Abstract
Purpose
The homeobox B8 (HOXB8) functions as a sequence-specific transcription factor that is involved in development. Increased expression of this gene is associated with a wide variety of tumor; however, its function in gastric cancer has not been clarified. In the present study, the expression of HOXB8 in gastric cancer tissues and influence of HOXB8 on gastric cancer cellular were evaluated.
Methods
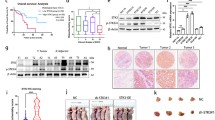
The expression levels of HOXB8 mRNA in human gastric cancer tissues were analyzed through quantitative RT-PCR. To test the role of HOXB8 in gastric cancer metastasis, the cell transwell assay was performed. Microarray, ChIP-qPCR, and Western blot were used to explore the possible mechanism that HOXB8 promotes gastric cancer cells metastasis.
Results
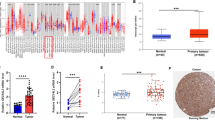
In this study, we found that HOXB8 showed higher expression in metastatic tissues than no-metastatic tissues. Overexpression of HOXB8 can promote gastric cancer cells migration and invasion, while silencing HOXB8 leads to the opposite results. Overexpression of HOXB8 also increases the rate of metastasis in NCI-N87 mice, while silencing HOXB8 has the opposite results. Furthermore, HOXB8 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transformation of AGS cells. We also found that ZEB2 can interact with HOXB8 and may be a downstream factor of HOXB8 by using microarray. Knockdown of ZEB2 can inhibit HOXB8-induced migration and invasion capacity, as well as the epithelial–mesenchymal transformation in gastric cancer cells.
Conclusions
The results showed that HOXB8 plays an important role in the development and metastasis of gastric carcinoma.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang YS et al (2011) Wdr5 mediates self-renewal and reprogramming via the embryonic stem cell core transcriptional network. Cell 145:183–197
Bhattacharjee A, Ghangal R, Garg R, Jain M (2015) Genome-wide analysis of homeobox gene family in legumes: identification, gene duplication and expression profiling. PLoS ONE 10:e0119198
Chen SK, Kurdyukov S, Kereszt A, Wang XD, Gresshoff PM, Rose RJ (2009) The association of homeobox gene expression with stem cell formation and morphogenesis in cultured Medicago truncatula. Planta 230:827–840
Chen WM et al. (2016a) Expression of Helios in gastric tumor cells predicts better survival in gastric cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142(11):2375–2382
Chen Y et al (2016) SOX2 inhibits metastasis in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142:1221–1230
Fu J et al (2010) Ubiquitin ligase cullin 7 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human choriocarcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 285:10870–10879
Fujino T, Yamazaki Y, Largaespada DA, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Hirokawa K, Nakamura T (2001) Inhibition of myeloid differentiation by Hoxa9, Hoxb8, and Meis homeobox genes. Exp Hematol 29:856–863
Grigore AD, Jolly MK, Jia D, Farach-Carson MC, Levine H (2016) Tumor Budding: The Name is EMT. Partial EMT. J Clin Med. doi:10.3390/jcm5050051
Haria D, Naora H (2013) Homeobox gene deregulation: impact on the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Hallm 1:67–76
Hsu SH et al (2013) Proinflammatory homeobox gene, ISX, regulates tumor growth and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 73:508–518
Liang L, Sun H, Zhang W, Zhang M, Yang X, Kuang R, Zheng H (2016) Meta-analysis of EMT datasets reveals different types of EMT. PLoS ONE 11:e0156839
Liu H, Zhang X, Li J, Sun B, Qian H, Yin Z (2015a) The biological and clinical importance of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in circulating tumor cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141:189–201
Liu YJ, Zhu Y, Yuan HX, Zhang JP, Guo JM, Lin ZM (2015b) Overexpression of HOXC11 homeobox gene in clear cell renal cell carcinoma induces cellular proliferation and is associated with poor prognosis. Tumour Biol 36:2821–2829
Nantajit D, Lin D, Li JJ (2015) The network of epithelial–mesenchymal transition: potential new targets for tumor resistance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141:1697–1713
Salmanidis M et al (2013) Hoxb8 regulates expression of microRNAs to control cell death and differentiation. Cell Death Differ 20:1370–1380
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2013) Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 63:11–30
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65:5–29
Stavnes HT et al (2013) HOXB8 expression in ovarian serous carcinoma effusions is associated with shorter survival. Gynecol Oncol 129:358–363
Techasen A, Namwat N, Loilome W, Duangkumpha K, Puapairoj A, Saya H, Yongvanit P (2014) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates epithelial mesenchymal transition mediators ZEB2 and S100A4 to promote cholangiocarcinoma progression. J Hepato-biliary Pancreat Sci 21:703–711
Wang Y et al (2014) CUL4A induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer metastasis by regulating ZEB1 expression. Cancer Res 74:520–531
Yang YC et al (2009) A tumorigenic homeobox (HOX) gene expressing human gastric cell line derived from putative gastric stem cell. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:1016–1023
Zhang H et al (2013) KLF8 involves in TGF-beta-induced EMT and promotes invasion and migration in gastric cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139:1033–1042
Authors’ contributions
WJD extracted mRNA, performed qRT-PCR and WB analyses, and drafted the manuscript. CYQ assisted with data interpretation, designed the project, secured the funding, and drafted the manuscript. MZ and MMC provided patient samples and clinicopathological data. WJD assisted with data interpretation and revised the manuscript. CYQ provided patient samples and clinicopathological data, assisted with data interpretation, and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional and/or National Research Committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81400610); The Project-sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM (No. 20144802); Program of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning for Youth (No. 20134Y043).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Wen-Jin Ding and Min Zhou have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, WJ., Zhou, M., Chen, MM. et al. HOXB8 promotes tumor metastasis and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition via ZEB2 targets in gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 385–397 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2283-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2283-4