Abstract
Purpose
Our aim was to examine the prognostic significance of ERbeta1 and ERbeta2 expression in ERalpha-negative breast carcinomas.
Materials and methods
We evaluated nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of ERbeta1 and ERbeta2 by immunohistochemistry in a group of 95 patients with long follow-up. ERbeta1 and ERbeta2 status was correlated with clinicopathological parameters and disease outcome. Univariate and multivariate analyses of ERbeta1 and ERbeta2 as independent markers of disease-free survival (DFS) were carried out using the Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
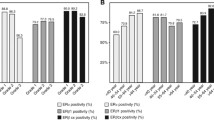
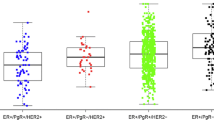
Nuclear ERbeta1 (nERbeta1) and nERbeta2 status was positively correlated (p = 0.01). nERbeta1 positivity was associated with low histological grade (p = 0.01) in all patients and in the nERbeta2-positive subgroup (p = 0.03) but not in the nERbeta2-negative (p = 0.27). nERbeta2 positivity was associated with lymph node involvement and tumor relapse in all cases (p < 0.00 and p < 0.00, respectively) and in the nERbeta1-negative subgroup (p < 0.00 and p < 0.00, respectively) but not in the nERbeta1-positive (p = 0.09 and p = 0.20, respectively). nERbeta2 positivity was associated with poor DFS in all patients (log-rank p <0.00), in the post-menopausal patient subgroup (log-rank p = 0.02) and in the HER2-negative (triple-negative) subgroup (log-rank p = 0.04). Cox multivariate analysis including ERbeta1, ERbeta2 and established clinicopathological variables highlighted ERbeta2 as an independent marker of early disease recurrence (hazard ratio 4.87; 95 % confidence interval 1.07–22.3; p = 0.04).
Conclusion
High nERbeta2 is an independent marker of early relapse in ERalpha-negative breast carcinoma, and in particular, in the nERbeta1-negative, the post-menopausal patient and the triple-negative subgroups. These findings suggest that inhibition of expression and/or function of ERbeta2 could improve disease outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- nERβ1:
-
Nuclear estrogen receptor β1
- nERβ2:
-
Nuclear estrogen receptor β2
- PgR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- FFPE:
-
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
References
Chantzi NI, Meligova AK, Dhimolea E, Petrou CC, Mitsiou DJ, Magafa V, Pechtelidou A, Florentin I, Kitraki E, Cordopatis P, Tiniakos DG, Alexis MN (2011) Insights into ectopic estrogen receptor expression, nucleocytoplasmic distribution and interaction with chromatin obtained with new antibodies to estrogen receptors α and β. Steroids 76:974–985. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.201105010
Dey P, Jonsson P, Hartman J, Williams C, Ström A, Gustafsson JÅ (2012) Estrogen receptors β1 and β2 have opposing roles in regulating proliferation and bone metastasis genes in the prostate cancer cell line PC3. Mol Endocrinol 26:1991–2003. doi:10.1210/me.20121227
Esslimani-Sahla M, Kramar A, Simony-Lafontaine J, Warner M, Gustafsson JA, Rochefort H (2005) Increased estrogen receptor betacx expression during mammary carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 11:3170–3174. doi:10.1158/10780432CCR042298
Fujimura T, Takahashi S, Urano T, Ogawa S, Ouchi Y, Kitamura T, Muramatsu M, Inoue S (2001) Differential expression of estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) and its C-terminal truncated splice variant ERbetacx as prognostic predictors in human prostatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:692–699. http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2001.6038
Gruvberger-Saal SK, Bendahl PO, Saal LH, Laakso M, Hegardt C, Eden P, Peterson C, Malmstrom P, Isola J, Borg A, Ferno M (2007) Estrogen receptor beta expression is associated with tamoxifen response in ERalpha-negative breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:1987–1994. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1823
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC (1999) Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 17:1474–1481
Honma N, Horii R, Iwase T, Saji S, Younes M, Takubo K, Matsuura M, Ito Y, Akiyama F, Sakamoto G (2008) Clinical importance of estrogen receptor-beta evaluation in breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant tamoxifen therapy. J Clin Oncol 26:3727–3734. doi:10.1200/JCO2007142968
Hou YF, Yuan ST, Li HC, Wu J, Lu JS, Liu G, Lu LJ, Shen ZZ, Ding J, Shao ZM (2004) ERbeta exerts multiple stimulative effects on human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene 23:5799–57806. doi:10.1038/sjonc1207765
Jang ER, Lim SJ, Lee ES, Jeong G, Kim TY, Bang YJ, Lee JS (2004) The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A sensitizes estrogen receptor alpha-negative breast cancer cells to tamoxifen. Oncogene 23:1724–1736. doi:10.1038/sjonc1207315
Jensen EV, Cheng G, Palmieri C, Saji S, Mäkelä S, Van Noorden S, Wahlström T, Warner M, Coombes RC, Gustafsson JA (2001) Estrogen receptors and proliferation markers in primary and recurrent breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:15197–15202. doi:10.1073/pnas.211556298
Leung YK, Mak P, Hassan S, Ho SM (2006) Estrogen receptor (ER)-beta isoforms: a key to understanding ER-beta signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13162–13167. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605676103
Leung YK, Lam HM, Wu S, Song D, Levin L, Cheng L, Wu CL, Ho SM (2010) Estrogen receptor beta2 and beta5 are associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer, and promote cancer cell migration and invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:675–689. doi:10.1677/ERC090294
Leung YK, Lee MT, Lam HM, Tarapore P, Ho SM (2012) Estrogen receptor-beta and breast cancer: translating biology into clinical practice. Steroids 77:727–737. doi:10.1016/j.steroids201203008
Marotti JD, Collins LC, Hu R, Tamimi RM (2010) Estrogen receptor-beta expression in invasive breast cancer in relation to molecular phenotype: results from the Nurses’ Health Study. Mod Pathol 23:197–204. doi:10.1038/modpathol2009158
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100:229–235. doi:10.1007/s1054901220406
Middleton LP, Perkins GH, Tucker SL, Sahin AA, Singletary SE (2007) Expression of ERa and ERb in lobular carcinoma in situ. Histopathology 50:875–888. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02689.x
Miller WR, Anderson TJ, Dixon JM, Saunders PT (2006) Oestrogen receptor beta and neoadjuvant therapy with tamoxifen: prediction of response and effects of treatment. Br J Cancer 94:1333–1338. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603082
Murphy LC, Leygue E (2012) The role of estrogen receptor-β in breast cancer. Semin Reprod Med 30:5–13. doi:10.1016/j.steroids201203008
Nakopoulou L, Lazaris AC, Panayotopoulou EG, Giannopoulou I, Givalos N, Markaki S, Keramopoulos A (2004) The favourable prognostic value of oestrogen receptor beta immunohistochemical expression in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 57:523–528. doi:10.1136/jcp2003008599
Novelli F, Milella M, Melucci E, Di Benedetto A, Sperduti I, Perrone-Donnorso R, Perracchio L, Venturo I, Nistico C, Fabi A, Buglioni S, Natali PG, Mottolese M (2008) A divergent role for estrogen receptor-beta in node-positive and node-negative breast cancer classified according to molecular subtypes: an observational prospective study. Breast Cancer Res 10:R74. doi:10.1186/bcr2139
O’Neill PA, Davies MP, Shaaban AM, Innes H, Torevell A, Sibson DR, Foster CS (2004) Wild-type oestrogen receptor beta (ERbeta1) mRNA and protein expression in Tamoxifen-treated post-menopausal breast cancers. Br J Cancer 91:1694–1702. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602183
Palmieri C, Saji S, Sakaguchi H, Cheng G, Sunters A, O’Hare MJ, Warner M, Gustafsson JA, Coombes RC, Lam EW (2004) The expression of oestrogen receptor(ER)-beta and its variant, but not ERalpha, in adult human mammary fibroblasts. Mol Endocrinol 33:35–50. doi:10.1677/jme00330035
Paruthiyil S, Parmar H, Kerekatte V, Cunha GR, Firestone GL, Leitman DC (2004) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation by causing a G2 cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res 64:423–428. doi:10.1158/00085472CAN032446
Peng B, Lu B, Leygue E, Murphy LC (2003) Putative functional characteristics of human estrogen receptor-beta isoforms. J Mol Endocrinol 30:13–29. doi:10.1677/jme.0.0300013
Rhodes A, Jasani B, Balaton AJ, Miller KD (2000) Immunohistochemical demonstration of oestrogen and progesterone receptors: correlation of standards achieved on in house tumours with that achieved on external quality assessment material in over 150 laboratories from 26 countries. J Clin Pathol 53:292–301. doi:10.1136/jcp534292
Risbridger GP, Davis ID, Birrell SN, Tilley WD (2010) Breast and prostate cancer: more similar than different. Nat Rev Cancer 10:205–212. doi:10.1038/nrc2795
Secreto FJ, Monroe DG, Dutta S, Ingle JN, Spelsberg TC (2007) Estrogen receptor alpha/beta isoforms, but not betacx, modulate unique patterns of gene expression and cell proliferation in Hs578T cells. J Cell Biochem 101:1125–1147. doi:10.1002/jcb21205
Shaaban AM, Jarvis C, Moore F, West C, Dodson A, Foster CS (2005) Prognostic significance of estrogen receptor Beta in epithelial hyperplasia of usual type with known outcome. Am J Surg Pathol 29:1593–1599
Shaaban AM, Green AR, Karthik S, Alizadeh Y, Hughes TA, Harkins L, Ellis IO, Robertson JF, Paish EC, Saunders PT, Groome NP, Speirs V (2008) Nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of ERbeta1, ERbeta2, and ERbeta5 identifies distinct prognostic outcome for breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 14:5228–5235. doi:10.1158/1078-0432CCR074528
Skliris GP, Leygue E, Curtis-Snell L, Watson PH, Murphy LC (2006) Expression of oestrogen receptor-beta in oestrogen receptor-alpha negative human breast tumours. Br J Cancer 95:616–626. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc6603295
Skliris GP, Leygue E, Watson PH, Murphy LC (2008) Estrogen receptor alpha negative breast cancer patients: estrogen receptor beta as a therapeutic target. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 109:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.12.010
Ström A, Hartman J, Foster JS, Kietz S, Wimalasena J, Gustafsson JA (2004) Estrogen receptor beta inhibits 17 beta-estradiol-stimulated proliferation of the breast cancer cell line T47D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:1566–1571. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308319100
Thomas C, Gustafsson JÅ (2011) The different roles of ER subtypes in cancer biology and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 11:597–608. doi:10.1038/nrc3093
Tonetti DA, Rubenstein R, DeLeon M, Zhao H, Pappas SG, Bentrem DJ, Chen B, Constantinou A, Jordan VC (2003) Stable transfection of an estrogen receptor beta cDNA isoform into MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 87:47–55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2003.07.003
Weigel MT, Dowsett M (2010) Current and emerging biomarkers in breast cancer: prognosis and prediction. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:R245–R262. doi:10.1677/ERC100136
Weitsman GE, Skliris G, Ung K, Peng B, Younes M, Watson PH, Murphy LC (2006) Assessment of multiple different estrogen receptor-beta antibodies for their ability to immunoprecipitate under chromatin immunoprecipitation conditions. Breast Cancer Res Treat 100:23–31. doi:10.1007/s1054900692295
Younes M, Honma N (2011) Estrogen receptor β. Arch Pathol Lab Med 135:63–66. doi:10.1043/20100448RAR1
Zhou Y, Yau C, Gray JW, Chew K, Dairkee SH, Moore DH, Eppenberger U, Eppenberger-Castori S, Benz CC (2007) Enhanced NF kappa B and AP-1 transcriptional activity associated with antiestrogen resistant breast cancer. BMC Cancer 7:59. doi:10.1186/14712407759
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr B. Steele (IBMCB-NHRF) for reviewing and editing the manuscript and Ms C. Vlachou for secretarial assistance. This research has been supported by EU European Social Fund and Greek national funds through the Operational Program “Education and Lifelong Learning” of the NSRF-Research Funding Program: Projects THALES 85355 and by the Greek Ministry of Development through grant 03ED644.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Νiki Ι. Chantzi and Dina G. Tiniakos contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chantzi, Ν.Ι., Tiniakos, D.G., Palaiologou, M. et al. Estrogen receptor beta 2 is associated with poor prognosis in estrogen receptor alpha-negative breast carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 1489–1498 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1467-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-013-1467-4