Abstract
Background
The Karyopherin proteins are involved in the shuttling of cargo proteins, and certain RNAs, across the nuclear pore complex into and out of the cell nucleus. Karyopherin β1 (Kpnβ1) is a member of the Karyopherin β superfamily of nuclear transport proteins. In addition to the nuclear import function, Kpnβ1 is associated with the occurrence of tumors. This study investigated the expression and biologic function of Kpnβ1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Methods
The prognostic value of Kpnβ1 expression was evaluated using immunohistochemical staining. The role of Kpnβ1 on cell proliferation- and cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) was also determined.
Results
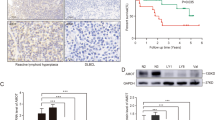
We demonstrated that Kpnβ1 mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly higher in DLBCL B-cells and DLBCL cell lines than in normal CD19 purified B-cells. Immunohistochemical analysis suggested that the expression of Kpnβ1 was correlated with Ki-67 (P < 0.001). Kaplan–Meier curve showed that high expression of Kpnβ1 was significantly associated with shorter overall survival. In addition, Kpnβ1 was associated with the proliferation of DLBCL cells. Importantly, we found that Kpnβ1 could interact with p65 and promote CAM-DR via accelerating NF-κB activation in DLBCL.
Conclusions
Patients with tumors highly expressing Kpnβ1 have poorer overall survivals. Kpnβ1 interacts with p65 and enhances CAM-DR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus L, van der Watt PJ, Leaner VD (2014) Inhibition of the nuclear transporter, Kpnβ1, results in prolonged mitotic arrest and activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in cervical cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 35:1121–1131
Bai H, Wei J, Deng C, Yang X, Wang C, Xu R (2013) MicroRNA-21 regulates the sensitivity of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells to the CHOP chemotherapy regimen. Int J Hematol 97:223–231
Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ, Malim MH, Ballard DW (1997) Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-κB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10057–10062
de Graaf AO, de Witte T, Jansen JH (2004) Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: new therapeutic targets in hematological cancer? Leukemia 18:1751–1759
de Graaf AO, van Krieken JH, Tonnissen E, Wissink W, van de Locht L, Overes I, Dolstra H, de Witte T, van der Reijden BA, Jansen JH (2005) Expression of C-IAP1, C-IAP2 and SURVIVIN discriminates different types of lymphoid malignancies. Br J Haematol 130:852–859
Gugasyan R, Grumont R, Grossmann M, Nakamura Y, Pohl T, Nesic D, Gerondakis S (2000) Rel/NF-κB transcription factors: key mediators of B-cell activation. Immunol Rev 176:134–140
Hang Q, Fei M, Hou S, Ni Q, Lu C, Zhang G, Gong P, Guan C, Huang X, He S (2012) Expression of Spy1 protein in human non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas is correlated with phosphorylation of p27 Kip1 on Thr187 and cell proliferation. Med Oncol 29:3504–3514
Harel A, Forbes DJ (2004) Importin beta: conducting a much larger cellular symphony. Mol Cell 16:319–330
Landowski TH, Olashaw NE, Agrawal D, Dalton WS (2003) Cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) is associated with activation of NF-κB (RelB/p50) in myeloma cells. Oncogene 22:2417–2421
Liang P, Zhang H, Wang G, Li S, Cong S, Luo Y, Zhang B (2013) KPNB1, XPO7 and IPO8 mediate the translocation ofNF-κB/p65 into the nucleus. Traffic 14:1132–1143
Liston P, Fong WG, Korneluk RG (2003) The inhibitors of apoptosis: there is more to life than Bcl2. Oncogene 22:8568–8580
Lwin T, Hazlehurst LA, Li Z, Dessureault S, Sotomayor E, Moscinski LC, Dalton WS, Tao J (2007) Bone marrow stromal cells prevent apoptosis of lymphoma cells by upregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins associated with activation of NF-κB (RelB/p52) in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells. Leukemia 21:1521–1531
Martens-de Kemp SR, Nagel R, Stigter-van Walsum M, van der Meulen IH, van Beusechem VW, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH (2013) Functional genetic screens identify genes essential for tumor cell survival in head and neck and lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:1994–2003
Mosammaparast N, Pemberton LF (2004) Karyopherins: from nuclear-transport mediators to nuclear-function regulators. Trends Cell Biol 14:547–556
Mraz M, Zent CS, Church AK, Jelinek DF, Wu X, Pospisilova S, Ansell SM, Novak AJ, Kay NE, Witzig TE, Nowakowski GS (2011) Bone marrow stromal cells protect lymphoma B-cells from rituximab-induced apoptosis and targeting integrin α-4-β-1 (VLA-4) with natalizumab can overcome this resistance. Br J Haematol 155:53–64
Munzert G, Kirchner D, Stobbe H, Bergmann L, Schmid RM, Dohner H, Heimpel H (2002) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 gene overexpression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: analysis of NF-κ B/Rel-regulated inhibitors of apoptosis. Blood 100:3749–3756
Odqvist L, Montes-Moreno S, Sanchez-Pacheco RE, Young KH, Martin-Sanchez E, Cereceda L, Sanchez-Verde L, Pajares R, Mollejo M, Fresno MF, Mazorra F, Ruiz-Marcellan C, Sanchez-Beato M, Piris MA (2014) NFκB expression is a feature of both activated B-cell-like and germinal center B-cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol 27:1331–1337
Ok CY, Xu-Monette ZY, Tzankov A, O’Malley DP, Montes-Moreno S, Visco C, Moller MB, Dybkaer K, Orazi A, Zu Y, Bhagat G, Richards KL, Hsi ED, Han van Krieken J, Ponzoni M, Farnen JP, Piris MA, Winter JN, Medeiros LJ, Young KH (2014) Prevalence and clinical implications of cyclin D1 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) treated with immunochemotherapy: a report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program. Cancer 120:1818–1829
Schaller T, Pollpeter D, Apolonia L, Goujon C, Malim MH (2014) Nuclear import of SAMHD1 is mediated by a classical karyopherin alpha/beta1 dependent pathway and confers sensitivity to VpxMAC induced ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Retrovirology 11:29
Schreck R, Albermann K, Baeuerle PA (1992) Nuclear factor κB: an oxidative stress-responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic Res Commun 17:221–237
Shaffer AL 3rd, Young RM, Staudt LM (2012) Pathogenesis of human B cell lymphomas. Annu Rev Immunol 30:565–610
Shen Y, Yao Y, Li JM, Chen QS, You JH, Zhao HJ, Chen S, Shen ZX (2008) Prognostic factors analysis for R-CHOP regimen therapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 29:252–257
Tao T, Cheng C, Ji Y, Xu G, Zhang J, Zhang L, Shen A (2012) Numbl inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by suppressing TRAF5-mediated NF-κB activation. Mol Biol Cell 23:2635–2644
van der Watt PJ, Maske CP, Hendricks DT, Parker MI, Denny L, Govender D, Birrer MJ, Leaner VD (2009) The Karyopherin proteins, Crm1 and Karyopherin β1, are overexpressed in cervical cancer and are critical for cancer cell survival and proliferation. Int J Cancer 124:1829–1840
van der Watt PJ, Stowell CL, Leaner VD (2013) The nuclear import receptor Kpnβ1 and its potential as an anticancer therapeutic target. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 23:1–10
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS Jr (1998) NF-κB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281:1680–1683
Wang Y, Huang Y, Xu X, Tang J, Huang X, Zhu J, Liu J, Miao X, Wu Y, Yang F, Ji L, He S (2014) Expression of small glutamine-rich TPR-containing protein A (SGTA) in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas promotes tumor proliferation and reverses cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR). Leuk Res 38:955–963
Yang L, Hu B, Zhang Y, Qiang S, Cai J, Huang W, Gong C, Zhang T, Zhang S, Xu P, Wu X, Liu J (2015) Suppression of the nuclear transporter-KPNβ1 expression inhibits tumor proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol 32:128
Zhao Q, Fu WJ, Zhang CY, Du J, Xi H, Hou J (2013) The clinical characteristics and prognostic analysis of 147 cases of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 34:737–740
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81201858, 81372537) and Natural Scientific Foundation of Jiangsu Province Grant (No. BK2012231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Additional information
Song He and Xiaobing Miao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Miao, X., Wu, Y. et al. Upregulation of nuclear transporter, Kpnβ1, contributes to accelerated cell proliferation- and cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 561–572 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2057-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2057-4