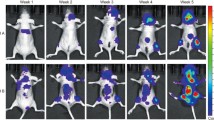
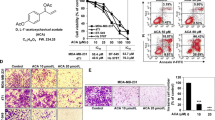
Abstract
Purpose
In previous studies, we demonstrated that green tea (Camellia sinensis, CS) water extract had potent anti-tumor and anti-metastasis effects in the 4T1 mouse breast cancer xenograft model, and the metronomic regimen (0.0125 mg/kg twice a week for 4 weeks) of zoledronic acid (ZOL) was also effective in decreasing tumor burden and metastasis when compared with the conventional regimen. This study aimed to investigate the combined use of CS water extract and metronomic ZOL against tumor metastasis and bone destruction in MDA-MB-231-TXSA human breast cancer.
Methods
Female nude mice were injected with MDA-MB-231-TXSA cells into the marrow space of tibia and were treated with CS water extract and/or metronomic ZOL for 4 weeks. Tumor growth and metastasis to lungs and livers were assessed by in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Abilities of migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231-TXSA cells were also evaluated in vitro.
Results
Our results demonstrated that combination of CS and ZOL had the most potent effects on tumor burden and metastasis to bone, lung and liver, while treatment with CS or ZOL alone significantly protected the bone from cancer-induced osteolysis. In vitro, the combined use of CS + ZOL significantly inhibited MDA-MB-231-TXSA cell migration and invasion. Mechanistic zymography studies showed that the enzyme activities of MMP-9 and MMP-2 were significantly suppressed by CS and CS + ZOL.
Conclusions
The combination of CS plus metronomic ZOL demonstrated potent anti-tumor, anti-metastasis and anti-osteolysis effects against breast cancer, suggesting the potential clinical application against breast cancer patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettuzzi S, Brausi M, Rizzi F, Castagnetti G, Peracchia G, Corti A (2006) Chemoprevention of human prostate cancer by oral administration of green tea catechins in volunteers with high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia: a preliminary report from a one-year proof-of principle study. Cancer Res 66:1234–1240
Chacko SM, Thambi PT, Kuttan R, Nishigaki I (2010) Beneficial effects of green tea: a literature review. Chin Med 5:13
Daubine F, Le Gall C, Gasser J, Green J, Clezardin P (2007) Antitumor effects of clinical dosing regimens of bisphosphonates in experimental breast cancer bone metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst 994:322–330
Eliza WL, Fai CK, Chung LP (2012) Efficacy of Yun Zhi (Coriolus versicolor) on survival in cancer patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 6(1):78–87
Evdokiou A, Labrinidis A, Bouralexis S, Hay S, Findlay DM (2003) Induction of cell death of human osteogenic sarcoma cells by zoledronic acid resembles anoikis. Bone 33:216–228
Facchini G, Caraglia M, Morabito A, Marra M, Piccirillo MC, Bochicchio AM, Striano S, Marra L, Nasti G, Ferrari E, Leopardo D, Vitale G, Gentilini D, Tortoriello A, Catalano A, Budillon A, Perrone F, Iaffaioli RV (2010) Metronomic administration of zoledronic acid and taxotere combination in castration resistant prostate cancer patients: phase I ZANTE trial. Cancer Biol Ther 10:543–548
Farabegoli F, Papi A, Orlandi M (2011) (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulates EGFR, MMP-2, MMP-9 and EMMPRIN and inhibits the invasion of MCF-7 tamoxifen-resistant cells. Biosci Rep 31(2):99–108
Fitzgerald JB, Schoeberl B, Nielsen UB, Sorger PK (2006) Systems biology and combination therapy in the quest for clinical efficacy. Nat Chem Biol 22(3):1737–1754
Forester SC, Lambert JD (2011) The role of antioxidant versus pro-oxidant effects of green tea polyphenols in cancer prevention. Mol Nutr Food Res 55(6):844–854
Gu JW, Makey KL, Tucker KB, Chinchar E, Mao X, Pei I, Thomas EY, Miele L (2013) EGCG, a major green tea catechin suppresses breast tumor angiogenesis and growth via inhibiting the activation of HIF-1α and NFκB, and VEGF expression. Vasc Cell 5(1):9
Hsuuw YD, Chan WH (2007) Epigallocatechin gallate dose-dependently induces apoptosis or necrosis in human MCF-7 cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1095:428–440
Labrinidis A, Hay S, Liapis V, Findlay DM, Evdokiou A (2010) Zoledronic acid protects against osteosarcoma-induced bone destruction but lacks efficacy against pulmonary metastases in a syngeneic rat model. Int J Cancer 127:345–354
Lam YC, Cheng CW, Peng H, Law CK, Huang XZ, Bian ZX (2009) Cancer patients’ attitudes toward Traditional Chinese Medicine: a Hong Kong survey. Chinese Med 4:25
Lee JH, Jin H, Shim HE, Kim HN, Ha H, Lee ZH (2010) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits osteoclastogenesis by down-regulating c-Fos expression and suppressing the nuclear factor-kappaB signal. Mol Pharmacol 77(1):17–25
Lee SH, Kim BJ, Choi HJ, Cho SW, Shin CS, Park SY, Lee YS, Lee SY, Kim HH, Kim GS, Koh JM (2012) (−)-Epigallocathechin-3-gallate, an AMPK activator, decreases ovariectomy-induced bone loss by suppression of bone resorption. Calcif Tissue Int 90(5):404–410
Liang G, Tang A, Lin X, Li L, Zhang S, Huang Z, Tang H, Li QQ (2010) Green tea catechins augment the antitumor activity of doxorubicin in an in vivo mouse model for chemoresistant liver cancer. Int J Oncol 37(1):111–123
Luo KW, Ko CH, Yue GGL, Lee MY, Siu WS, Lee JK, Shum WT, Fung KP, Leung PC, Li G, Evdokiou A, Lau CBS (2013) Anti-tumor and anti-osteolysis effects of the metronomic use of zoledronic acid in primary and metastatic breast cancer mouse models. Cancer Lett 339(1):42–48
Luo KW, Ko CH, Yue GGL, Lee JKM, Lee M, Li G, Fung KP, Leung PC, Lau CBS (2014) Green tea (Camellia sinensis) extract inhibits both the metastasis and osteolytic components of mammary cancer 4T1 lesions in mice. J Nutr Biochem 25(4):395–403
Martin CK, Dirksen WP, Carlton MM, Lanigan LG, Pillai SP, Werbeck JL, Simmons JK, Hildreth BE, London CA, Toribio RE, and Rosol TJ (2013) Combined zoledronic acid and meloxicam reduced bone loss and tumour growth in an orthotopic mouse model of bone-invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma. Vet Comp Oncol. doi:10.1111/vco.12037
Mazumder ME, Beale P, Chan C, Yu JQ, Huq F (2012) Epigallocatechin gallate acts synergistically in combination with cisplatin and designed trans-palladiums in ovarian cancer cells. Anticancer Res 32(11):4851–4860
Okamoto S, Jiang Y, Kawamura K, Shingyoji M, Fukamachi T, Tada Y, Takiguchi Y, Tatsumi K, Shimada H, Hiroshima K, Kobayashi H, Tagawa M (2013) Zoledronic acid produces combinatory anti-tumor effects with cisplatin on mesothelioma by increasing p53 expression levels. PLoS One 8(3):e60297
Ottewell PD, Woodward JK, Lefley DV, Evans CA, Coleman RE, Holen I (2009) Anticancer mechanisms of doxorubicin and zoledronic acid in breast cancer tumor growth in bone. Mol Cancer Ther 8:2821–2832
Pasquier E, Kavallaris M, Andre N (2011) Metronomic chemotherapy: new rationale for new directions. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7:455–465
Peng L, Song XH, Shi XG, Li JX, Ye CX (2008) An improved HPLC method for simultaneous determination of phenolic compounds, purine alkaloids and theanine in Camellia species. J Food Compost Anal 21:559–563
Qiao J, Gu C, Shang W, Du J, Yin W, Zhu M, Wang W, Han M, Lu W (2011) Effect of green tea on pharmacokinetics of 5-fluorouracil in rats and pharmacodynamics in human cell lines in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol 49(6):1410–1415
Rachner TD, Singh SK, Schoppet M, Benad P, Bornhauser M, Ellenrieder V, Ebert R, Jakob F, Hofbauer LC (2010) Zoledronic acid induces apoptosis and changes the TRAIL/OPG ratio in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 287:109–116
Ryan P, Saleh I, Stassen LF (2009) Osteonecrosis of the jaw: a rare and devastating side effect of bisphosphonates. Postgrad Med J 85:674–677
Sellmeyer DE (2010) Atypical fractures as a potential complication of long-term bisphosphonate therapy. JAMA 304(13):1480–1484
Terranova VP, Hujanen ES, Martin GR (1986) Basement membrane and the invasive activity of metastatic tumor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 77:311–316
Thangapazham RL, Passi N, Maheshwari RK (2007) Green tea polyphenol and epigallocatechin gallate induce apoptosis and inhibit invasion in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 6(12):1938–1943
Wood J, Bonjean K, Ruetz S, Bellahcene A, Devy L, Foidart JM, Castronovo V, Green JR (2002) Novel antiangiogenic effects of the bisphosphonate compound zoledronic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:1055–1061
Yeh P, Kishony R (2007) Networks from drug–drug surfaces. Mol Syst Biol 3:85
Zhang FL, Casey PJ (1996) Protein prenylation: molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu Rev Biochem 65:241–269
Zhao X, Xu X, Guo L, Ragaz J, Guo H, Wu J, Shao Z, Zhu J, Guo X, Chen J, Zhu B, Wang Z, Hu X (2010) Biomarker alterations with metronomic use of low-dose zoledronic acid for breast cancer patients with bone metastases and potential clinical significance. Breast Cancer Res Treat 124:733–743
Zhou F, Zhou H, Wang T, Mu Y, Wu B, Guo DL, Zhang XM, Wu Y (2012) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits proliferation and migration of human colon cancer SW620 cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33(1):120–126
Zinonos I, Labrinidis A, Lee M, Liapis V, Hay S, Ponomarev V, Diamond P, Zannettino AC, Findlay DM, Evdokiou A (2009) Apomab, a fully human agonistic antibody to DR5, exhibits potent antitumor activity against primary and metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 8:2969–2980
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Focused Innovations Scheme (Major Area Scheme A—Phase 2) of The Chinese University of Hong Kong. The authors would like to thank Dr. Sammy Siu, Ms. Anita Shum and Mr. Jimmy Cheng for their technical support on the IVIS and micro-CT analysis.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, KW., Ko, CH., Yue, G.GL. et al. The combined use of Camellia sinensis and metronomic zoledronic acid in a breast cancer-induced osteolysis mouse model. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 1025–1036 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1882-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1882-1