Abstract
Purpose
Abnormal expression of miRNAs is closely related to a variety of human cancers. The purpose of this study is to identify new tumor suppressor miRNA and elucidate its physiological function and mechanism in renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods
The expression of miR-145 in 45 RCC and adjacent normal tissues was performed by quantitative RT-PCR. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis and cycle assays were carried out for functional analysis after miR-145 transfection. Two target genes of miR-145 were identified by luciferase reporter assay. The altered expression of 84 epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related genes after miR-145 transfection was detected by RT2 Profiler EMT PCR array.
Results
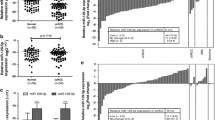
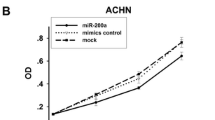
The expression of miR-145 was downregulated in RCC compared to their normal adjacent tissues. Restoring miR-145 expression in RCC cell lines dramatically suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and induced cell apoptosis and G2-phase arrest. We further validated those miR-145 targets two oncogenes, ANGPT2 and NEDD9 in RCC. In addition, miR-145 was found to regulate numerous genes involved in the EMT.
Conclusions
These findings demonstrate that miR-145 functions as tumor suppressor in RCC, suggesting that miR-145 may be a potential therapeutic target for RCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldewijns M, Thijssen V, Van den Eynden G, Van Laere S, Bluekens A, Roskams T, Van Poppel H, De Bruine A, Griffioen A, Vermeulen P (2007) High-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma has a higher angiogenic activity than low-grade renal cell carcinoma based on histomorphological quantification and qRT–PCR mRNA expression profile. Br J Cancer 96(12):1888–1895
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E (2005) Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human micro RNA genes. Cell 120(1):21–24
Bullock A, Zhang L, O’Neill A, Percy A, Sukhatme V, Mier J, Atkins M, Bhatt R (2010) Plasma angiopoietin-2 (ANG2) as an angiogenic biomarker in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). J Clin Oncol 2010(28):4630
Cabodi S, del Pilar Camacho-Leal M, Di Stefano P, Defilippi P (2010) Integrin signalling adaptors: not only figurants in the cancer story. Nat Rev Cancer 10(12):858–870
Chang J-X, Gao F, Zhao G-Q, Zhang G-J (2012) Expression and clinical significance of NEDD9 in lung tissues. Med Oncol 29(4):2654–2660
Chen B, Li H, Zeng X, Yang P, Liu X, Zhao X, Liang S (2012) Roles of microRNA on cancer cell metabolism. J Transl Med 10:228. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-10-228
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Tatarano S, Kawahara K, Uchida Y, Nishiyama K, Fujimura L, Kikkawa N, Seki N, Nakagawa M (2010) miR-145 and miR-133a function as tumour suppressors and directly regulate FSCN1 expression in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer 102(5):883–891
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ (2005) Renal-cell carcinoma. New Engl J Med 353(23):2477–2490
Etoh T, Inoue H, Tanaka S, Barnard GF, Kitano S, Mori M (2001) Angiopoietin-2 is related to tumor angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma possible in vivo regulation via induction of proteases. Cancer Res 61(5):2145–2153
Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C (1982) Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 6(7):655–664
Ha T-Y (2011) MicroRNAs in human diseases: from cancer to cardiovascular disease. Immune Netw 11(3):135–154
Honda H, Oda H, Nakamoto T, Honda Z-I, Sakai R, Suzuki T, Saito T, Nakamura K, Nakao K, Ishikawa T (1998) Cardiovascular anomaly, impaired actin bundling and resistance to Src-induced transformation in mice lacking p130Cas. Nat Genet 19(4):361–365
Hu B, Cheng S-Y (2009) Angiopoietin-2: development of inhibitors for cancer therapy. Curr Oncol Rep 11(2):111–116
Inui M, Martello G, Piccolo S (2010) MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 11(4):252–263
Izumchenko E, Singh MK, Plotnikova OV, Tikhmyanova N, Little JL, Serebriiskii IG, Seo S, Kurokawa M, Egleston BL, Klein-Szanto A (2009) NEDD9 promotes oncogenic signaling in mammary tumor development. Cancer Res 69(18):7198–7206
Kim M, Gans JD, Nogueira C, Wang A, Paik J-H, Feng B, Brennan C, Hahn WC, Cordon-Cardo C, Wagner SN (2006) Comparative oncogenomics identifies NEDD9 as a melanoma metastasis gene. Cell 125(7):1269–1281
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294(5543):853–858
Liang C–C, Park AY, Guan J-L (2007) In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc 2(2):329–333
Natarajan M, Stewart J, Golemis EA, Pugacheva E, Alexandropoulos K, Cox BD, Wang W, Grammer J, Gladson C (2005) HEF1 is a necessary and specific downstream effector of FAK that promotes the migration of glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 25(12):1721–1732
Naumnik W, Naumnik B, Niewiarowska K, Ossolinska M, Chyczewska E (2013) Angiogenic axis angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2/tie-2 in non-small cell lung cancer: a bronchoalveolar lavage and serum study. Neurobiol Respir Spring 341–348
Noh JH, Chang YG, Kim MG, Jung KH, Kim JK, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q, Kim S-J, Kwon SH (2013) miR-145 functions as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2 in liver cancer. Cancer Lett 335(2):455–462
Oliner J, Min H, Leal J, Yu D, Rao S, You E, Tang X, Kim H, Meyer S, Han SJ (2004) Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by selective inhibition of angiopoietin-2. Cancer Cell 6(5):507–516
Pascual D, Borque A (2008) Epidemiology of kidney cancer. Adv Urol 2008:782381
Redova M, Poprach A, Besse A, Iliev R, Nekvindova J, Lakomy R, Radova L, Svoboda M, Dolezel J, Vyzula R, Slaby O (2012) MiR-210 expression in tumor tissue and in vitro effects of its silencing in renal cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol 34(1):481–491. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0573-2
Reeves DJ, Liu CY (2009) Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemoth Pharm 64(1):11–25
Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B (2009) Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet 373(9669):1119–1132
Speranza MC, Frattini V, Pisati F, Kapetis D, Porrati P, Eoli M, Pellegatta S, Finocchiaro G (2012) NEDD9, a novel target of miR-145, increases the invasiveness of glioblastoma. Oncotarget 3(7):723
Thurston G, Daly C (2012) The complex role of angiopoietin-2 in the angiopoietin–tie signaling pathway. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2(9):a006550
Zaman M, Chen Y, Deng G, Shahryari V, Suh S, Saini S, Majid S, Liu J, Khatri G, Tanaka Y (2010) The functional significance of microRNA-145 in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 103(2):256–264
Zhao L, Chen X, Cao Y (2011) New role of microRNA: carcinogenesis and clinical application in cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 43(11):831–839
Zhou L, Chen J, Li Z, Li X, Hu X, Huang Y, Zhao X, Liang C, Wang Y, Sun L (2010) Integrated profiling of microRNAs and mRNAs: microRNAs located on Xq27. 3 associate with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 5(12):e15224
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Shenzhen in China (No. 201102006) and Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (No. 2011B031800381).
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ruijing Lu and Ziliang Ji have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, R., Ji, Z., Li, X. et al. miR-145 functions as tumor suppressor and targets two oncogenes, ANGPT2 and NEDD9, in renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 140, 387–397 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1577-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1577-z