Abstract
Purpose
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) plays an important role in the growth and metastasis of many solid tumors. Strategies that target EGFR hold promising therapeutic potential for the treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as EGFR is normally overexpressed in these tumors. This study was designed to determine whether an anti-EGFR immunotoxin has anti-tumor activity against NSCLC, and if so, to further investigate the possible mechanisms of cytotoxicity.
Methods
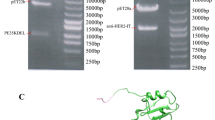
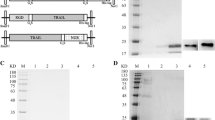
A fusion protein of anti-EGFR single-chain variable fragment (anti-EGFR scFv) and the plant toxin gelonin (rGel) was constructed, expressed in bacteria, and purified to homogeneity. Cytotoxicity of anti-EGFR scFv/rGel (E/rG) immunotoxin was assessed on A549, HCC827, and H1975 cells (EGFR-overexpressing NSCLC-derived cell lines) and A549 xenografts in nude mice.
Results
Cytotoxicity experiments using E/rG on A549, HCC827, and H1975 cells demonstrated that E/rG can specifically inhibit proliferation of these cells, whereas it did not affect the proliferation of Raji cells that do not express EGFR. Treatment for A549 xenografts in nude mice with E/rG resulted in significant suppression of tumor growth compared to controls. Immunofluorescence in frozen tissue sections confirmed that E/rG could specifically bind to tumor tissues in nude mice bearing A549 tumor xenografts, while rGel alone showed no binding activity. Furthermore, E/rG inhibited the growth of A549 cells by cytotoxic effects that blocked tumor proliferation, and the immunotoxin-induced cell death may be mediated by autophagy.
Conclusions
These results showed that E/rG might have significant potential as a novel clinical therapeutic agent against human NSCLC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-ME:
-
2-mercaptoethanol
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- GuHCl:
-
Guanidine hydrochloride
- scFv:
-
Single-chain variable fragment
- rGel:
-
Recombinant gelonin toxin
- G4S:
-
Glycine–glycine–glycine–glycine–serine
- MVD:
-
Microvessel density
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl β-d-thiogalactoside
- PEA:
-
Pseudomonas exotoxin A
- TUNEL:
-
TdT-mediated dUTP-X nick end labeling
References
Allen TM (2002) Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2(10):750–763
Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W, Ruhl J, Howlader N, Tatalovich Z, Cho H, Mariotto A, Eisner MP, Lewis DR, Cronin K, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Stinchcomb DG, Edwards BK (eds) (2009) SEER Cancer statistics review, 1975–2007. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda
Baluna R, Sausville EA, Stone MJ, StetlerStevenson MA, Uhr JW, Vitetta ES (1996) Decreases in levels of serum fibronectin predict the severity of vascular leak syndrome in patients treated with ricin A chain-containing immunotoxins. Clin Cancer Res 2(10):1705–1712
Borghaei H, Langer CJ, Millenson M, Ruth KJ, Litwin S, Tuttle H, Seldomridge JS, Rovito M, Mintzer D, Cohen R, Treat J (2008) Phase II study of paclitaxel, carboplatin, and cetuximab as first line treatment, for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) results of OPN-017. J Thorac Oncol 3(11):1286–1292
Brekke OH, Sandlie I (2003) Therapeutic antibodies for human diseases at the dawn of the twenty-first century. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2(1):52–62
Brereton HM, Chamberlain D, Yang RC, Tea M, McNeil S, Coster DJ, Williams KA (2007) Single chain antibody fragments for ocular use produced at high levels in a commercial wheat variety. J Biotechnol 129(3):539–546
Bruell D, Stocker M, Huhn M, Redding N, Kupper M, Schumacher P, Paetz A, Bruns CJ, Haisma HJ, Fischer R, Finnern R, Barth S (2003) The recombinant anti-EGF receptor immunotoxin 425(scFv)-ETA’ suppresses growth of a highly metastatic pancreatic carcinoma cell line. Int J Oncol 23(4):1179–1186
Bruell D, Bruns CJ, Yezhelyev M, Huhn M, Muller J, Ischenko I, Fischer R, Finnern R, Jauch KW, Barth S (2005) Recombinant anti-EGFR immunotoxin 425(scFv)-ETA’ demonstrates anti-tumor activity against disseminated human pancreatic cancer in nude mice. Int J Mol Med 15(2):305–313
Bush T, Freeman D, Ogbagabriel S, Belmontes B, Kozlosky C, Baher A, Johnson C, Van G, Cerretti D, Radinsky R (2005) Activity of panitumumab alone and in combination with chemotherapy against mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr)-expressing non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) cell lines and xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 11(24):9047s–9047s
Cao Y, Marks JD, Marks JW, Cheung LH, Kim S, Rosenblum MG (2009) Construction and Characterization of Novel, Recombinant Immunotoxins Targeting the Her2/neu Oncogene Product: in vitro and in vivo Studies. Cancer Res 69(23):8987–8995
Fish-Steagall A, Searcy P, Sipples R (2006) Clinical experience with anti-EGFR therapy. Semin Oncol Nurs 22(1 Suppl 1):10–19
FitzGerald DJ, Wayne AS, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I (2011) Treatment of hematologic malignancies with immunotoxins and antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Res 71(20):6300–6309. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1374
Frankel AE, Woo J-H, Neville DM (2009) Immunotoxins Principles of Cancer Biotherapy. In: Oldham RK, Dillman RO (eds). Springer, Netherlands, pp 407–449. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-2289-9_11
Freeman DJ, Bush T, Ogbagabriel S, Belmontes B, Juan T, Plewa C, Van G, Johnson C, Radinsky R (2009) Activity of panitumumab alone or with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines expressing mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cancer Ther 8(6):1536–1546
Herbst RS, Shin DM (2002) Monoclonal antibodies to target epidermal growth factor receptor-positive tumors—A new paradigm for cancer therapy. Cancer 94(5):1593–1611
Karamouzis MV, Grandis JR, Argiris A (2007) Therapies directed against epidermal growth factor receptor in aerodigestive carcinomas. Jama-J Am Med Assoc 298(1):70–82
Lutterbuese R, Raum T, Kischel R, Hoffmann P, Mangold S, Rattel B, Friedrich M, Thomas O, Lorenczewski G, Rau D, Schaller E, Herrmann I, Wolf A, Urbig T, Baeuerle PA, Kufer P (2010) T cell-engaging BiTE antibodies specific for EGFR potently eliminate KRAS-and BRAF-mutated colorectal cancer cells. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 107(28):12605–12610
Martinez-Torrecuadrada JL, Cheung LH, Lopez-Serra P, Barderas R, Canamero M, Ferreiro S, Rosenblum MG, Casal JI (2008) Antitumor activity of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3-specific immunotoxins in a xenograft mouse model of bladder carcinoma is mediated by apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 7(4):862–873
Mendelsohn J (2001) The epidermal growth factor receptor as a target for cancer therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer 8(1):3–9
Mohamedali KA, Kedar D, Sweeney P, Kamat A, Davis DW, Eve BY, Huang S, Thorpe PE, Dinney CP, Rosenblum MG (2005) The vascular-targeting fusion toxin VEGF(121)/rGel inhibits the growth of orthotopic human bladder carcinoma tumors. Neoplasia 7(10):912–920
Nimmanapalli R, Lyu MA, Du M, Keating MJ, Rosenblum MG, Gandhi V (2007) The growth factor fusion construct containing B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) and the toxin rGel induces apoptosis specifically in BAFF-R-positive CLL cells. Blood 109(6):2557–2564
Pastan I (2003) Immunotoxins containing Pseudomonas exotoxin A: a short history. Cancer Immunol Immunother 52(5):338–341
Pirie CM, Hackel BJ, Rosenblum MG, Wittrup KD (2011) Convergent potency of internalized gelonin immunotoxins across varied cell lines, antigens, and targeting moieties. J Biol Chem 286(6):4165–4172. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.186973
Presta L (2003) Antibody engineering for therapeutics. Curr Opin Struct Biol 13(4):519–525
Roovers RC, Laeremans T, Huang L, De Taeye S, Verkleij AJ, Revets H, de Haard HJ, Henegouwen PMPV (2007) Efficient inhibition of EGFR signalling and of tumour growth by antagonistic anti-EGFR Nanobodies. Cancer Immunol Immun 56(3):303–317
Rosenblum MG, Cheung LH, Liu YY, Marks JW (2003) Design, expression, purification, and characterization, in vitro and in vivo, of an antimelanoma single-chain Fv antibody fused-to the toxin gelonin. Cancer Res 63(14):3995–4002
Rossi A, Maione P, Gridelli C (2006) Cetuximab in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 59(2):139–149
Schaffitzel C, Hanes J, Jermutus L, Pluckthun A (1999) Ribosome display: an in vitro method for selection and evolution of antibodies from libraries. J Immunol Methods 231(1–2):119–135
Schmidt M, Reiser P, Hills D, Gullick WJ, Wels W (1998) Expression of an oncogenic mutant EGF receptor markedly increases the sensitivity of cells to an EGF-receptor-specific antibody-toxin. Int J Cancer 75(6):878–884
Schrama D, Reisfeld RA, Becker JC (2006) Antibody targeted drugs as cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(2):147–159
Selbo PK, Sivam G, Fodstad O, Sandvig K, Berg K (2000) Photochemical internalisation increases the cytotoxic effect of the immunotoxin MOC31-gelonin. Int J Cancer 87(6):853–859. doi:10.1002/1097-0215(20000915)87:6<853:AID-IJC15>3.0.CO;2-0
Siegall CB, Liggitt D, Chace D, Mixan B, Sugai J, Davidson T, Steinitz M (1997) Characterization of vascular leak syndrome induced by the toxin component of Pseudomonas exotoxin-based immunotoxins and its potential inhibition with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin Cancer Res 3(3):339–345
Smallshaw JE, Ghetie V, Rizo J, Fulmer JR, Trahan LL, Ghetie MA, Vitetta ES (2003) Genetic engineering of an immunotoxin to eliminate pulmonary vascular leak in mice. Nat Biotechnol 21(4):387–391
Society AC (2010) Cancer Facts and Figures 2010. American Cancer Society, Atlanta
Sridhar SS, Seymour L, Shepherd FA (2003) Inhibitors of epidermal-growth-factor receptors: a review of clinical research with a focus on non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol 4(7):397–406
Stirpe FOS, Pihl A (1980) Gelonin, a new inhibitor of protein synthesis, nontoxic to intact cells. Isolation, characterization, and preparation of cytotoxic complexes with concanavalin A. J Biol Chem 255:6947–6953
Stish BJ, Oh S, Vallera DA (2008) Anti-glioblastoma effect of a recombinant bispecific cytotoxin cotargeting human IL-13 and EGF receptors in a mouse xenograft model. J Neuro-Oncol 87(1):51–61
Veenendaal LM, Jin HQ, Ran S, Cheung L, Navone N, Marks JW, Waltenberger J, Thorpe P, Rosenblum MG (2002a) In vitro and in vivo studies of a VEGF121/rGelonin chimeric fusion toxin targeting the neovasculature of solid tumors (vol 99, pg 7866, 2002). Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 99(16):10941
Veenendaal LM, Jin H, Ran S, Cheung L, Navone N, Marks JW, Waltenberger J, Thorpe P, Rosenblum MG (2002b) In vitro and in vivo studies of a VEGF121/rGelonin chimeric fusion toxin targeting the neovasculature of solid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(12):7866–7871
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by China National Science and Technology Programs of Significant New Drugs to Create (No.2009ZX09103-714) and the National Key Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China (No. 2010CB529900).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xikun Zhou, Ji Qiu, and Zhen Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Qiu, J., Wang, Z. et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activities of anti-EGFR single-chain variable fragment fused with recombinant gelonin toxin. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 1081–1090 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1181-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1181-7