Abstract
Background
Lysyl oxidase-like 4 (LOXL4) has been found up-regulated in a variety of human malignancies, but its clinical significance and functional roles in gastric cancer (GC) remain unknown.
Methods
Lysyl oxidase-like 4 (LOXL4) expression level in tumor tissues and human GC cell lines was evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting and immunohistochemical analyses. Its clinical significance was inferred from the analysis of 379 tissue samples of patients with GC using tissue microarray. The roles of LOXL4 in cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro were analyzed by gene over-expression, RNA interference and recombinant protein. Effects of LOXL4 on regulation of focal adhesion kinase/Src kinase (FAK/Src) pathway were examined by Western blotting.
Results
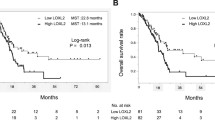
Lysyl oxidase-like 4 (LOXL4) was up-regulated in GC tissues relative to paired non-tumor tissues, and this over-expression was significantly associated with tumor size, depth of tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis, tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stages and poorer overall survival. Over-expression of LOXL4 has promotive effects on GC cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro, consistent with this, LOXL4 knockdown has inhibitive effects on GC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Furthermore, recombinant human LOXL4 protein also promoted GC cell proliferation and migration. Subsequent mechanistic studies showed that LOXL4 could activate FAK/Src pathway to enhance cell–extracellular matrix adhesion.
Conclusions
Taken together, our data reveal that up-regulation of LOXL4 expression is a frequent event in GC progression, contributes to tumor cell proliferation and metastasis, and LOXL4 may be a potential independent prognostic marker and therapeutic target for GC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ERK:
-
Extracellular regulated kinase
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- LOX:
-
Lysyl oxidase
- LOXL4:
-
Lysyl oxidase-like 4
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- rhLOXL4:
-
Recombinant human LOXL4 protein
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- TNM:
-
Tumor node metastasis
References
Abe J, Takahashi M, Ishida M, Lee JD, Berk BC (1997) c-Src is required for oxidative stress-mediated activation of big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1. J Biol Chem 272:20389–20394
Bae YS, Kang SW, Seo MS, Baines IC, Tekle E, Chock PB, Rhee SG (1997) Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced generation of hydrogen peroxide. Role in EGF receptor-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 272:217–221
Baker AM, Cox TR, Bird D, Lang G, Murray GI, Sun XF, Southall SM, Wilson JR, Erler JT (2011) The role of lysyl oxidase in SRC-dependent proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Natl Cancer Inst 103:407–424
Baker AM, Bird D, Lang G, Cox TR, Erler JT (2013) Lysyl oxidase enzymatic function increases stiffness to drive colorectal cancer progression through FAK. Oncogene 32:1863–1868
Crew KD, Neugut AI (2006) Epidemiology of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 12:354–362
Csiszar K (2001) Lysyl oxidases: a novel multifunctional amine oxidase family. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 70:1–32
Görögh T, Weise JB, Holtmeier C, Rudolph P, Hedderich J, Gottschlich S, Hoffmann M, Ambrosch P, Csiszar K (2007) Selective upregulation and amplification of the lysyl oxidase like-4 (LOXL4) gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Pathol 212:74–82
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Jones RJ, Brunton VG, Frame MC (2000) Adhesion-linked kinases in cancer; emphasis on src, focal adhesion kinase and PI 3-kinase. Eur J Cancer 36:1595–1606
Kagan HM, Li W (2003) Lysyl Oxidase: properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of the cell. J Cell Biochem 88:660–672
Kaplan KB, Swedlow JR, Morgan DO, Varmus HE (1995) c-Src enhances the spreading of src−/− fibroblasts on fibronectin by a kinase-independent mechanism. Genes Dev 9:1505–1517
Kim Y, Roh S, Park JY, Kim Y, Cho DH, Kim JC (2009) Differential expression of the LOX family genes in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Oncol Rep 22:799–804
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Fong SF, Nieva DR, Sullivan CM, Edwards EM, Sommer P, Csiszar K, Hendrix MJ (2002) A molecular role for lysyl oxidase in breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res 62:4478–4483
Li J, Yang X-M, Wang Y-H, Feng M-X, Liu X-J, Zhang Y-L, Huang S, Wu Z, Xue F, Qin W-X, Gu J-R, Xia Q, Zhang Z-G (2014) Monoamine oxidase A suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by inhibiting the adrenergic system and its transactivation of EGFR signaling. J Hepatol 60:1225–1234
Ma MZ, Zhuang C, Yang XM, Zhang ZZ, Ma H, Zhang WM, You HY, Qin W, Gu J, Yang S, Cao H, Zhang ZG (2014) CTHRC1 acts as a prognostic factor and promotes invasiveness of gastrointestinal stromal tumors by activating Wnt/PCP-Rho signaling. Neoplasia 16:265–278
Mäki JM, Tikkanen H, Kivirikko KI (2001) Cloning and characterization of a fifth human lysyl oxidase isoenzyme: the third member of the lysyl oxidase-related subfamily with four scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domains. Matrix Biol 20:493–496
Manes S, Mira E, Gomez-Mouton C, Lacalle RA, Martinez C (2000) Cells on the move: a dialogue between polarization and motility. IUBMB Life 49:89–96
Maung K, Easty DJ, Hill SP, Bennett DC (1999) Requirement for focal adhesion kinase in tumor cell adhesion. Oncogene 18:6824–6828
Nada S, Yagi T, Takeda H, Tokunaga T, Nakagawa H, Ikawa Y, Okada M, Aizawa S (1993) Constitutive activation of Src family kinases in mouse embryos that lack Csk. Cell 73:1125–1135
Naylor GM, Gotoda T, Dixon M, Shimoda T, Gatta L, Owen R, Tompkins D, Axon A (2006) Why does Japan have a high incidence of gastric cancer? Comparison of gastritis between UK and Japanese patients. Gut 55:1545–1552
Payne SL, Fogelgren B, Hess AR, Seftor EA, Wiley EL, Fong SF, Csiszar K, Hendrix MJ, Kirschmann DA (2005) Lysyl oxidase regulates breast cancer cell migration and adhesion through a hydrogen peroxide-mediated mechanism. Cancer Res 65:11429–11436
Payne SL, Hendrix MJ, Kirschmann DA (2007) Paradoxical roles for lysyl oxidases in cancer—a prospect. J Cell Biochem 101:1338–1354
Peng L, Ran Y-L, Hai H, Yu L, Liu Q, Zhou Z, Sun Y-M, Sun L-C, Pan J, Sun L-X, Zhao P, Yang Z-H (2009) Secreted LOXL2 is a novel therapeutic target that promotes gastric cancer metastasis via the Src/FAK pathway. Carcinogenesis 30:1660–1669
Schlaepfer DD, Jones KC, Hunter T (1998) Multiple Grb2-mediated integrin-stimulated signaling pathways to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase: summation of both c-Src and focal adhesion kinase-initiated tyrosine phosphorylation events. Mol Cell Biol 18:2571–2585
Stracke ML, Liotta LA (1992) Multi-step cascade of tumor cell metastasis. In Vivo 6:309–316
Sun W, Haller DG (2001) Recent advances in the treatment of gastric cancer. Drugs 61:1545–1551
Weise JB, Rudolph P, Heiser A, Kruse ML, Hedderich J, Cordes C, Hoffmann M, Brant O, Ambrosch P, Csiszar K, Görögh T (2008) LOXL4 is a selectively expressed candidate diagnostic antigen in head and neck cancer. Eur J Cancer 44:1323–1331
Wong CC, Zhang H, Gilkes DM, Chen J, Wei H, Chaturvedi P, Hubbi ME, Semenza GL (2012) Inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 block breast cancer metastatic niche formation and lung metastasis. J Mol Med (Berl) 90:803–815
Wu G, Guo Z, Chang X, Kim MS, Nagpal JK, Liu J, Maki JM, Kivirikko KI, Ethier SP, Trink B, Sidransky D (2007) LOXL1 and LOXL4 are epigenetically silenced and can inhibit Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in human bladder cancer. Cancer Res 67:4123–4129
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the stuff of the tumor microenvironment research group of State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes for assistance with this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This project was approved by committee of Renji Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine for the use of samples. All tissue samples were obtained with the consent of patients and in accordance with the China Ethical Review Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Rong-kun Li and Wen-yi Zhao have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Rk., Zhao, Wy., Fang, F. et al. Lysyl oxidase-like 4 (LOXL4) promotes proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer via FAK/Src pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 269–281 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1823-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1823-z