Abstract
Objectives
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1), a member of the IGFBP super family, was identified as a potent tumor suppressor in several carcinomas. IGFBP-rP1 was down-regulated in primary breast cancer tissues and several breast cancer cell lines but overexpressed in senescent human mammary epithelial cells (HMECs), suggesting that IGFBP-rP1 might be a tumor suppressor in breast cancer and the tumor suppressor role of IGFBP-rP1 might be associated with cellular senescence. The aim of the study was to observe the effect of IGFBP-rP1 on cellular senescence and the molecular events mediating this biological effect in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Methods
DNA fragment-encoding IGFBP-rP1 was cloned in-frame N-terminally to EGFP gene to generate IGFBP-rP1-EGFP fusion protein expression plasmid (pEGFP-IGFBP-rP1). The plasmid pEGFP-IGFBP-rP1 was then transfected into MCF-7 cells, and the proliferation, cell cycle distribution, cellular senescence, and cell cycle-related protein expression of MCF-7 cells were examined by trypan blue exclusion, flow cytometry, senescence-associated galactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining, and Western blot analysis, respectively. Two shRNA plasmid vectors against p21 or p53 gene were constructed and stably transfected into the MCF-7 cells to determine the involvement of p21 or p53 in cellular senescence induced by IGFBP-rP1.
Results
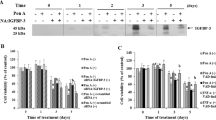
Transfection of IGFBP-rP1 or addition of condition medium (CM) from IGFBP-rP1-transfected cells in MCF-7 cells caused induction of a variety of senescent phenotypes, such as decrease in cell proliferation, increase in G0/G1 cell cycle arrest cells, change in cell morphology, and increase in senescence-associated galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity. IGFBP-rP1-induced growth arrest is associated with enhanced expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 and dephosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRB). Cell proliferation block and cellular senescence induction in response to IGFBP-rP1 were partially reversed by p21 knockdown in MCF-7 cells. Knockdown of p53 in MCF-7 cells did not influence the growth inhibition, cellular senescence, and p21 expression of the cells in response to IGFBP-rP1 transfection.
Conclusions
Results from this study suggest that cellular senescence induced by IGFBP-rP1 is mediated at least in part by p21 enhanced expression, which regulated through the p53-independent pathway. IGFBP-rP1 might be one of the key molecules that trigger cellular senescence in breast cancer. Restoration of IGFBP-rP1 function might have therapeutic significance in breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta JC, O’Loghlen A, Banito A, Guijarro MV, Augert A, Raguz S, Fumagalli M, Da Costa M, Brown C, Popov N, Takatsu Y, Melamed J, d’Adda di Fagagna F, Bernard D, Hernando E, Gil J (2008) Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 133(6):1006–1018. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.038
Akaogi K, Sato J, Okabe Y, Sakamoto Y, Yasumitsu H, Miyazaki K (1996) Synergistic growth stimulation of mouse fibroblasts by tumor-derived adhesion factor with insulin-like growth factors and insulin. Cell Growth Differ 7(12):1671–1677
Alexander K, Hinds PW (2001) Requirement for p27(KIP1) in retinoblastoma protein-mediated senescence. Mol Cell Biol 21(11):3616–3631. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.11.3616-3631.2001
Aliouat-Denis CM, Dendouga N, Van den Wyngaert I, Goehlmann H, Steller U, van de Weyer I, Van Slycken N, Andries L, Kass S, Luyten W, Janicot M, Vialard JE (2005) p53-independent regulation of p21Waf1/Cip1 expression and senescence by Chk2. Mol Cancer Res 3(11):627–634. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-05-0121
Bavik C, Coleman I, Dean JP, Knudsen B, Plymate S, Nelson PS (2006) The gene expression program of prostate fibroblast senescence modulates neoplastic epithelial cell proliferation through paracrine mechanisms. Cancer Res 66(2):794–802. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1716
Bond J, Haughton M, Blaydes J, Gire V, Wynford-Thomas D, Wyllie F (1996) Evidence that transcriptional activation by p53 plays a direct role in the induction of cellular senescence. Oncogene 13(10):2097–2104
Burger AM, Zhang X, Li H, Ostrowski JL, Beatty B, Venanzoni M, Papas T, Seth A (1998) Down-regulation of T1A12/mac25, a novel insulin-like growth factor binding protein related gene, is associated with disease progression in breast carcinomas. Oncogene 16(19):2459–2467. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201772
Campisi J (2001) Cellular senescence as a tumor-suppressor mechanism. Trends Cell Biol 11(11):S27–S31
Campisi J (2005) Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell 120(4):513–522. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.003
Campisi J, d’Adda di Fagagna F (2007) Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Natl Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(9):729–740. doi:10.1038/nrm2233
Chen Y, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, Ye F, Knosel T, Lund P, Deutschmann N, Schluns K, Kotb WF, Sers C, Yasumoto H, Usui T, Petersen I (2007) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) has potential tumour-suppressive activity in human lung cancer. J Pathol 211(4):431–438. doi:10.1002/path.2132
Datto MB, Li Y, Panus JF, Howe DJ, Xiong Y, Wang XF (1995) Transforming growth factor beta induces the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 through a p53-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(12):5545–5549
Dimri GP (2005) What has senescence got to do with cancer? Cancer Cell 7(6):505–512. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.05.025
Dotto GP (2000) p21(WAF1/Cip1): more than a break to the cell cycle? Biochim Biophys Acta 1471(1):M43–M56
Fuxe J, Akusjarvi G, Goike HM, Roos G, Collins VP, Pettersson RF (2000) Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of p15INK4B inhibits human glioma cell growth, induces replicative senescence, and inhibits telomerase activity similarly to p16INK4A. Cell Growth Differ 11(7):373–384
Kato MV, Sato H, Tsukada T, Ikawa Y, Aizawa S, Nagayoshi M (1996) A follistatin-like gene, mac25, may act as a growth suppressor of osteosarcoma cells. Oncogene 12(6):1361–1364
Kim KS, Seu YB, Baek SH, Kim MJ, Kim KJ, Kim JH, Kim JR (2007) Induction of cellular senescence by insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 through a p53-dependent mechanism. Mol Biol Cell 18(11):4543–4552. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-03-0280
Kitagawa M, Higashi H, Jung HK, Suzuki-Takahashi I, Ikeda M, Tamai K, Kato J, Segawa K, Yoshida E, Nishimura S, Taya Y (1996) The consensus motif for phosphorylation by cyclin D1-Cdk4 is different from that for phosphorylation by cyclin A/E-Cdk2. EMBO J 15(24):7060–7069
Kortlever RM, Higgins PJ, Bernards R (2006) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a critical downstream target of p53 in the induction of replicative senescence. Nat Cell Biol 8(8):877–884. doi:10.1038/ncb1448
Landberg G, Ostlund H, Nielsen NH, Roos G, Emdin S, Burger AM, Seth A (2001) Downregulation of the potential suppressor gene IGFBP-rP1 in human breast cancer is associated with inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein, cyclin E overexpression and increased proliferation in estrogen receptor negative tumors. Oncogene 20(27):3497–3505. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204471
Lowe SW, Sherr CJ (2003) Tumor suppression by Ink4a-Arf: progress and puzzles. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13(1):77–83
Ma Y, Lu B, Ruan W, Wang H, Lin J, Hu H, Deng H, Huang Q, Lai M (2008) Tumor suppressor gene insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) induces senescence-like growth arrest in colorectal cancer cells. Exp Mol Pathol 85(2):141–145. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2008.04.005
Michieli P, Chedid M, Lin D, Pierce JH, Mercer WE, Givol D (1994) Induction of WAF1/CIP1 by a p53-independent pathway. Cancer Res 54(13):3391–3395
Narita M, Nunez S, Heard E, Lin AW, Hearn SA, Spector DL, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW (2003) Rb-mediated heterochromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during cellular senescence. Cell 113(6):703–716
Oh Y, Nagalla SR, Yamanaka Y, Kim HS, Wilson E, Rosenfeld RG (1996) Synthesis and characterization of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-7. Recombinant human mac25 protein specifically binds IGF-I and -II. J Biol Chem 271(48):30322–30325
Ruan W, Xu E, Xu F, Ma Y, Deng H, Huang Q, Lv B, Hu H, Lin J, Cui J, Di M, Dong J, Lai M (2007) IGFBP7 plays a potential tumor suppressor role in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther 6(3):354–359
Sage J, Miller AL, Perez-Mancera PA, Wysocki JM, Jacks T (2003) Acute mutation of retinoblastoma gene function is sufficient for cell cycle re-entry. Nature 424(6945):223–228. doi:10.1038/nature01764nature01764
Sato J, Hasegawa S, Akaogi K, Yasumitsu H, Yamada S, Sugahara K, Miyazaki K (1999) Identification of cell-binding site of angiomodulin (AGM/TAF/Mac25) that interacts with heparan sulfates on cell surface. J Cell Biochem 75(2):187–195. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19991101)75:2<187:AID-JCB1>3.0.CO;2-R
Serrano M, Hannon GJ, Beach D (1993) A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature 366(6456):704–707. doi:10.1038/366704a0
Shelton DN, Chang E, Whittier PS, Choi D, Funk WD (1999) Microarray analysis of replicative senescence. Curr Biol 9(17):939–945
Smith P, Nicholson LJ, Syed N, Payne A, Hiller L, Garrone O, Occelli M, Gasco M, Crook T (2007) Epigenetic inactivation implies independent functions for insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-related protein 1 and the related IGFBPL1 in inhibiting breast cancer phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res 13(14):4061–4068. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3052
Sprenger CC, Damon SE, Hwa V, Rosenfeld RG, Plymate SR (1999) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) is a potential tumor suppressor protein for prostate cancer. Cancer Res 59(10):2370–2375
Stein GH, Dulic V (1995) Origins of G1 arrest in senescent human fibroblasts. Bioessays 17(6):537–543. doi:10.1002/bies.950170610
Stein GH, Drullinger LF, Soulard A, Dulic V (1999) Differential roles for cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p16 in the mechanisms of senescence and differentiation in human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 19(3):2109–2117
Subramanian A, Sharma A, Mokbel K (2008) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 107(2):181–194. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9549-0
Suzuki H, Igarashi S, Nojima M, Maruyama R, Yamamoto E, Kai M, Akashi H, Watanabe Y, Yamamoto H, Sasaki Y, Itoh F, Imai K, Sugai T, Shen L, Issa JP, Shinomura Y, Tokino T, Toyota M (2010) IGFBP7 is a p53-responsive gene specifically silenced in colorectal cancer with CpG island methylator phenotype. Carcinogenesis 31(3):342–349. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgp179
Swisshelm K, Ryan K, Tsuchiya K, Sager R (1995) Enhanced expression of an insulin growth factor-like binding protein (mac25) in senescent human mammary epithelial cells and induced expression with retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(10):4472–4476
te Poele RH, Okorokov AL, Jardine L, Cummings J, Joel SP (2002) DNA damage is able to induce senescence in tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 62(6):1876–1883
Wajapeyee N, Serra RW, Zhu X, Mahalingam M, Green MR (2008) Oncogenic BRAF induces senescence and apoptosis through pathways mediated by the secreted protein IGFBP7. Cell 132(3):363–374. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.032
Wei W, Hemmer RM, Sedivy JM (2001) Role of p14(ARF) in replicative and induced senescence of human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 21(20):6748–6757. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.20.6748-6757.2001
Weinberg RA (1995) The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81(3):323–330
Wilson HM, Birnbaum RS, Poot M, Quinn LS, Swisshelm K (2002) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 inhibits proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells via a senescence-like mechanism. Cell Growth Differ 13(5):205–213
Xu HJ, Zhou Y, Ji W, Perng GS, Kruzelock R, Kong CT, Bast RC, Mills GB, Li J, Hu SX (1997) Reexpression of the retinoblastoma protein in tumor cells induces senescence and telomerase inhibition. Oncogene 15(21):2589–2596. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201446
Yamauchi T, Umeda F, Masakado M, Isaji M, Mizushima S, Nawata H (1994) Purification and molecular cloning of prostacyclin-stimulating factor from serum-free conditioned medium of human diploid fibroblast cells. Biochem J 303(Pt 2):591–598
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Xicai Wang (Tumor Institute of Yunnan Province, Tumor Hospital of Yunnan Province, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University) and Dr. Wenhai Yan (Department of Pathophysiology, Basic Medicine School, Zhengzhou University) for the technical assistance and suggestions. This work was supported by the Innovation Group Foundation Grant of Luohe Science and Technology Bureau (No. LK2010-46-13-1) and by the College Foundation of Luohe Medical College (No. LHMC2010-01).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shuguang Zuo, Chang Liu, and Jianguo Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, S., Liu, C., Wang, J. et al. IGFBP-rP1 induces p21 expression through a p53-independent pathway, leading to cellular senescence of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138, 1045–1055 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1153-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1153-y