancer therapy. Oncogene 27:190–199. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210913
Semnani RT, Venugopal PG, Leifer CA, Mostbock S, Sabzevari H, Nutman TB (2008) Inhibition of TLR3 and TLR4 function and expression in human dendritic cells by helminth parasites. Blood 112:1290–1298. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-04-149856
Shirota H, Tross D, Klinman DM (2015) CpG oligonucleotides as cancer vaccine adjuvants. Vaccines 3:390–407. doi:10.3390/vaccines3020390
Sioud M, Saeboe-Larssen S, Hetland TE, Kaern J, Mobergslien A, Kvalheim G (2013) Silencing of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase enhances dendritic cell immunogenicity and antitumour immunity in cancer patients. Int J Oncol 43:280–288. doi:10.3892/ijo.2013.1922
Smits EL, Ponsaerts P, Berneman ZN, Van Tendeloo VF (2008) The use of TLR7 and TLR8 ligands for the enhancement of cancer immunotherapy. Oncologist 13:859–875. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0097
Stier S, Maletzki C, Klier U, Linnebacher M (2013) Combinations of TLR ligands: a promising approach in cancer immunotherapy. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:271246. doi:10.1155/2013/271246
Strober W (2001) Trypan blue exclusion test of cell viability. Curr Protoc Immunol. doi:10.1002/0471142735.ima03bs21 (Appendix 3: Appendix 3B )
Swiecki M, Colonna M (2015) The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat Rev Immunol 15:471–485. doi:10.1038/nri3865
Tas SW et al (2007) Noncanonical NF-κB signaling in dendritic cells is required for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) induction and immune regulation. Blood 110:1540–1549. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-11-056010
Torres S, Hernandez JC, Giraldo D, Arboleda M, Rojas M, Smit JM, Urcuqui-Inchima S (2013) Differential expression of Toll-like receptors in dendritic cells of patients with dengue during early and late acute phases of the disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7:e2060. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002060
Trinchieri G, Sher A (2007) Cooperation of Toll-like receptor signals in innate immune defence. Nat Rev Immunol 7:179–190. doi:10.1038/nri2038
Upchurch KC, Boquin JR, Yin W, Xue Y, Joo H, Kane RR, Oh S (2015) New TLR7 agonists with improved humoral and cellular immune responses. Immunol Lett 168:89–97. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2015.09.007
Urtreger A, Ladeda V, Puricelli L, Rivelli A, Vidal M, Delustig E, Joffe E (1997) Modulation of fibronectin expression and proteolytic activity associated with the invasive and metastatic phenotype in two new murine mammary tumor cell lines. Int J Oncol 11:489–496
Utaisincharoen P, Anuntagool N, Chaisuriya P, Pichyangkul S, Sirisinha S (2002) CpG ODN activates NO and iNOS production in mouse macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7). Clin Exp Immunol 128:467–473
Vasilakos JP, Tomai MA (2013) The use of Toll-like receptor 7/8 agonists as vaccine adjuvants. Expert Rev Vaccines 12:809–819. doi:10.1586/14760584.2013.811208
Verinaud L et al (2015) Nitric oxide plays a key role in the suppressive activity of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Cell Mol Immunol 12:384–386. doi:10.1038/cmi.2014.94
Vremec D, O’Keeffe M, Hochrein H, Fuchsberger M, Caminschi I, Lahoud M, Shortman K (2007) Production of interferons by dendritic cells, plasmacytoid cells, natural killer cells, and interferon-producing killer dendritic cells. Blood 109:1165–1173. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-05-015354
Wang R, Lu M, Zhang J, Chen S, Luo X, Qin Y, Chen H (2011) Increased IL-10 mRNA expression in tumor-associated macrophage correlated with late stage of lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:62. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-30-62
Wang HL, Xu H, Lu WH, Zhu L, Yu YH, Hong FZ (2014) In vitro and in vivo evaluations of human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16)-derived peptide-loaded dendritic cells (DCs) with a CpG oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG-ODN) adjuvant as tumor vaccines for immunotherapy of cervical cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet 289:155–162. doi:10.1007/s00404-013-2938-1
Wingender G et al (2006) Systemic application of CpG-rich DNA suppresses adaptive T cell immunity via induction of IDO. Eur J Immunol 36:12–20. doi:10.1002/eji.200535602
Xiong H et al (2004) Inhibition of interleukin-12 p40 transcription and NF-κB activation by nitric oxide in murine macrophages and dendritic cells. J Biol Chem 279:10776–10783. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313416200
Xiong W et al (2010) Human Flt3L generates dendritic cells from canine peripheral blood precursors: implications for a dog glioma clinical trial. PLoS One 5:e11074. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011074
Yang J, Yang Y, Fan H, Zou H (2014) Tolerogenic splenic Ido+ dendritic cells from the mice treated with induced-Treg cells suppress collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol Res 2014:831054. doi:10.1155/2014/831054
Zent CS et al (2012) Phase I clinical trial of CpG oligonucleotide 7909 (PF-03512676) in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 53:211–217. doi:10.3109/10428194.2011.608451
Zhao BG, Vasilakos JP, Tross D, Smirnov D, Klinman DM (2014) Combination therapy targeting toll like receptors 7, 8 and 9 eliminates large established tumors. J Immunother Cancer 2:12. doi:10.1186/2051-1426-2-12
Zheng X et al (2013) Silencing IDO in dendritic cells: a novel approach to enhance cancer immunotherapy in a murine breast cancer model. Int J Cancer 132:967–977. doi:10.1002/ijc.27710
Zhu Q et al (2008) Toll-like receptor ligands synergize through distinct dendritic cell pathways to induce T cell responses: implications for vaccines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:16260–16265. doi:10.1073/pnas.0805325105
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Tecnológicas (CONICET PIP 114-201101-00353 to M.C.; PIP 11220120100261 to A.S.); Doctoral Fellowship to M.A.M.A. and M.F.G.); Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT-2012-0830; PICT-2013-0310, PICT-2015-3309 to M.C.; PICT 2014-0334 to A.S.); Fundación Bunge y Born (“Jorge Oster” fellowship to M.A.M.A) and Liga Argentina de Lucha contra el Cáncer (LALCEC, “Jorgelina Ortiz De Rozas De Alvarez” fellowship to M.A.M.A.). We wish to thank Dr Alejandro Montaner (Instituto Milsten, CONICET, Argentina) who kindly provided human TLR9 agonists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Tecnológicas (CONICET PIP 114-201101-00353 to M.C.; PIP 11220120100261 to A.S.); Doctoral Fellowship to M.A.M.A. and M.F.G.); Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT-2012-0830; PICT-2013-0310, PICT-2015-3309 to M.C.; PICT 2014-0334 to A.S.); Fundación Bunge y Born (“Jorge Oster” fellowship to M.A.M.A) and Liga Argentina de Lucha contra el Cáncer (LALCEC, “Jorgelina Ortiz De Rozas De Alvarez” fellowship to M.A.M.A.).
Conflict of interest
Author Mariela A. Moreno Ayala declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author María Florencia Gottardo declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author María Soledad Gori declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Alejandro Nicola declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Carla Caruso declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Andrea De Laurentiis declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Mercedes Imsen declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Slobodanka Klein declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Elisa Bal de Kier Joffé declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Gabriela Salamone declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Maria G. Castro declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Adriana Seilicovich declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Marianela Candolfi declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal work was conducted according to the NIH guidelines and was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Buenos Aires (CD Res. Nº120/2011). The generation of human DCs has been approved by the Ethical Committee of the Academia Nacional de Medicina (Buenos Aires, Argentina, CEIANM 76/2015). All blood donors provided written informed consent for the collection of samples and subsequent analysis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreno Ayala, M.A., Gottardo, M.F., Gori, M.S. et al. Dual activation of Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 impairs the efficacy of antitumor vaccines in murine models of metastatic breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 1713–1732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2421-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2421-7