Abstract
Purpose
Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (CIN) has been associated with better therapeutic results in studies of various tumors. Herein, we explored the relationship between timing (onset) of CIN and clinical outcomes of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods
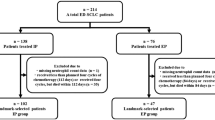
Patients with stage IV NSCLC receiving at least two cycles of first-line doublet chemotherapy (gemcitabine plus platinum) were reviewed retrospectively. Subjects were stratified by onset of CIN into two groups: early-onset (lowest neutrophil count of cycles 1–2 <2.0 × 109/L) and non-early-onset. The non-early-onset group was further subdivided into late-onset (lowest neutrophil count of cycles 3–6 <2.0 × 109/L) and absence of neutropenia.
Results
A total of 123 patients were studied. Significantly better disease control rate, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were observed in early-onset versus non-early-onset patients. Median PFS of 5.1 and 3.8 months (p = 0.0016) and median OS of 16.7 and 11.2 months (p = 0.0004) were achieved for these groups, respectively. Patient subsets with late-onset and absence of neutropenia showed similarly poor clinical outcomes, with 4.8 and 3.8 months median PFS (p = 0.5067) and 13.0 and 11.2 months median OS (p = 0.6304), respectively.
Conclusions
Timing of CIN is predictive of prognosis in patients with metastatic NSCLC receiving gemcitabine/platinum doublet chemotherapy. Better clinical outcomes were achieved when onset of neutropenia was early versus late or absent altogether. Further research is warranted to determine whether above findings are applicable to other chemotherapeutic regimens.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzoli CG, Giaccone G, Temin S (2010) American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update on chemotherapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. J Oncol Pract 6:39–43
Banerji U, Ashley S, Coward J, Hughes S, Zee Y, Benepal T, Norton A, Eisen T, O’Brien M (2006) The association of chemotherapy induced neutropenia on treatment outcomes in small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 54:371–377
Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, Cicenas S, Szczésna A, Juhász E, Esteban E, Molinier O, Brugger W, Melezínek I, Klingelschmitt G, Klughammer B, Giaccone G, SATURN investigators (2010) Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 11:521–529
Di Maio M, Gridelli C, Gallo C, Shepherd F, Piantedosi FV, Cigolari S, Manzione L, Illiano A, Barbera S, Robbiati SF, Frontini L, Piazza E, Ianniello GP, Veltri E, Castiglione F, Rosetti F, Gebbia V, Seymour L, Chiodini P, Perrone F (2005) Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and treatment efficacy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet Oncol 6:669–677
Edge SBBD, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A (2009) AJCC cancer staging handbook, 7th edn. Springer, New York
Han Y, Yu Z, Wen S, Zhang B, Cao X, Wang X (2012) Prognostic value of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia in early-stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131:483–490
Hotta K, Kiura K, Toyooka S, Takigawa N, Soh J, Fujiwara Y, Tabata M, Date H, Tanimoto M (2007) Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations on treatment outcome after first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy in Japanese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2:632–637
Iranzo V, Sirera R, Bremnes RM, Blasco A, Jantus-Lewintre E, Tarón M, Berrocal A, Blasco S, Caballero C, Del Pozo N, Rosell R, Camps C (2011) Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia does not correlate with DNA repair gene polymorphisms and treatment efficacy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Clin Lung Cancer 12:224–230
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Kalikaki A, Koutsopoulos A, Hatzidaki D, Trypaki M, Kontopodis E, Stathopoulos E, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V, Voutsina A (2010) Clinical outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving front-line chemotherapy according to EGFR and K-RAS mutation status. Lung Cancer 69:110–115
Kim JJ, Park JY, Kim DY, Kim JH, Kim YM, Nam JH, Kim YT (2010) Is chemotherapy-induced neutropenia a prognostic factor in patients with ovarian cancer? Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 89:623–628
Kishida Y, Kawahara M, Teramukai S, Kubota K, Komuta K, Minato K, Mio T, Fujita Y, Yonei T, Nakano K, Tsuboi M, Shibata K, Atagi S, Kawaguchi T, Furuse K, Fukushima M (2009) Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia as a prognostic factor in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from Japan Multinational Trial Organization LC00-03. Br J Cancer 101:1537–1542
Kvinnsland S (1999) The leucocyte nadir, a predictor of chemotherapy efficacy? Br J Cancer 80:1681
Lin CC, Hsu HH, Sun CT, Shih JY, Lin ZZ, Yu CJ, Chen GG, Hsin MK, Lam KC, Leung L, Yang CH, Mok T (2010) Chemotherapy response in East Asian non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring wild-type or activating mutation of epidermal growth factor receptors. J Thorac Oncol 5:1424–1429
Mayers C, Panzarella T, Tannock IF (2001) Analysis of the prognostic effects of inclusion in a clinical trial and of myelosuppression on survival after adjuvant chemotherapy for breast carcinoma. Cancer 91:2246–2257
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, Chewaskulyong B, Jiang H, Duffield EL, Watkins CL, Armour AA, Fukuoka M (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361:947–957
Pallis AG, Agelaki S, Kakolyris S, Kotsakis A, Kalykaki A, Vardakis N, Papakotoulas P, Agelidou A, Geroyianni A, Agelidou M, Hatzidaki D, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V (2008) Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia as a prognostic factor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with front-line docetaxel-gemcitabine chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 62:356–363
Paz-Ares L, De Marinis F, Dediu M, Thomas M, Pujol JL, Bidoli P, Molinier O, Sahoo TP, Laack E, Reck M, Jaime JC, Melemed S, John WJ, Chouaki N, Zimmermann A, Visseren-Grul C, Gridelli C (2012) PARAMOUNT: Final overall survival (OS) results of the phase III study of maintenance pemetrexed (pem) plus best supportive care (BSC) versus placebo (plb) plus BSC immediately following induction treatment with pem plus cisplatin (cis) for advanced nonsquamous (NS) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol 30(Suppl 18): Abstract LBA7507
Rankin EM, Mill L, Kaye SB, Atkinson R, Cassidy L, Cordiner J, Cruickshank D, Davis J, Duncan ID, Fullerton W (1992) A randomised study comparing standard dose carboplatin with chlorambucil and carboplatin in advanced ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 65:275–281
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R, Johnson DH (2006) Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355:2542–2550
Wacker B, Nagrani T, Weinberg J, Witt K, Clark G, Cagnoni PJ (2007) Correlation between development of rash and efficacy in patients treated with the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in two large phase III studies. Clin Cancer Res 13:3913–3921
Wu M, Zhao J, Song SW, Zhuo M, Wang X, Bai H, Wang S, Yang L, An T, Zhang Y, Duan J, Wang Y, Guo Q, Liu X, Liu N, Wang J (2010) EGFR mutations are associated with prognosis but not with the response to front-line chemotherapy in the Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 67:343–347
Yamanaka T, Matsumoto S, Teramukai S, Ishiwata R, Nagai Y, Fukushima M (2007) Predictive value of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia for the efficacy of oral fluoropyrimidine S-1 in advanced gastric carcinoma. Br J Cancer 97:37–42
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, S.H., Kim, S.Y., Kim, J.H. et al. Timing of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia is a prognostic factor in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective analysis in gemcitabine-plus-platinum-treated patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 409–417 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1341-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1341-9