Abstract
Background
The relationship between diabetes and pancreatic cancer has been established by more than several decades of research. However, serum levels of CEA and CA 19-9 in diabetic pancreatic cancer has not been shown.
Methods
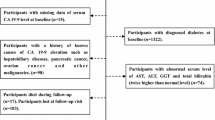
Preoperative serum levels of CEA and CA 19-9 and clinicopathological characteristics were retrospectively analyzed in 79 with or 229 without diabetes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) patients.
Results
Of the 308 PDA patients enrolled, 79 (25.6%) patients had diabetes. The percentage of new-onset diabetes (i.e. <24 months in duration) was 57% (45/79) in PDA patients coupled with diabetes. Among diabetic PDA patients, mean total bilirubin and fasting blood glucose significantly increased in comparison with control groups (8.54 ± 14.88 vs. 4.16 ± 6.12; 170.22 ± 106.96 vs. 95.84 ± 15.76; P < 0.05). No significant differences were observed in mean levels of serum CA 19-9 and CEA levels between two groups. However, when the value of CEA and CA 19-9 was analyzed as a dichotomous variable, elevated CEA (≥5 ng/ml) and CA 19-9 (≥500 U/ml) levels were strongly correlated with the presence of diabetes in PDA patients.
Conclusion
Elevated CEA (≥5 ng/ml) and CA19-9 (≥500 U/ml) levels have an association with diabetic pancreatic cancer. New-onset diabetes combined with higher CA 19-9 and/or CEA might be regarded as a useful tool to screen early pancreatic cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banfi G, Ardemagni A, Bravi S et al (1996) Are diabetic metabolic compensation and CA19.9 really correlated? Int J Biol Markers 11:207–210
Cersosimo E, Pisters PW, Pesola G et al (1991) Insulin secretion and action in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer 67:486–493
Chang MC, Chang YT, Su TC et al (2007) Adiponectin as a potential differential marker to distinguish pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 35:16–21
Chari ST, Klee GG, Miller LJ et al (2001) Islet amyloid polypeptide is not a satisfactory marker for detecting pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 121:640–645
Chari ST, Leibson CL, Rabe KG et al (2005) Probability of pancreatic cancer following diabetes: a population-based study. Gastroenterology 129:504–511
Chari ST, Leibson CL, Rabe KG et al (2008) Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus: prevalence and temporal association with diagnosis of cancer. Gastroenterology 134:95–101
Clark CG, Mitchell PE (1961) Diabetes mellitus and primary carcinoma of the pancreas. Br Med J 2:1259–1262
Duffy JP, Eibl G, Reber HA et al (2003) Influence of hypoxia and neoangiogenesis on the growth of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 2:12
Everhart J, Wright D (1995) Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Assoc 273:1605–1609
Fry LC, Monkemuller K, Malfertheiner P (2008) Molecular markers of pancreatic cancer: development and clinical relevance. Langenbecks Arch Surg 393:883–890
Gullo L, Pezzilli R, Morselli-Labate AM (1994) Diabetes and the risk of pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 331:81–84
Guo Q, Zhang B, Dong X et al (2009) Elevated levels of plasma fibrinogen in patients with pancreatic cancer: possible role of a distant metastasis predictor. Pancreas 38:e75–e79
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E et al (2007) Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 57:43–66
Kang CM, Kim JY, Choi GH et al (2007) The use of adjusted preoperative CA 19-9 to predict the recurrence of resectable pancreatic cancer. J Surg Res 140:31–35
Kuang TT, Jin D, Wang D et al (2009) Clinical epidemiological analysis of the relationship between pancreatic cancer and diabetes mellitus: data from a single institution in China. J Digest Dis 10:26–29
Nakamura N, Aoji O, Yoshikawa T et al (1986) Elevated serum CA19-9 levels in poorly controlled diabetic patients. Jpn J Med 25:278–280
Noy A, Bilezikian JP (1994) Clinical review 63: diabetes and pancreatic cancer: clues to the early diagnosis of pancreatic malignancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 79:1223–1231
Ogawa Y, Tanaka M, Inoue K et al (2002) A prospective pancreatographic study of the prevalence of pancreatic carcinoma in patients with diabetes mellitus. Cancer 94:2344–2349
Pannala R, Leirness JB, Bamlet WR et al (2008) Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 134:981–987
Pannala R, Basu A, Petersen GM et al (2009) New-onset diabetes: a potential clue to the early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Lancet Oncol 10:88–95
Permert J, Larsson J, Ihse I et al (1991) Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: alteration of glucose metabolism. Int J Pancreatol 9:113–117
Permert J, Ihse I, Jorfeldt L et al (1993a) Improved glucose metabolism after subtotal pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg 80:1047–1050
Permert J, Ihse I, Jorfeldt L et al (1993b) Pancreatic cancer is associated with impaired glucose metabolism. Eur J Surg 159:101–107
Petit JM, Vaillant G, Olsson NO et al (1994) Elevated serum CA19-9 levels in poorly controlled diabetic patients. Relationship with Lewis blood group. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 18:17–20
Rivera F, Lopez-Tarruella S, Vega-Villegas ME et al (2009) Treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer: from gemcitabine single agent to combinations and targeted therapy. Cancer Treat Rev 35:335–339
Shimojo N, Naka K, Nakajima C et al (1990) The effect of non-insulin-dependent diabetes on serum concentrations of tumor-associated carbohydrate antigens of CA19-9, CA-50, and sialyl SSEA-1 in association with the Lewis blood phenotype. Clin Chim Acta 190:283–289
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (eds) (2002) UICC: TNM classification of malignant tumours. Wiley, London
Uygur-Bayramicli O, Dabak R, Orbay E et al (2007) Type 2 diabetes mellitus and CA 19-9 levels. World J Gastroenterol 13:5357–5359
Wang F, Gupta S, Holly EA (2006) Diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer in a population-based case-control study in the San Francisco Bay Area, California. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15:1458–1463
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30672072 and 30872531), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (no. Y206247), Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province, China (no. 2006C23G2010216) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of People’s Republic of China (no. 2007AA02Z476).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Q., Kang, M., Zhang, B. et al. Elevated levels of CA 19-9 and CEA in pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136, 1627–1631 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0820-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0820-0