Abstract
Purpose
Lysosome-associated protein transmembrane 4 beta (LAPTM4B), a novel oncoprotein, has been shown to be overexpressed in several human malignancies. Our purpose was to evaluate the expression of LAPTM4B in breast carcinoma and its significance, which was not previously studied by others.
Methods
Through immunohistochemistry, LAPTM4B expression was evaluated in 35 benign breast tumor specimens and 194 breast cancer specimens. The correlation of LAPTM4B expression with clinicopathological parameters was assessed using χ 2 analysis. The survival status of patients was analyzed using the Kaplan–Meier and log-rank tests. Cox regression was used for the multivariate analysis of prognostic factors.
Results
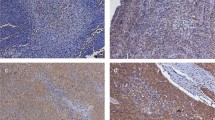
The immunohistochemistry results showed that the expression level of LAPTM4B in breast cancer cases was significantly higher than that in benign breast tumor tissues (P < 0.001). Moreover, statistical analysis also showed that high LAPTM4B expression was positively related to TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, and recurrence. Furthermore, it was also shown that patients with high LAPTM4B expression had significantly poorer overall survival and disease-free survival compared with patients with low expression of LAPTM4B (P = 0.019 and P = 0.005, respectively). Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that high LAPTM4B expression level was an independent prognostic factor for both overall survival and disease-free survival of patients with breast cancer (P = 0.041 and P = 0.023, respectively).
Conclusions
Overexpression of LAPTM4B may contribute to the tumor progression and poor prognosis of breast cancer, thus testing the expression of LAPTM4B will be helpful for predicting prognosis in breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson JR, Jatoi I, Keisch M, Esteva FJ, Makris A, Jordan VC (2009) Early breast cancer. Lancet 373(9673):1463–1479
Fan M, Liu Y, Zhou R, Zhang Q (2012) Association of LAPTM4B gene polymorphism with breast cancer susceptibility. Cancer Epidemiol. Epub ahead of print
Joensuu H, Pylkkänen L, Toikkanen S (1994) Bcl-2 protein expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 145:1191–1198
Kasper G, Vogel A, Klaman I, Grone J, Petersen I, Weber B (2005) The human LAPTM4B transcript is upregulated in various types of solid tumours and seems to play a dual functional role during tumour progression. Cancer Lett 224:93–103
Li L, Wei XH, Pan YP, Li HC, Yang H, He QH, Pang Y, Shan Y, Xiong FX, Shao GZ, Zhou RL (2010a) LAPTM4B: a novel cancer-associated gene motivates multidrug resistance through efflux and activating PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncogene 29:5785–5795
Li Y, Zou L, Li Q, Haibe-Kains B, Tian R, Li Y, Desmedt C, Sotiriou C, Szallasi Z, Iglehart JD, Richardson AL, Wang ZC (2010b) Amplification of LAPTM4B and YWHAZ contributes to chemotherapy resistance and recurrence of breast cancer. Nat Med 16:214–218
Liu XR, Zhou RL, Zhang QY, Zhang Y, Jin YY, Lin M, Rui JA, Ye DX (2004) Structure analysis and expressions of a novel tetratransmembrane protein, lysosome associated protein transmembrane 4 beta associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 10:1555–1559
Malamou-Mitsi V, Gogas H, Dafni U, Bourli A, Fillipides T, Sotiropoulou M, Vlachodimitropoulos D, Papadopoulos S, Tzaida O, Kafiri G, Kyriakou V, Markaki S, Papaspyrou I, Karagianni E, Pavlakis K, Toliou T, Scopa CD, Papakostas P, Bafaloukos D, Christodoulou C, Fountzilas G (2006) Evaluation of the prognostic and predictive value of p53 and Bcl-2 in breast cancer patients participating in a randomized study with dose-dense sequential adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 17:1504–1511
Martinez-Arribas F, Alvarez T, Del Val G, Martin-Garabato E, Nunez-Villar MJ, Lucas R, Sanchez J, Tejerina A, Schneider J (2007) Bcl-2 expression in breast cancer: a comparative study at the mRNA and protein level. Anticancer Res 27:219–222
Meng F, Luo C, Hu Y, Yin M, Lin M, Lou G, Zhou R (2010a) LAPTM4B-35 in cervical carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study. Int J Gynecol Pathol 29(6):587–593. Erratum in: Int J Gynecol Pathol 2011;30(3):314–315
Meng FL, Yin MZ, Song HT, Yang H, Lou G, Zhou RL (2010b) LAPTM4B-35 overexpression is an independent prognostic marker in endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer 20(5):745–750
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO (2007) Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 109(1):25–32
Ross JS, Fletcher JA, Linette GP, Stec J, Clark E, Ayers M, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, Bloom KJ (2003) The Her-2/neu gene and protein in breast cancer 2003: biomarker and target of therapy. Oncologist 8(4):307–325
Shao GZ, Zhou RL, Zhang QY, Zhang Y, Liu JJ, Rui JA, Wei X, Ye DX (2003) Molecular cloning and characterization of LAPTM4B, a novel gene upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 22:5060–5069
Yang Y, Yang H, McNutt MA, Xiong F, Nie X, Li L, Zhou R (2008) LAPTM4B overexpression is an independent prognostic marker in ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep 20(5):1077–1083
Yang H, Xiong FX, Lin M, Yang Y, Nie X, Zhou RL (2010) LAPTM4B-35 overexpression is a risk factor for tumor recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(2):275–281
Yin M, Li C, Li X, Lou G, Miao B, Liu X, Meng F, Zhang H, Chen X, Sun M, Ling Q, Zhou R (2011) Over-expression of LAPTM4B is associated with poor prognosis and chemotherapy resistance in stages III and IV epithelial ovarian cancer. J Surg Oncol 104(1):29–36
Yin M, Lou C, Zhang W, Meng F, Zhang H, Ning X, Zhou R, Dong X, Lou G (2012) LAPTM4B overexpression is a novel independent prognostic marker for metastatic ovarian tumors. Int J Gynecol Cancer 22(1):54–62
Zhou L, He XD, Cui QC, Zhou WX, Qu Q, Zhou RL, Rui JA, Yu JC (2008) Expression of LAPTM4B-35: a novel marker of progression, invasiveness and poor prognosis of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett 264(2):209–217
Zhou L, He XD, Yu JC, Zhou RL, Shan Y, Rui JA (2011) Overexpression of LAPTM4B-35 attenuates epirubicin-induced apoptosis of gallbladder carcinoma GBC-SD cells. Surgery 150(1):25–31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants form the special Fund for Scientific and Technological Renovation of Heilongjiang Province (GC07C350).
Conflict of interest
We declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, M., Jia, S., Wang, H. et al. Overexpression of LAPTM4B: an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 661–667 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1368-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1368-y