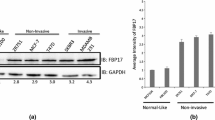
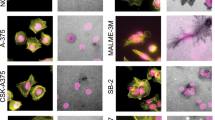
Abstract
Purpose
Invasion of cancer cells depends on the proteolytic degradation of extracellular matrix regulated by actin-driven membrane protrusions, called invadopodia. However, the mechanisms underlying invadopodia formation in cancer cells remain largely unknown.
Methods
By employing adenoviral transduction of breast cancer cells with either β-galactosidase (Ad-LacZ) or TIS21/BTG2/Pc3 (Ad-TIS21) gene, the regulation of invadopodia formation was investigated. Invasion activity was examined by invadopodia assay and Matrigel assay. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) was monitored by FACS-based analysis.
Results
Here, we observed that TIS21 suppressed invadopodia formation as well as invasion activity along with F-actin remodeling. The inhibition of TIS21-mediated invadopodia formation was accompanied with attenuation of ROS generation in the TIS21 expressers, indicating that TIS21-mediated inhibition of ROS plays a critical role for invadopodia formation by regulating actin-associated protein remodeling. This was further confirmed in the TIS21−/−MEF cells.
Conclusions
This is the first report to provide insight into invasion signals regulated by tumor suppressor, TIS21/BTG2/Pc3 gene, in the intractable breast cancer cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MEF:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblast
- NAC:
-
N-acetyl-l-cysteine
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- TIS21:
-
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-inducible sequence 21
- BTG2:
-
B-cell translocation gene 2
- Ad-TIS21:
-
Adenovirus carrying TIS21 cDNA
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
References
Artym VV, Zhang Y, Seillier-Moiseiwitsch F, Yamada KM, Mueller FC et al (2006) Dynamic interactions of cortactin and membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: defining the stages of invadopodia formation and function. Cancer Res 66:3034–3043
Ben Mahdi MH, Andrieu V, Pasquier C (2000) Focal adhesion kinase regulation by oxidative stress in different cell types. IUBMB Life 50:291–299
Bradbury A, Possenti R, Shooter EM et al (1991) Molecular cloning of PC3, a putatively secreted protein whose mRNA is induced by nerve growth factor and depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3353–3357
Buccione R, Orth JD, McNiven MA (2004) Foot and mouth: podosomes, invadopodia and circular dorsal ruffles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:647–657
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC (2002) Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2:563–572
Chiarugi P, Pani G, Giannoni E et al (2003) Reactive oxygen species as essential mediators of cell adhesion: the oxidative inhibition of a FAK tyrosine phosphatase is required for cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 161:933–944
Clark ES, Whigham AS, Yarbrough WG et al (2007) Cortactin is an essential regulator of matrix metalloproteinase secretion and extracellular matrix degradation in invadopodia. Cancer Res 67:4227–4235
Coopman PJ, Do MT, Thompson EW et al (1998) Phagocytosis of cross-linked gelatin matrix by human breast carcinoma cells correlates with their invasive capacity. Clin Cancer Res 4:507–515
Diaz B, Shani G, Pass I et al (2009) Tks5-dependent, nox-mediated generation of reactive oxygen species is necessary for invadopodia formation. Sci Signal 2:ra53
Eckert MA, Lwin TM, Chang AT et al (2011) Twist1-induced invadopodia formation promotes tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 19:372–386
Farioli-Vecchioli S, Cinà I, Ceccarelli M et al (2012) TIS21 knock-out enhances the frequency of medulloblastoma in Patched1 heterozygous mice by inhibiting the Cxcl3-dependent migration of cerebellar neurons. J Neurosci 32:15547–15564
Ficazzola MA, Fraiman M, Gitlin J et al (2001) Antiproliferative B cell translocation gene 2 protein is down-regulated post-transcriptionally as an early event in prostate carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 22:1271–1279
Fletcher BS, Lim RW, Varnum BC et al (1991) Structure and expression of TIS21, a primary response gene induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. J Biol Chem 266:14511–14518
Kawakubo H, Brachtel E, Hayashida T et al (2006) Loss of B-cell translocation gene-2 in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinoma is associated with tumor grade and overexpression of cyclin d1 protein. Cancer Res 66:7075–7082
Lim IK (2006) TIS21(/BTG2/PC3) as a link between ageing and cancer: cell cycle regulator and endogenous cell death molecule. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132:417–426
Lim IK, Lee MS, Lee SH et al (1995) Differential expression of TIS21 and TIS1 genes in the various organs of Balb/c mice, thymic carcinoma tissues and human cancer cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 121:279–284
Linder S, Aepfelbacher M (2003) Podosomes: adhesion hot-spots of invasive cells. Trends Cell Biol 13:376–385
Mader CC, Oser M, Magalhaes MA et al (2011) An EGFR-Src-Arg-cortactin pathway mediates functional maturation of invadopodia and breast cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res 71:1730–1741
Matsuda S, Rouault J, Magaud J et al (2001) In search of a function for the TIS21/PC3/BTG1/TOB family. FEBS Lett 497:67–72
Melamed J, Kernizan S, Walden PD (2002) Expression of B-cell translocation gene 2 protein in normal human tissues. Tissue Cell 34:28–32
Park S, Lee YJ, Lee HJ et al (2004) B-cell translocation gene 2 (Btg2) regulates vertebral patterning by modulating bone morphogenetic protein/smad signaling. Mol Cell Biol 24:10256–10262
Park TJ, Kim JY, Oh SP et al (2008) TIS21 negatively regulates hepatocarcinogenesis by disruption of cyclin B1-Forkhead box M1 regulation loop. Hepatology 47:1533–1543
Rouault JP, Falette N, Guéhenneux F et al (1996) Identification of BTG2, an antiproliferative p53-dependent component of the DNA damage cellular response pathway. Nat Genet 14:482–486
Schmidt M, Böhm D, von Törne C et al (2008) The humoral immune system has a key prognostic impact in node-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 68:5405–5413
Struckmann K, Schraml P, Simon R et al (2004) Impaired expression of the cell cycle regulator BTG2 is common in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 64:1632–1638
Stylli SS, Kaye AH, Lock P (2008) Invadopodia: at the cutting edge of tumour invasion. J Clin Neurosci 15:725–737
Takahashi F, Chiba N, Tajima K et al (2011) Breast tumor progression induced by loss of BTG2 expression is inhibited by targeted therapy with the ErbB/HER inhibitor lapatinib. Oncogene 30:3084–3095
Tobar N, Cáceres M, Santibáñez JF et al (2008) RAC1 activity and intracellular ROS modulate the migratory potential of MCF-7 cells through a NADPH oxidase and NFkappaB-dependent mechanism. Cancer Lett 267:125–132
Turner DP, Moussa O, Sauane M et al (2007) Prostate-derived ETS factor is a mediator of metastatic potential through the inhibition of migration and invasion in breast cancer. Cancer Res 67:1618–1625
van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ et al (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415:530–536
Yamaguchi H, Lorenz M, Kempiak S et al (2005a) Molecular mechanisms of invadopodium formation: the role of the N-WASP–Arp2/3 complex pathway and cofilin. J Cell Biol 168:441–452
Yamaguchi H, Wyckoff J, Condeelis J (2005b) Cell migration in tumors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:559–564
Yamaguchi H, Takeo Y, Yoshida S et al (2009) Lipid rafts and caveolin-1 are required for invadopodia formation and extracellular matrix degradation by human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:8594–8602
Acknowledgments
Authors greatly appreciate careful reading of this manuscript by Prof. Woon Ki Paik in Ajou University School of Medicine. This work was supported by the grants of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A121725) and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (131280).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, JA., Lim, I.K. TIS21/BTG2 inhibits invadopodia formation by downregulating reactive oxygen species level in MDA-MB-231 cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 1657–1665 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1484-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1484-3