Abstract
Objectives
The present study was designed to investigate the possible protective effects of berberine against cyclophosphamide (CP)-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.
Methods
The experimental rats were treated with berberine orally at a dose of 50 mg/kg for 11 consecutive days after the administration of a single intraperitoneal dose of CP (200 mg/kg). The hepatoprotective effect of berberine was evaluated by assaying liver function markers, the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), antioxidant defense system and gene expressions of both TNF-α and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2).
Results
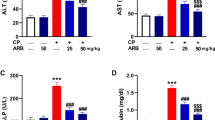
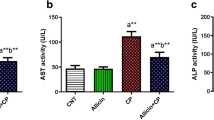
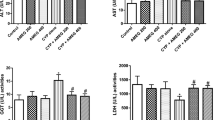
The biochemical results showed that administration of CP induced hepatic damage associated with a significant increase in the serum marker enzymes aspartate and alanine transaminases (AST, ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and a significant increase in serum total bilirubin accompanied with a decrease in serum albumin concentration. In addition, CP-administration induced oxidative stress in the liver as evident from the increased lipid peroxidation (LPO), declined glutathione (GSH) content and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities. Moreover, administration of CP was associated with a significant increase in serum TNF-α. Similarly, CP administration was accompanied by a significant increase in the mRNA expression of both TNF-α and COX-2 in the liver as indicated by the qPCR assay. Concomitant administration of berberine efficiently alleviated the altered biochemical parameters.
Conclusion
Berberine showed a marked hepatoprotective effect against CP-induced hepatotoxicity through alleviation of the elevated serum marker enzymes in addition to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory efficacies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann F, Preiss R (2001) Cyclophosphamide and related antican-cer drugs. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 764:173–192
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61(5):882–888
Beyaert R, Fiers W (1998) Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin. In: Mire-Sluis AR, Thorpe R (eds) Cytokines. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 335–359
Bukowski R (1999) The need for cytoprotection. Eur J Cancer 32A:S2–S4
Canadian Council on Animal Care (1993) Guide to the care and use of experimental animals, vol 2. CCAC, Ottawa
Cho BJ, Im EK, Kwon JH et al (2005) Berberine inhibits the production of lysophosphatidylcholine-induced reactive oxygen species and the ERK1/2 pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell 20:429–434
Choi BH, Ahn IS, Kim YH et al (2006) Berberine reduces the expression of adipogenic enzymes and inflammatory molecules of 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Exp Mol Med 38:599–605
Chomzynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Annu Rev Biochem 162:156–159
Cicero AF, Rovati LC, Setnikar I (2007) Eulipidemic effects of berberine administered alone or in combination with other natural cholesterol lowering agents. A single-blind clinical investigation. Arzneimittelforschung 57:26–30
Das UB, Mallick M, Debnath JM, Ghosh D (2002) Protective effect of ascorbic acid on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular gameto-genic and androgenic disorder in male rats. Asian J Androl 4:201–207
Feng AW, Gao W, Zhou GR, Yu R, Li N, Huang XL, Li QR, Li JS (2012) Berberine ameliorates COX-2 expression in rat small intestinal mucosa partially through PPARγ pathway during acute endotoxemia. Int Immunopharmacol 12:182–188
Ghosh D, Das UB, Ghosh S, Mallick M, Debnath J (2002) Testicular gametogenic and steroidogenic activities in cyclophosphamide treated rat: a correlative study with testicular oxidative stress. Drug Chem Toxicol 25:281–292
Gonzalez-Amaro R, Garcia-Monzon C, Garcia-Buey L, Moreno-Otero R, Alonso JL, Yague E, Pivel JP, Lopez-Cabrera M, Fernandez-Ruiz E, Sanchez-Madrid F (1994) Induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha production by human hepatocytes in chronic viral hepatitis. J Exp Med 179:841–848
Haque R, Bin-Hafeez B, Parvez S, Pandey S, Sayeed I, Ali M, Raisuddin S (2003) Aqueous extract of walnut (Juglans regia L.) protects mice against cyclophosphamide-induced biochemical toxicity. Hum Exp Toxicol 22:473–480
Hierholzer C, Harbrecht B, Menezes JM, Kane J, MacMicking J, Nathan CF, Peitzman AB, Billiar TR, Tweardy DJ (1998) Essential role of induced nitric oxide in the initiation of the inflammatory response after hemorrhagic shock. J Exp Med 187:917–928
Hsiang CY, Wu SL, Cheng SE, Ho TY (2005) Acetaldehyde-induced interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production is inhibited by berberine through nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway in HepG2 cells. J Biomed Sci 12:791–801
Hwang JM, Wang CJ, Chou FP et al (2002) Inhibitory effect of berberine on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage in rat liver. Arch Toxicol 76:664–670
IFCC (1983) Methods for the measurement of catalytic concentration of enzymes. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 18:521–534
Imanshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H (2008) Pharmacological and therapeutic effects of Berberis vulgaris and its active constituent, berberine. Phytother Res 22:999–1012
Jeong HW, Hsu KC, Lee JW, Ham M, Huh JY, Shin HJ, Kim WS, Kim JB (2009) Berberine suppresses proinflammatory responses through AMPK activation in macrophages. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:E955–E964
Kaplan LA, Pesce AJ (1984) Clinical chemistry: theory, analysis, and correlation. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 1032–1036
Kar M, Mishra D (1976) Catalase, peroxidase and polyphenoloxidase activities during rice leaf senescence. Plant Physiol 57:315–319
Ko YJ, Lee JS, Park BC, Shin HM, Kim JA (2007) Inhibitory effects of Zoagumhwan water extract and berberine on angiotensin II-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 expression and monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Vasc Pharmacol 47:189–196
Kumar G, Banu SG, Kannan V, Pandian RM (2005) Antihepatotoxic effect of β-carotene on paracetamol induced hepatic damage in rats. Ind J Exp Biol 43:351–355
Lahouel M, Fillastre JP (2004) Role of flavonoids in the prevention of haematoxicity due to chemotherapeutic agents. Haema 7:313–320
Lindley CMG, Hamilton JS, McCune S, Faucette SS, Shord RL, Hawke H et al (2002) The effect of cyclophosphamide with and without dexamethasone on cytochrome p450 3A4 and 2B6 in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 30:814–822
Luo A, Fan Y (2011) Antioxidant activities of berberine hydrochloride. J Med Plants Res 5:3702
Mahmoud AM, Hussein OE, Ramadan SA (2013) Amelioration of cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity by the brown seaweed Turbenaria ornata. Int J Clin Toxicol 1:9–17
Marklund SL, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47(3):469–474
McDiarmid MA, Iype PT, Koldner K, Jacobnson KD, Strickland PT (1991) Evidence for acrolein-modified DNA in peripheral blood leu-cocytes of cancer patients treated with cyclophosphamide. Mutat Res 248:93–99
Murray R (1984) Aspartate aminotransferase. In: Kaplan A et al (eds) Clinical Chemistry. The CV Mosby Co, St Louis, Toronto, Princeton, pp 1112–1116
Nussler AK, Billiar TR (1993) Inflammation, immunoregulation, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Leukoc Biol 54:171–178
Peng PL, Hsieh YS, Wang CJ, Hsu JL, Chou FP (2006) Inhibitory effect of berberine on the invasion of human lung cancer cells via decreased productions of urokinase-plasminogen activator and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 214:8–15
Preuss HG, Jarrell ST, Scheckenbach R, Lieberman S, Anderson RA (1998) Comparative effect of chromium vanadium and Gymnema sylvestre on sugar-induced blood pressure elevation in SHR. J Am Coll Nutr 17:116–123
Selvakumar E, Prahalathan C, Mythili Y, Varalakshmi P (2005) Mitigation of oxidative stress in cyclophosphamide-challenged hepatic tissue by DL-alpha-lipoic-acid. Mol Cell Biochem 272:179–185
Simeonova PP, Gallucci RM, Hulderman T, Wilson R, Kommineni C, Rao M, Luster MI (2001) The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in liver toxicity, inflammation, and fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 177:112–120
Sindhu G, Susithra M, Vijayalakshmi N (2012) Evaluation of the hepatoprotective effect of berberine in paracetamol induced experimental hepatotoxicity in Wistar rats. Int J Recent Sci Res 3(7):569–573
Sudharsan PT, Mythili Y, Selvakumar E, Varalakshmi P (2006) Lupeol and its ester exhibit protective role against cyclophosphamide-induced cardiac mitochondrial toxicity. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 47(2):205–210
Tang LQ, Wei W, Chen LM, Liu S (2006) Effects of berberine on diabetes induced by alloxan and a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 108:109–115
Teitz N (1986) Fundam of Clin Chem. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia
Uchida K (1999) Current status of acrolein as a lipid product. Trends Cardiovasc Med 9:109–113
Vane JR, Bakhle YS, Botting RM (1998) Cyclooxygenases 1 and 2. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 38:97–120
Webster D (1974) A study of the interaction of bromcresol green with isolated serum globulin fractions. Clin Chim Acta 53:109–115
Yu HH, Kim KJ, Cha JD et al (2005) Antimicrobial activity of berberine alone and in combination with ampicillin or oxacillin against methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Food 8:454–461
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Germoush, M.O., Mahmoud, A.M. Berberine mitigates cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity by modulating antioxidant status and inflammatory cytokines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 1103–1109 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1665-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1665-8